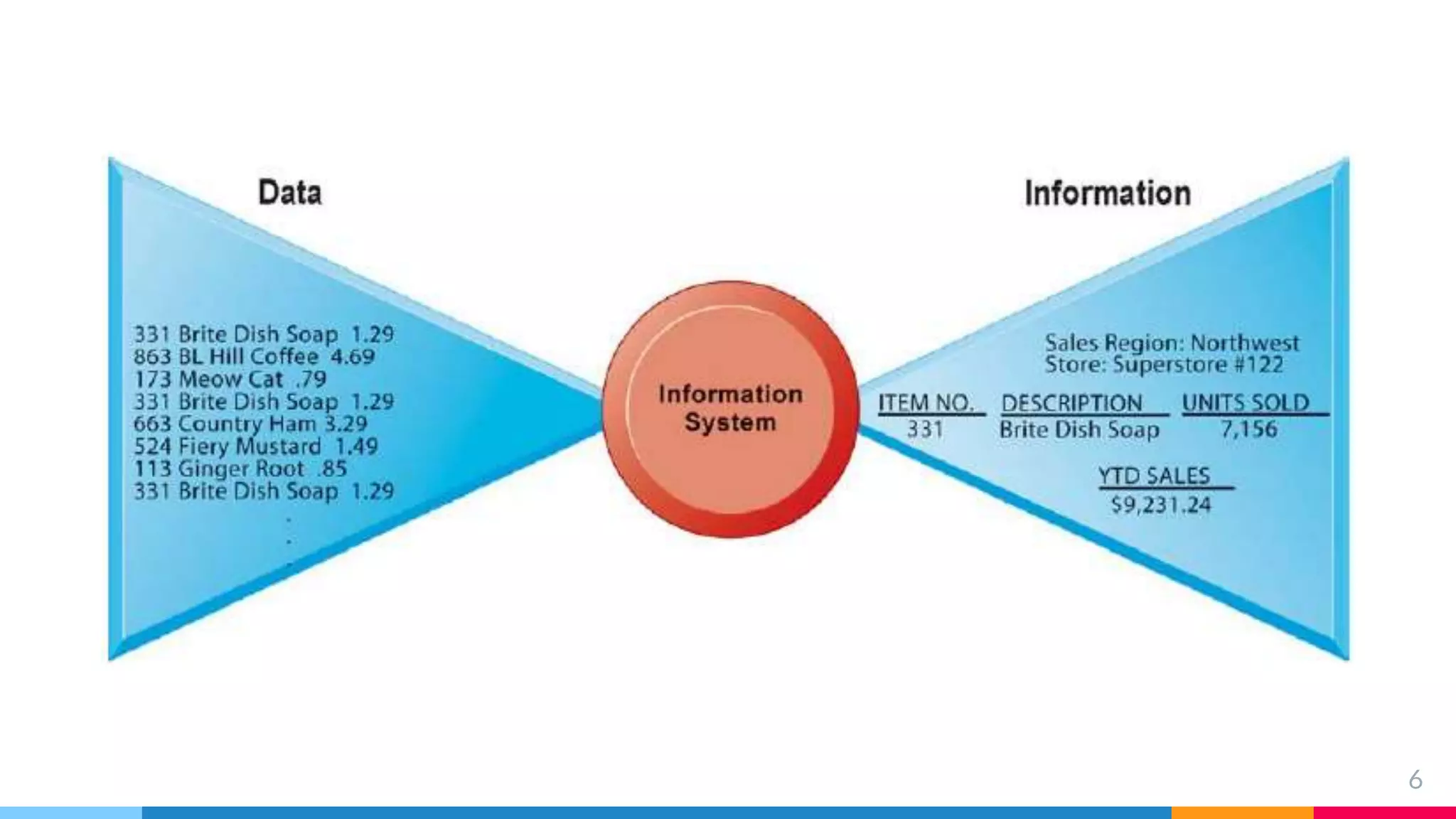
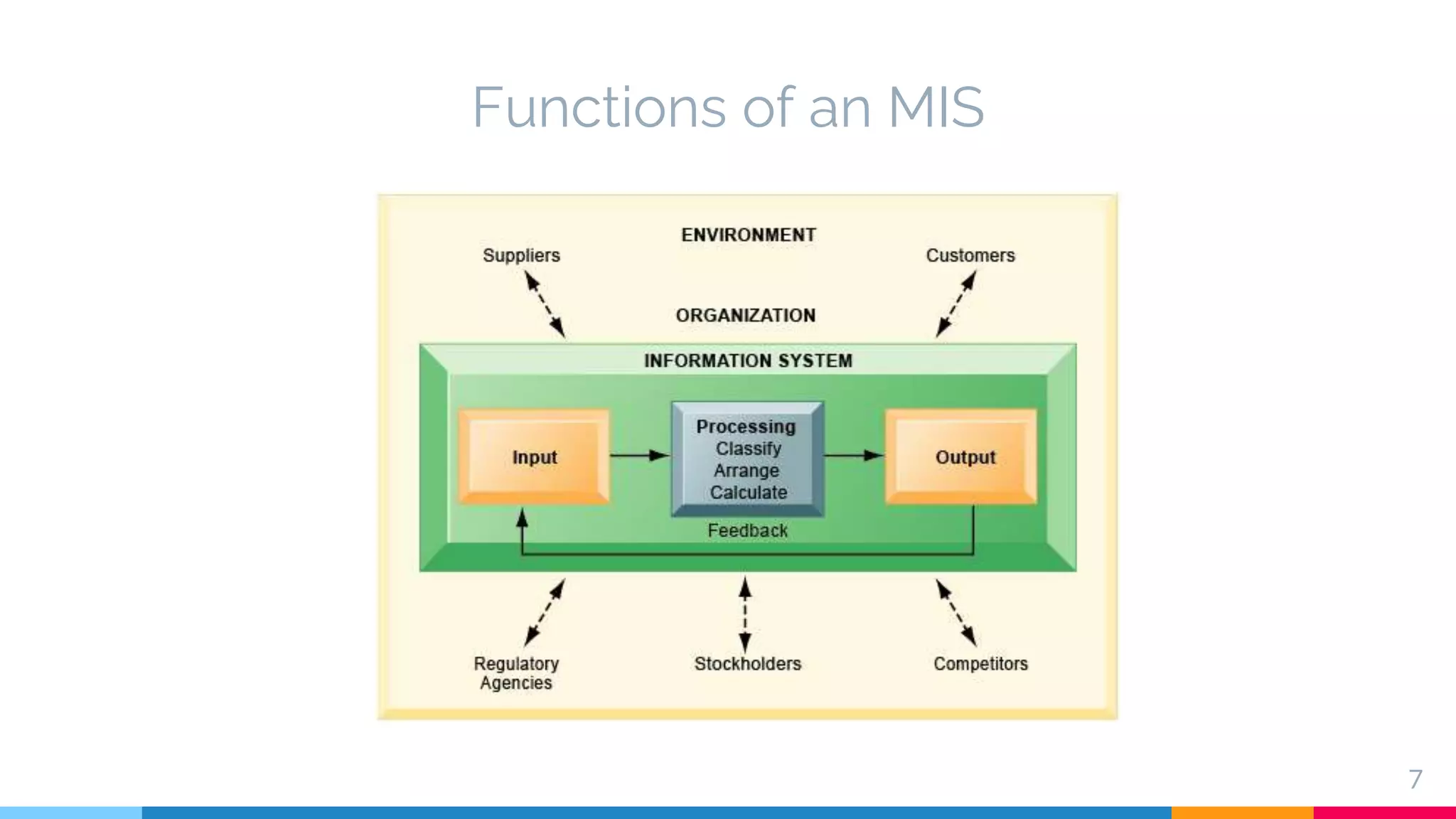
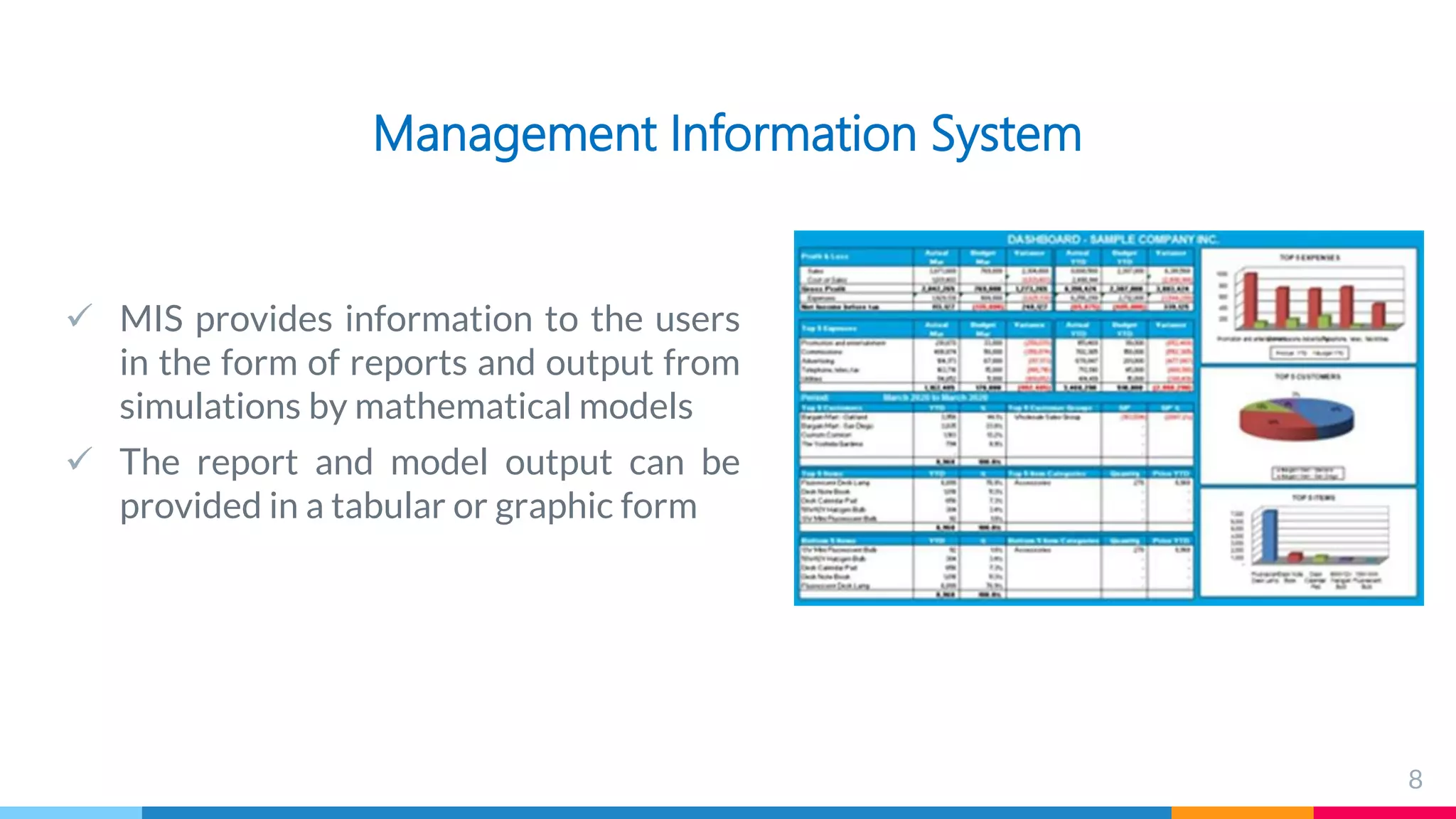
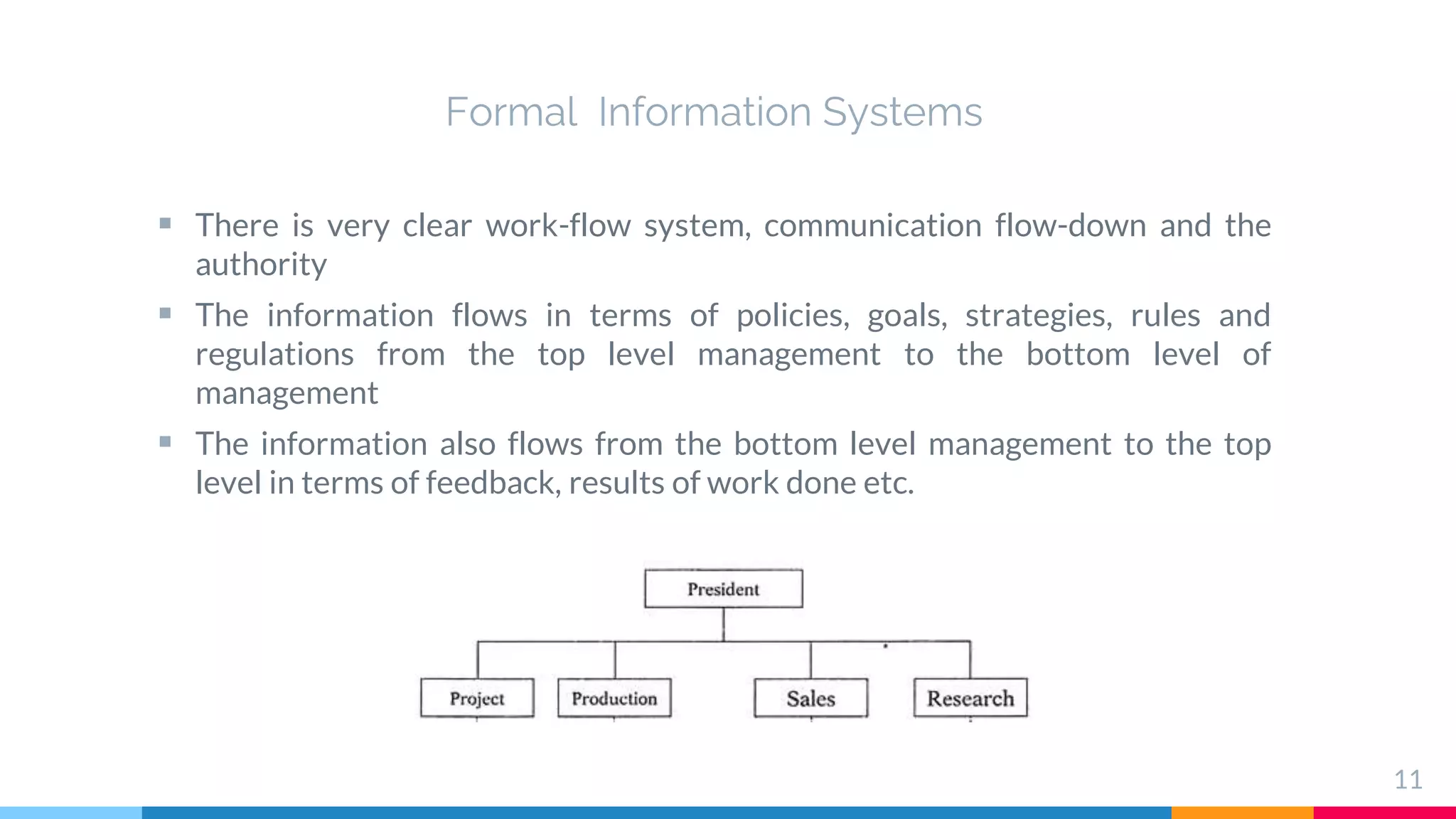
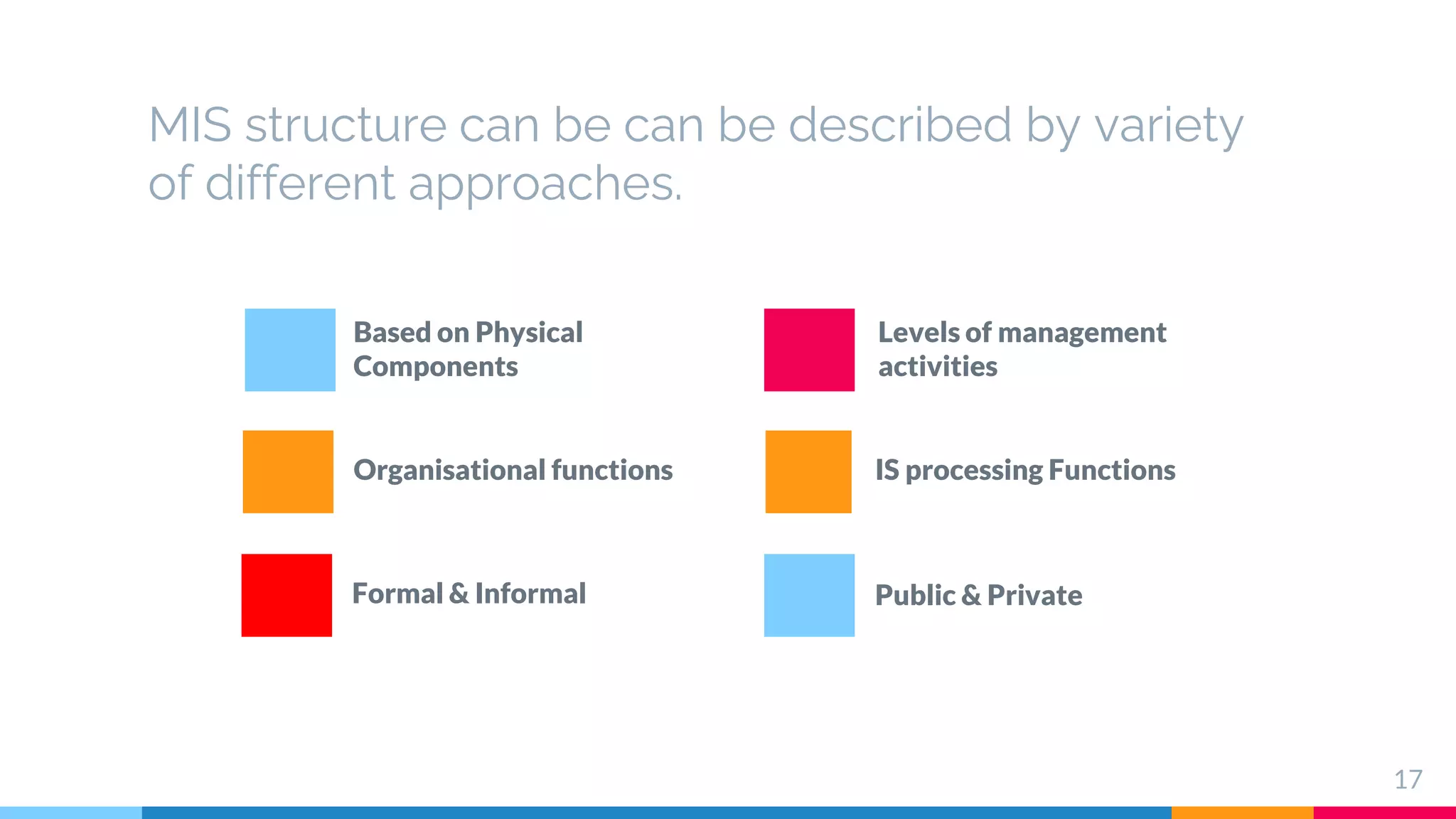
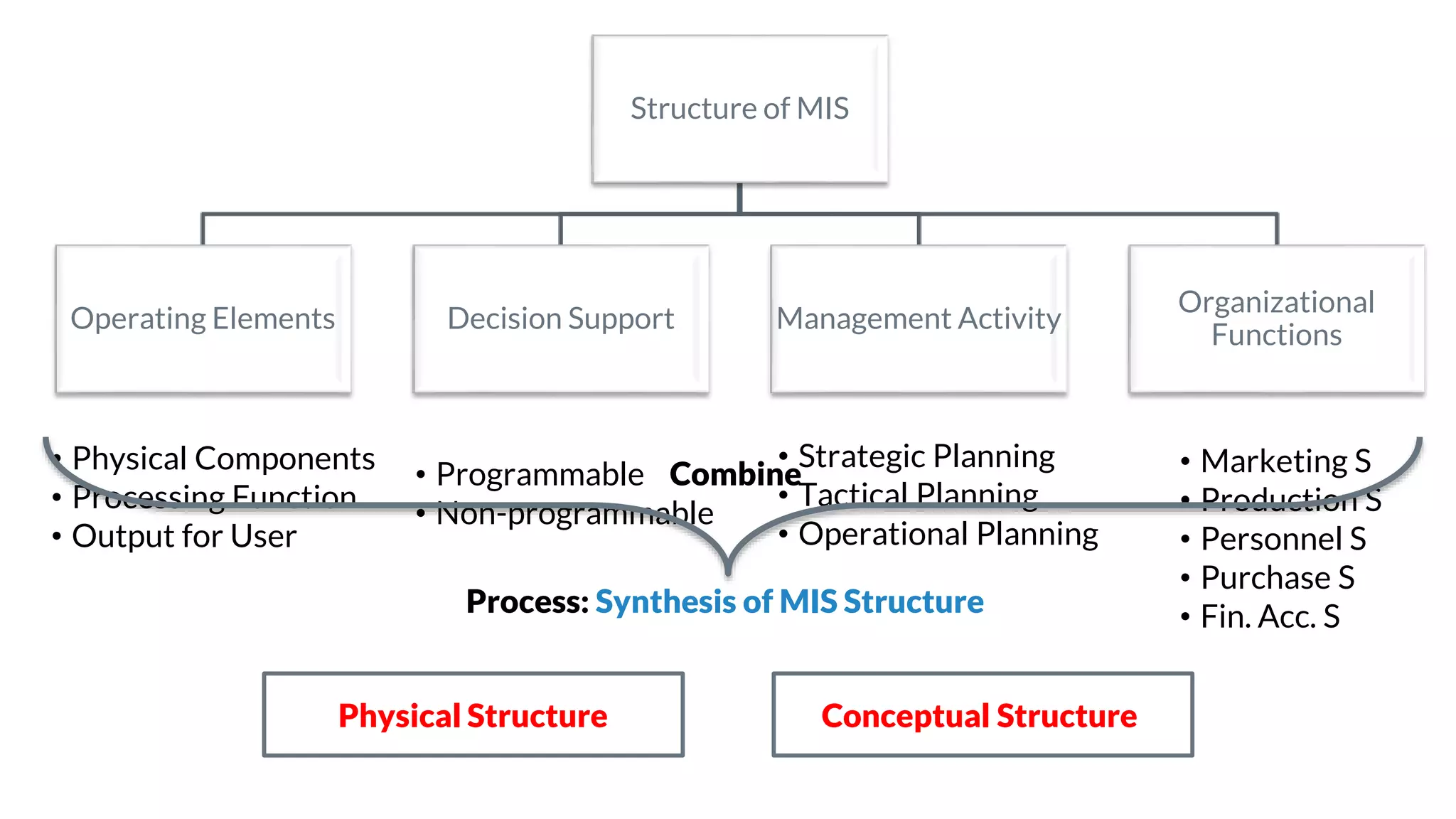
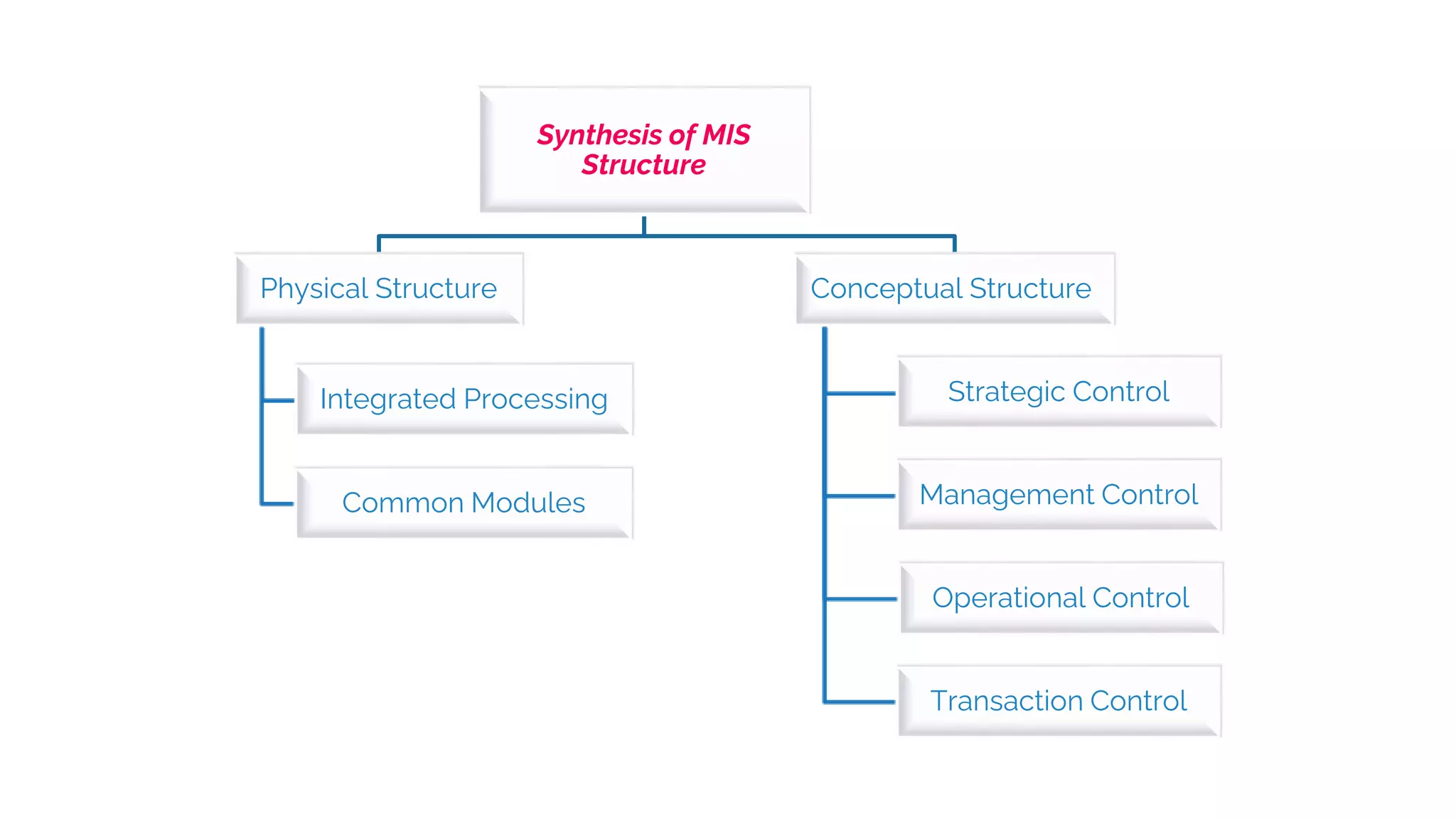
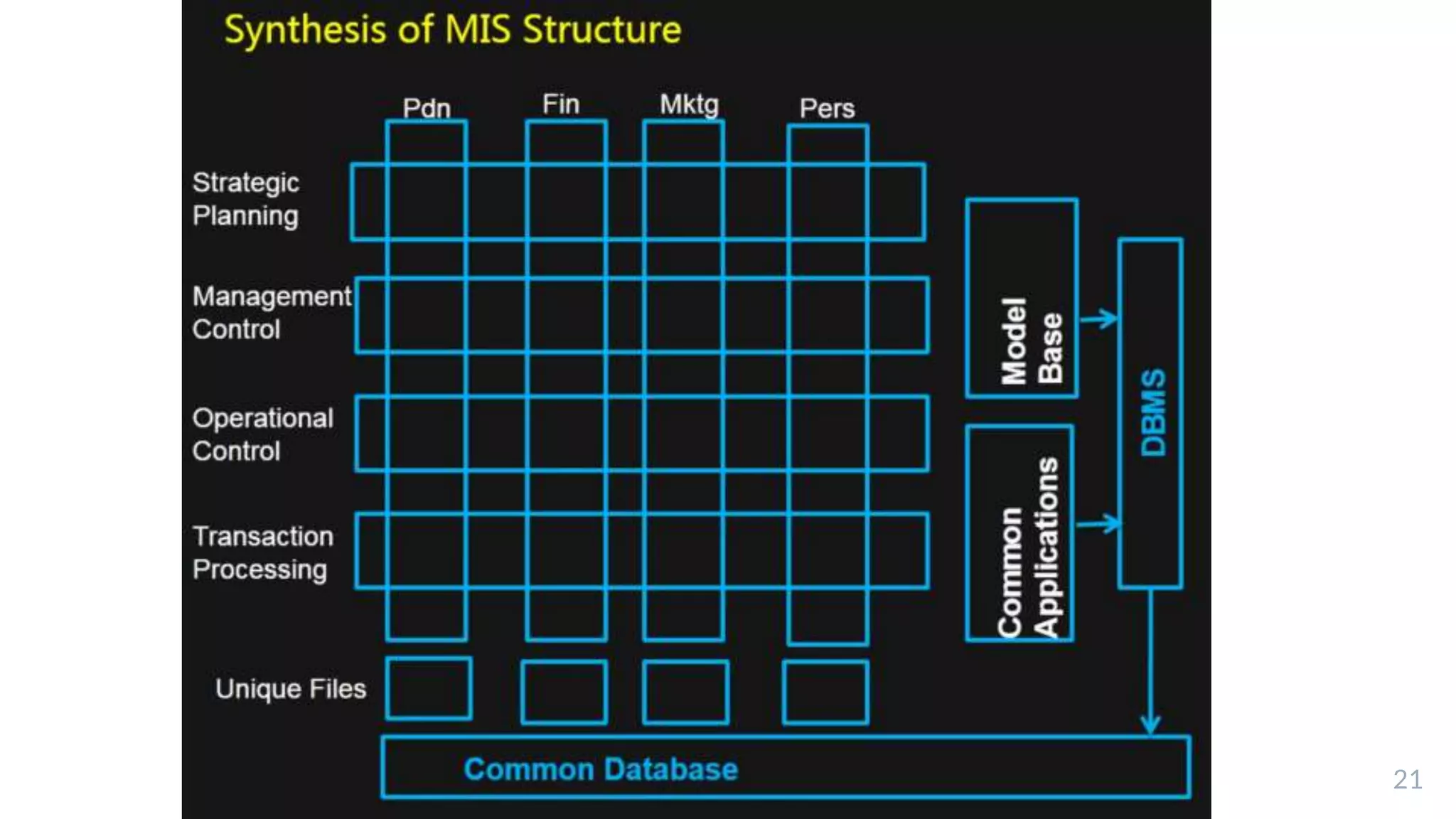
The document outlines the structure and functions of Management Information Systems (MIS), emphasizing its role in decision-making and information flow within an organization. It distinguishes between formal and informal information systems, detailing their information-sharing protocols, types, and purposes. Additionally, it touches upon public and private information systems, explaining their accessibility and operational differences.