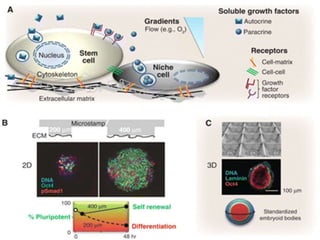
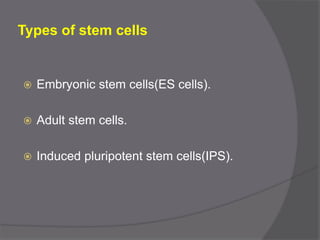
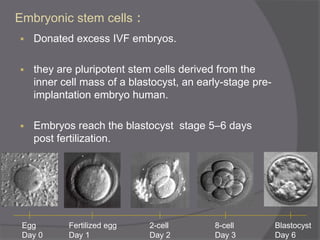
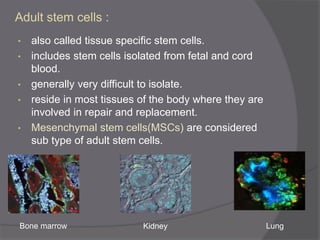
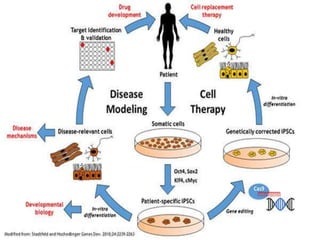
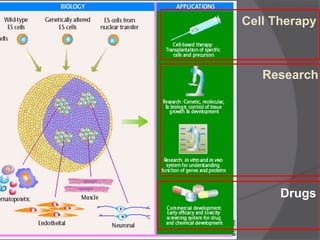
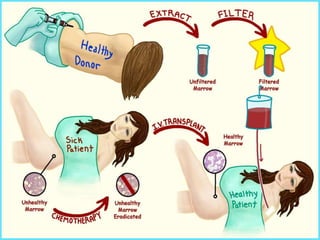
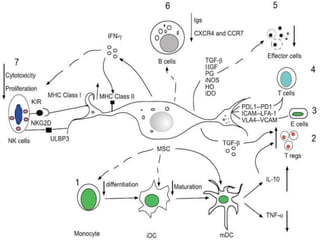
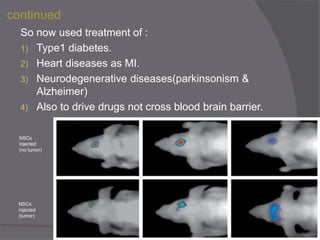
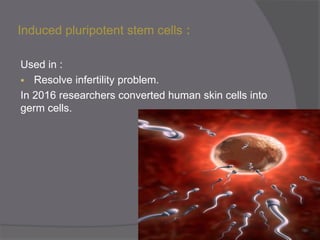
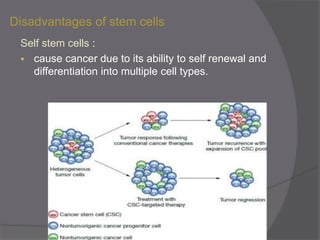
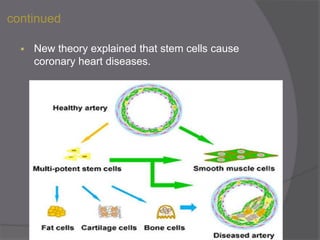
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into specialized cell types and can self-renew to produce more stem cells. There are three main types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells which are pluripotent, adult stem cells which reside in adult tissues, and induced pluripotent stem cells which are generated from adult cells. Stem cells are currently being researched for their potential uses in cell therapies, drug development and testing, and understanding human development. However, there are also disadvantages such as tumor formation and ethical issues regarding the use of embryonic stem cells. The future of stem cell research remains promising but still has many unanswered questions.