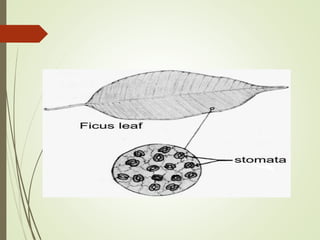
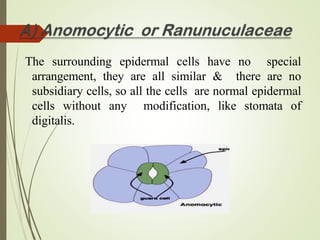
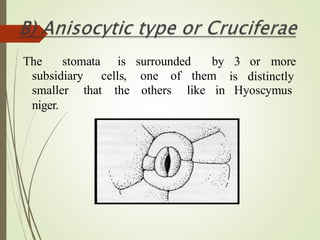
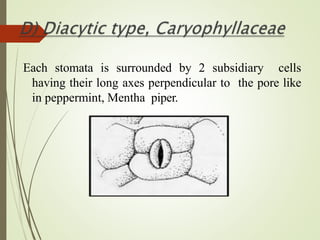
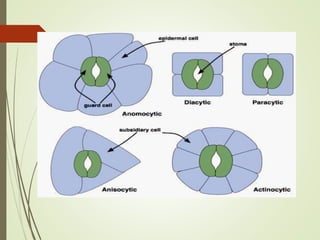
The document discusses the structure and types of stomata. Stomata are microscopic openings on plant surfaces surrounded by guard cells and subsidiary cells. There are four basic types of stomata distinguished by the arrangement of subsidiary cells: anomocytic (no arrangement), anisocytic (one smaller cell), paracytic (subsidiary cells parallel to pore), and diacytic (subsidiary cells perpendicular to pore). Examples of each type are provided. The structures allow for gas exchange and vary between dicotyledonous plant species.