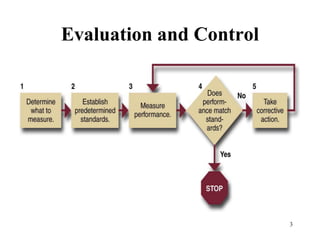
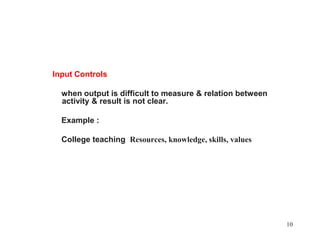
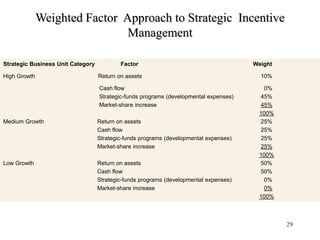
The document provides information about strategic management evaluation and control processes. It discusses measuring performance, comparing results to standards, identifying deviations, and taking corrective actions. Key aspects include setting measurable goals, benchmarking against best-in-class competitors, and using tools like the balanced scorecard to evaluate performance from multiple perspectives. Regular monitoring and analysis of variances is important to ensure the organization achieves its objectives.