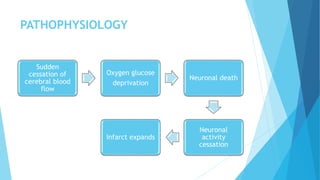
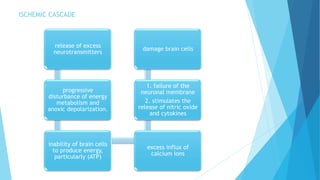
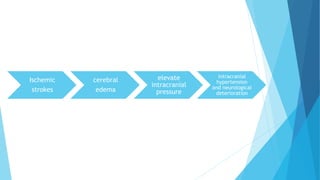
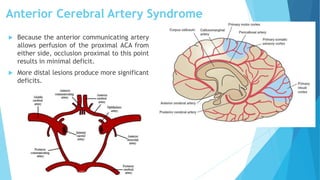
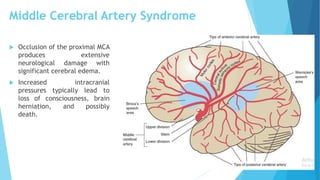
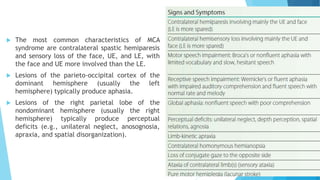
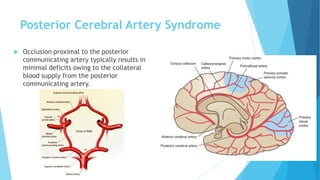
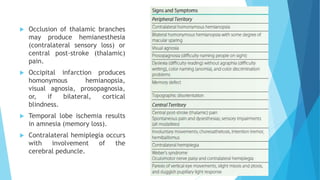
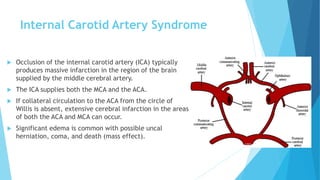
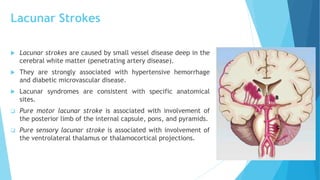
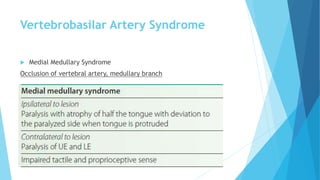
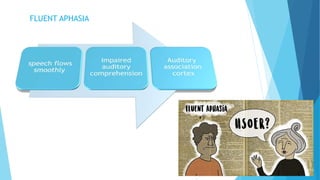
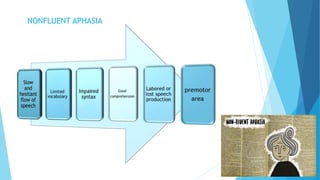
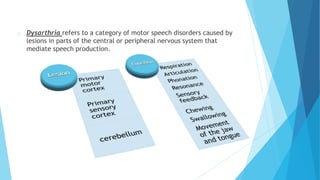
The document discusses stroke, including its types, risk factors, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations based on the artery affected. Ischemic stroke is more common than hemorrhagic and results from blockage of an artery depriving the brain of blood flow. Clinical features vary depending on the specific artery involved, such as contralateral weakness with middle cerebral artery stroke or visual field defects with posterior cerebral artery stroke. Complications can include altered consciousness, speech/language issues, and emotional or cognitive changes.


![DEFINITION
Stroke (cerebrovascular accident [CVA]) is the sudden loss of
neurological function caused by an interruption of the blood flow to
the brain.
REFERENCE: Physical rehabilitation / [edited by] Susan B. O’Sullivan, homas J. Schmitz, George D. Fulk. — 6th ed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke-191016142245/85/Stroke-3-320.jpg)
![TYPES
Ischemic stroke is the most common type, affecting about 80% of
individuals with stroke, and results when a clot blocks or impairs
blood flow, depriving the brain of essential oxygen and nutrients.
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when blood vessels rupture, causing
leakage of blood in or around the brain.
REFERENCE: Physical rehabilitation / [edited by] Susan B. O’Sullivan, homas J. Schmitz, George D. Fulk. — 6th ed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke-191016142245/85/Stroke-4-320.jpg)

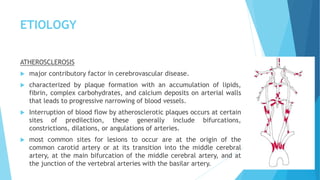


![RISK FACTORS
Hypertension
Heart Disease (HD)
Disorders Of Heart Rhythm
Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
Elevated Total Blood Cholesterol
(Hypercholesterolemia)
Elevated Low-density Lipoprotein (LDL
[“Bad”]) Cholesterol
Low Levels Of High-density Lipoprotein
(HDL [“Good”]) Cholesterol
Elevated Fasting Triglyceride Level
Marked Elevations Of Hematocrit
Family History, Age, Gender, And Race
(African American)
Atrial fibrillation
End-stage Renal Disease And Chronic Kidney
Disease
Sleep Apnea
Women With Early Menopause (Before 42
Years Of Age)
Pregnancy, Birth, And The First 6 Weeks
Postpartum In Older Women And African
Americans
Preeclampsia
cigarette smoking
Physical inactivity
Obesity
Diet
Cardiac Disorders Such As Rheumatic Heart
Valvular Disease, Endocarditis, Or Cardiac
Surgery](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stroke-191016142245/85/Stroke-9-320.jpg)