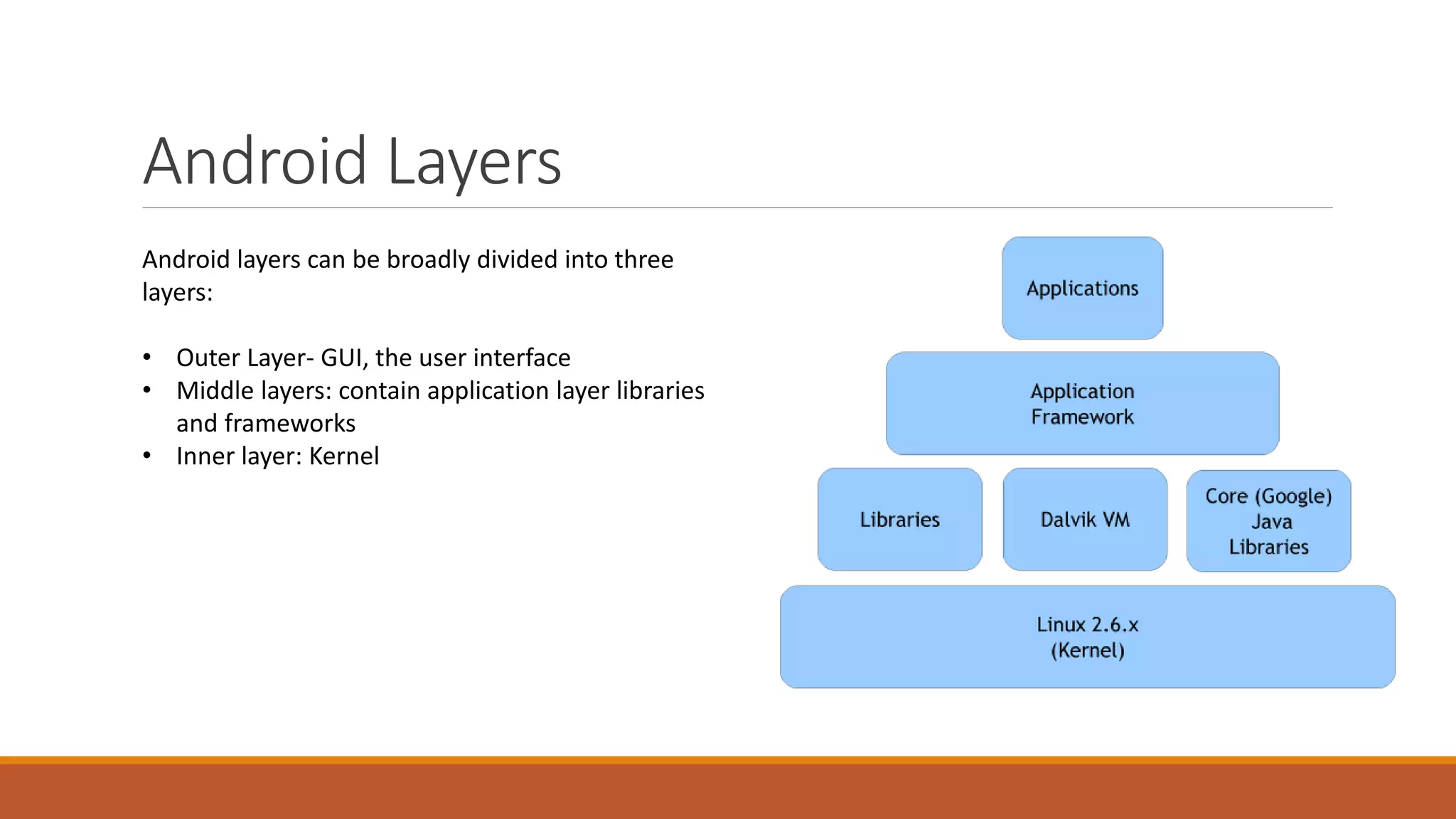
This document discusses using steganography techniques to hide Android applications. It describes hiding apps by replacing memory bits, rendering data in hidden mode, and hiding apps across Android's three layers - the outer GUI layer, middle application layer libraries, and inner kernel layer. The main process involves hiding the app from the application drawer, gaining root access, making it invisible in memory, and launching it from the dial pad using a broadcast receiver. Hidden applications could store passwords, log books, banking info, and personal data.