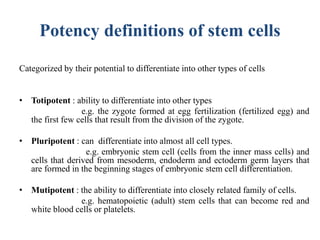
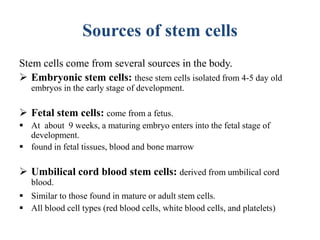
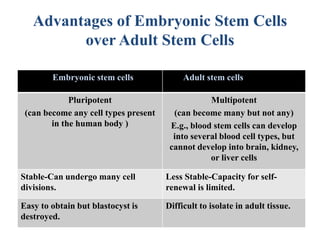
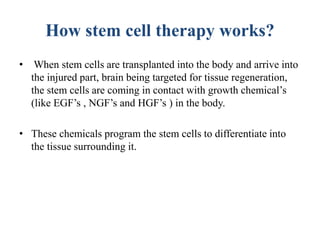
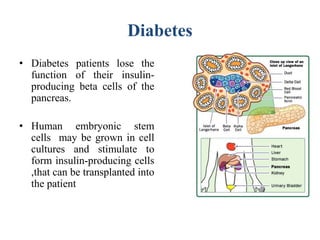
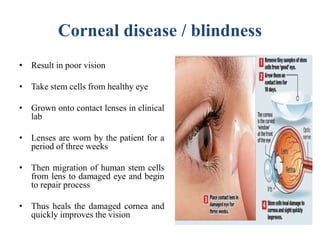
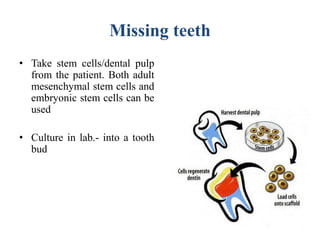
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that can differentiate into specialized cell types. There are several sources of stem cells including embryonic stem cells derived from early stage embryos, adult stem cells found in adult tissues, and fetal stem cells from fetuses. Stem cells are categorized by their potency, or ability to differentiate, with totipotent stem cells able to differentiate into all cell types and unipotent stem cells only able to produce their own cell type. Stem cell therapy works by transplanting stem cells into injured tissues where they receive signals to differentiate into the needed cell types to repair damage. Potential applications of stem cell therapy include treating diseases like diabetes, Parkinson's, and brain injuries.