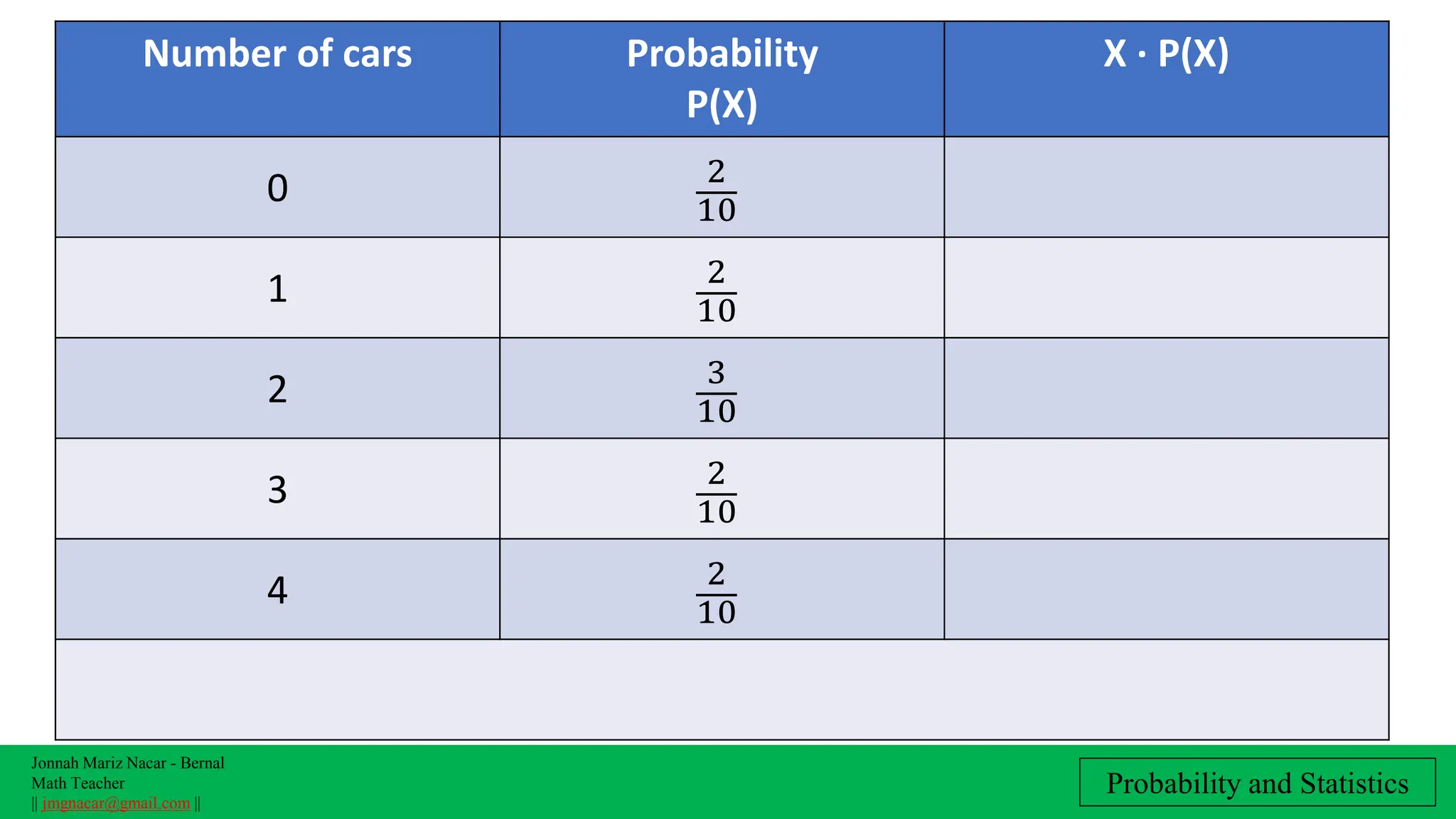
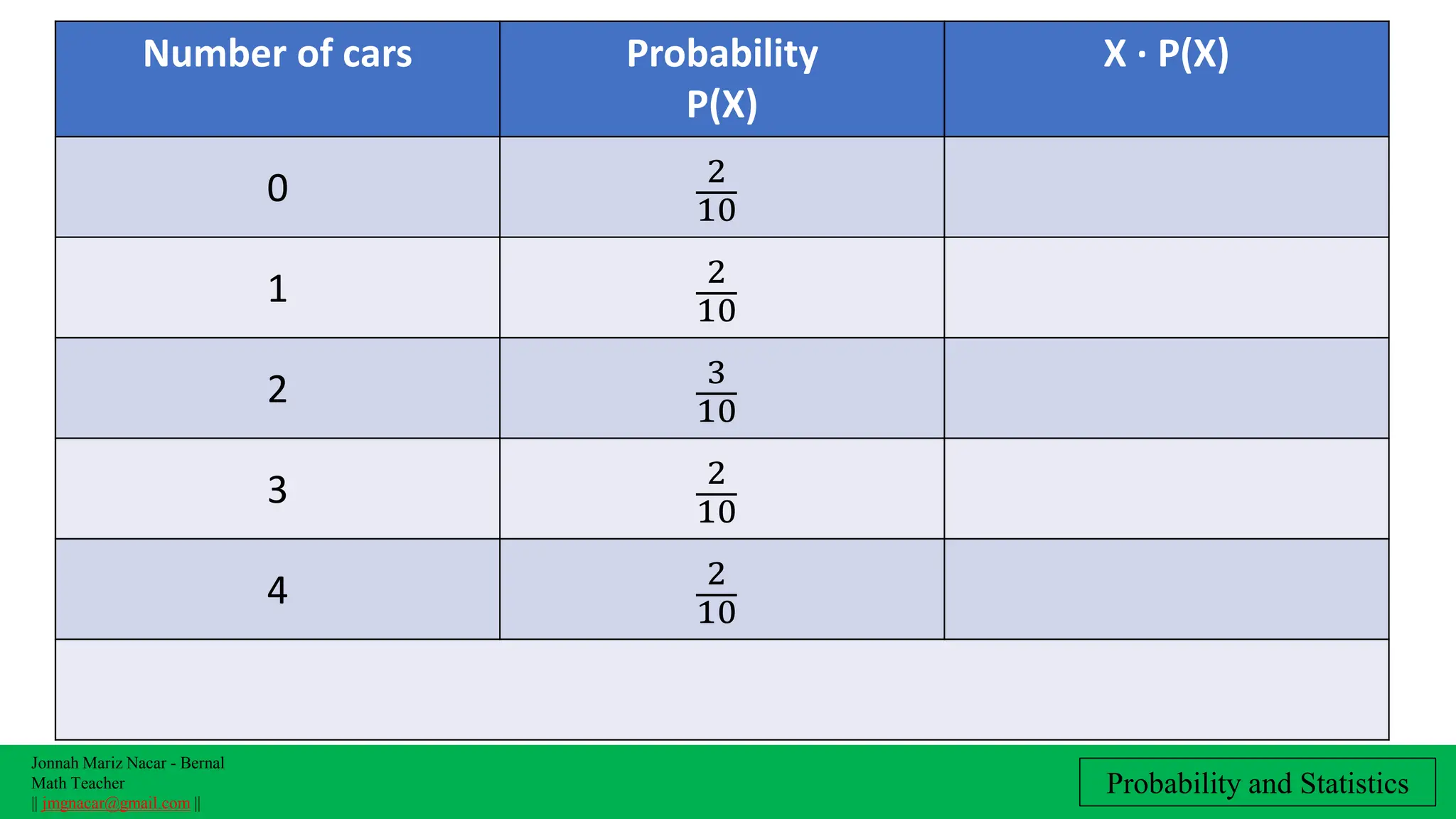
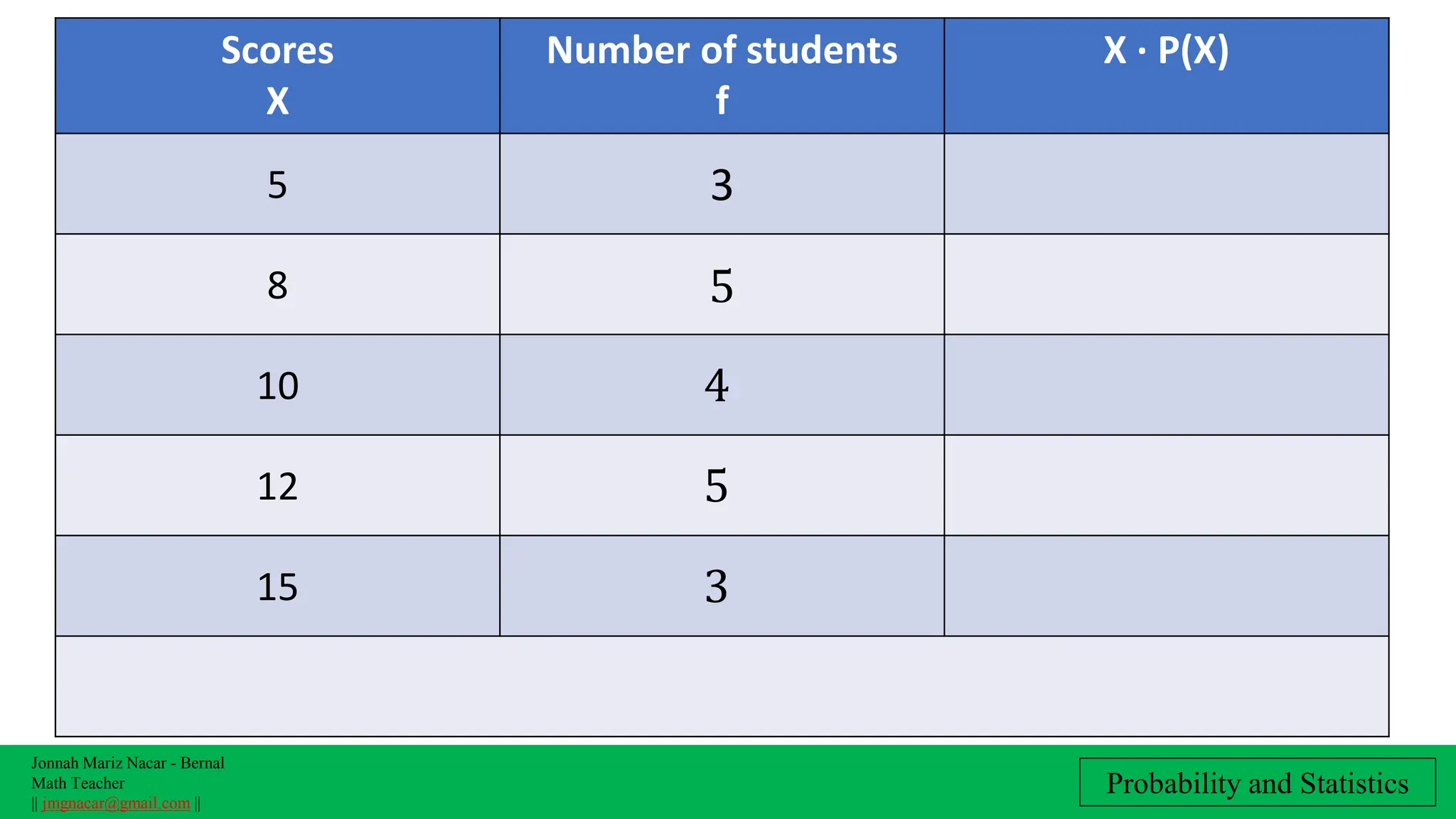
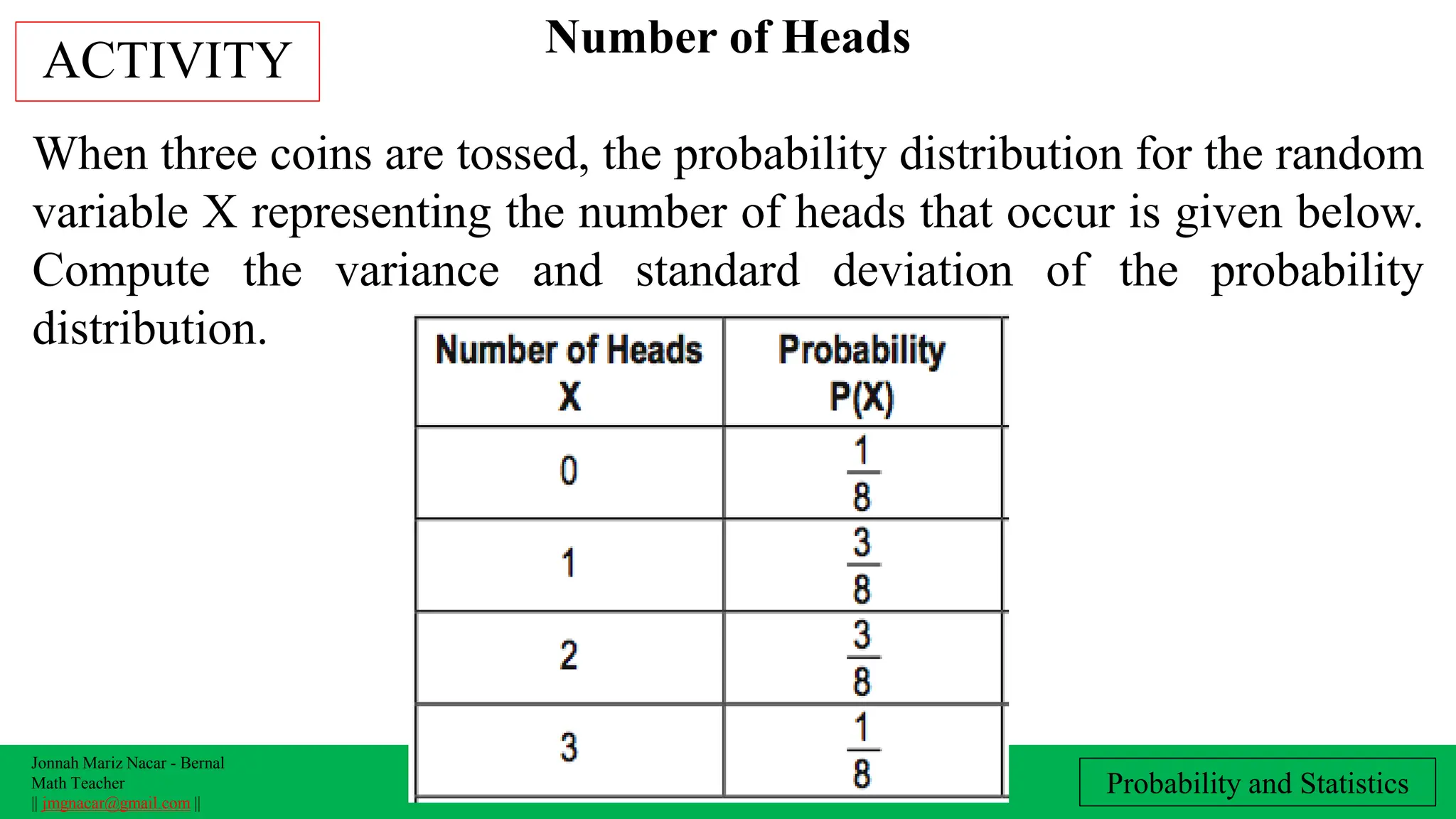
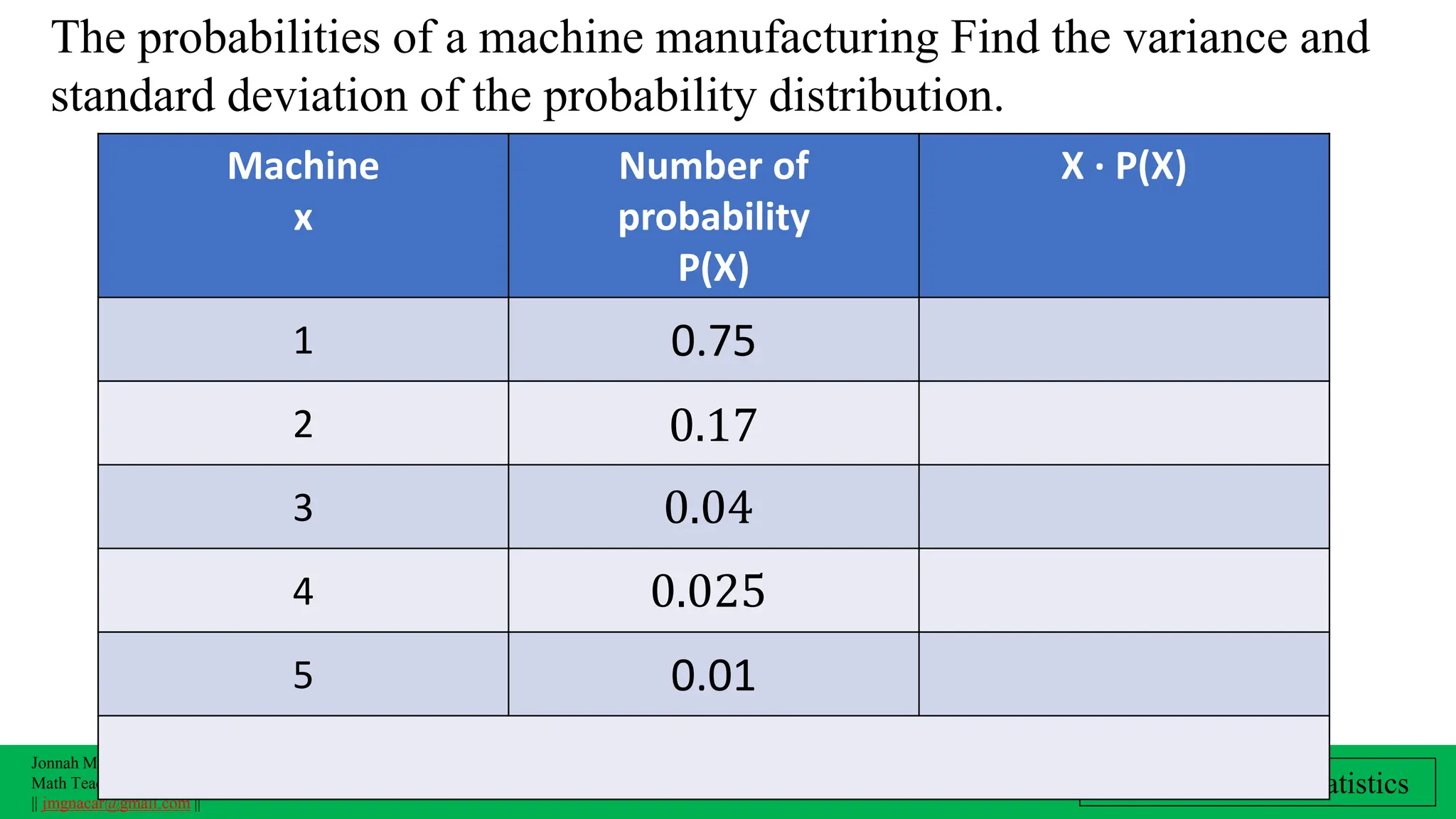
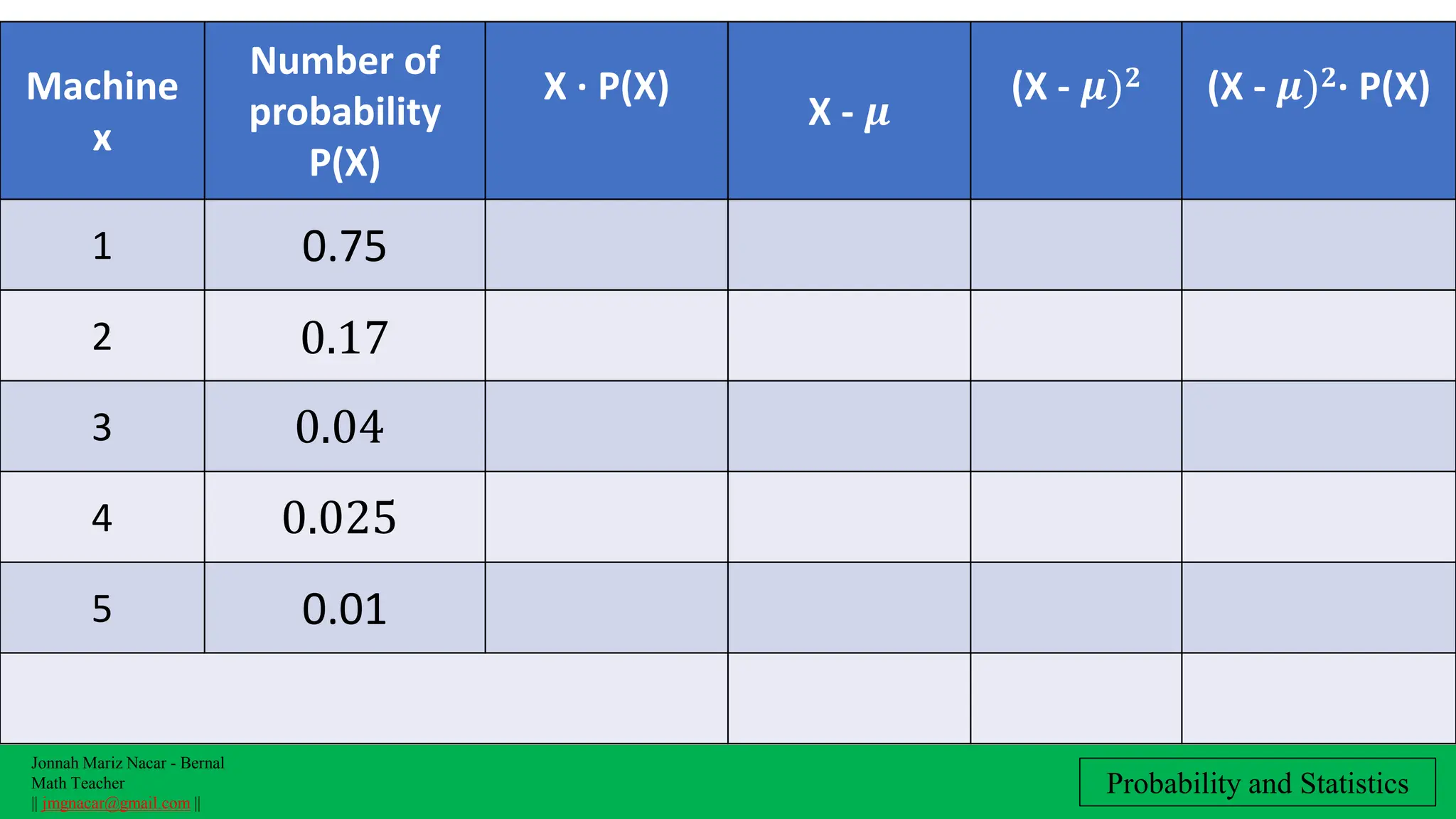
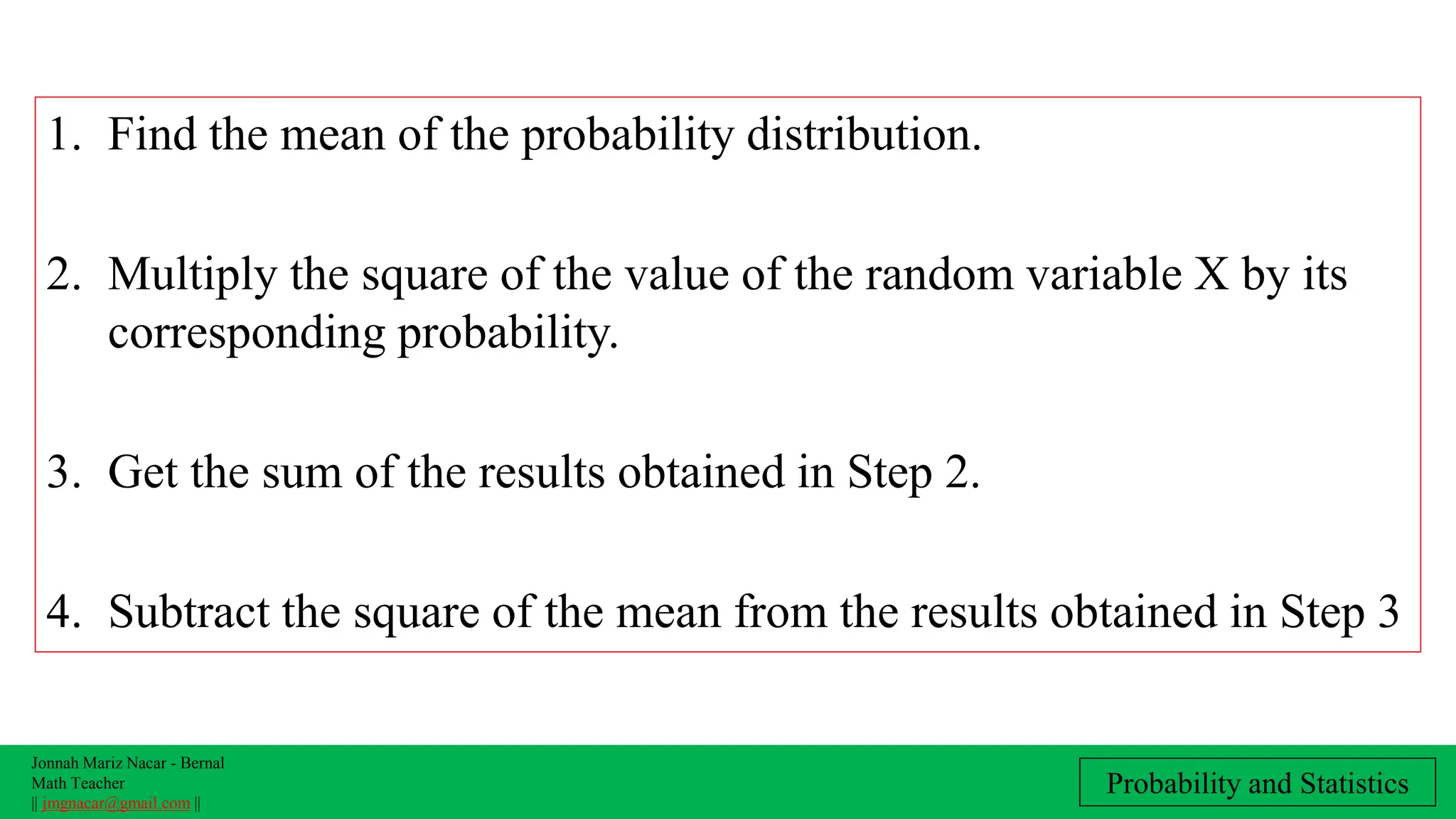
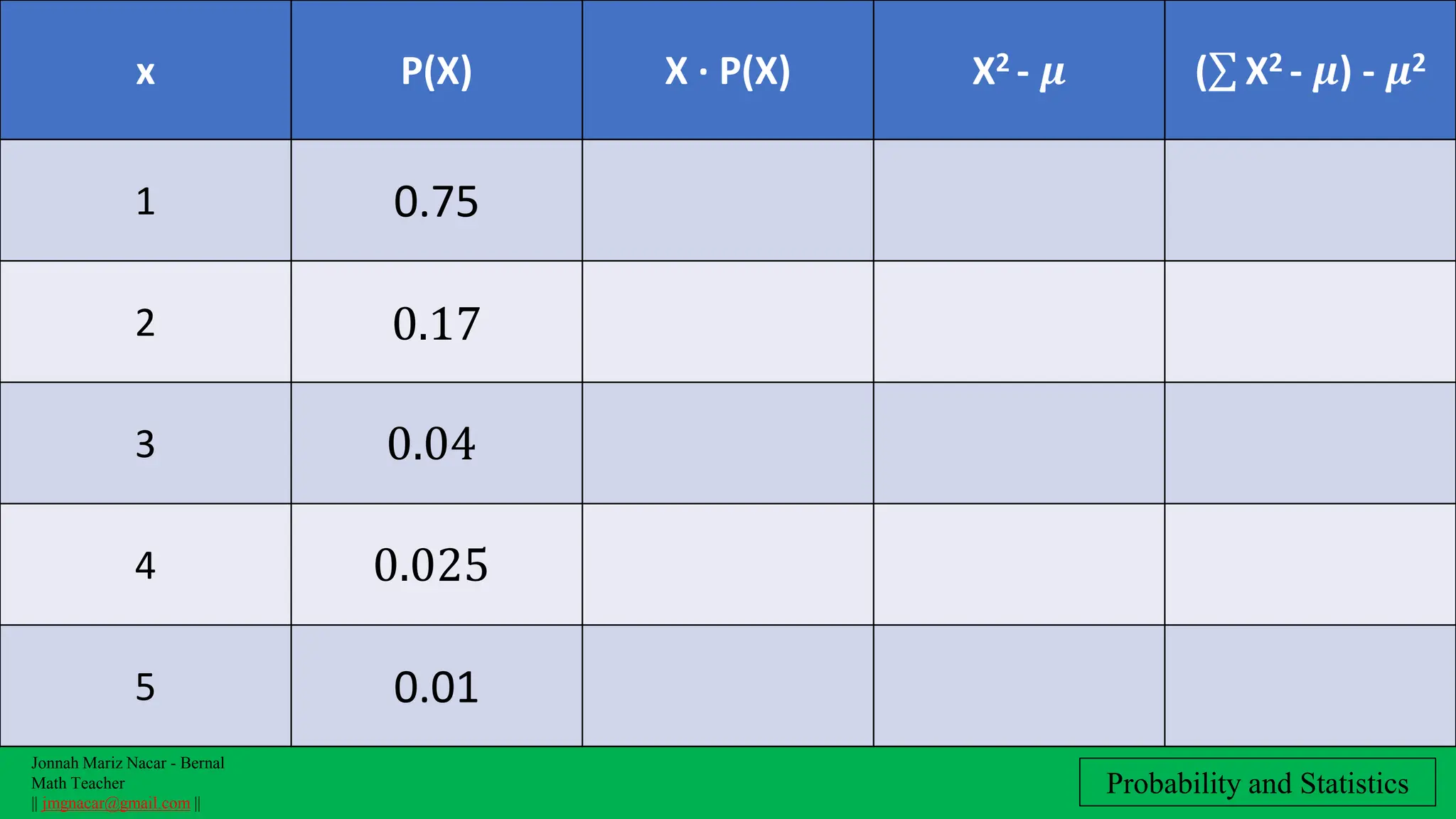
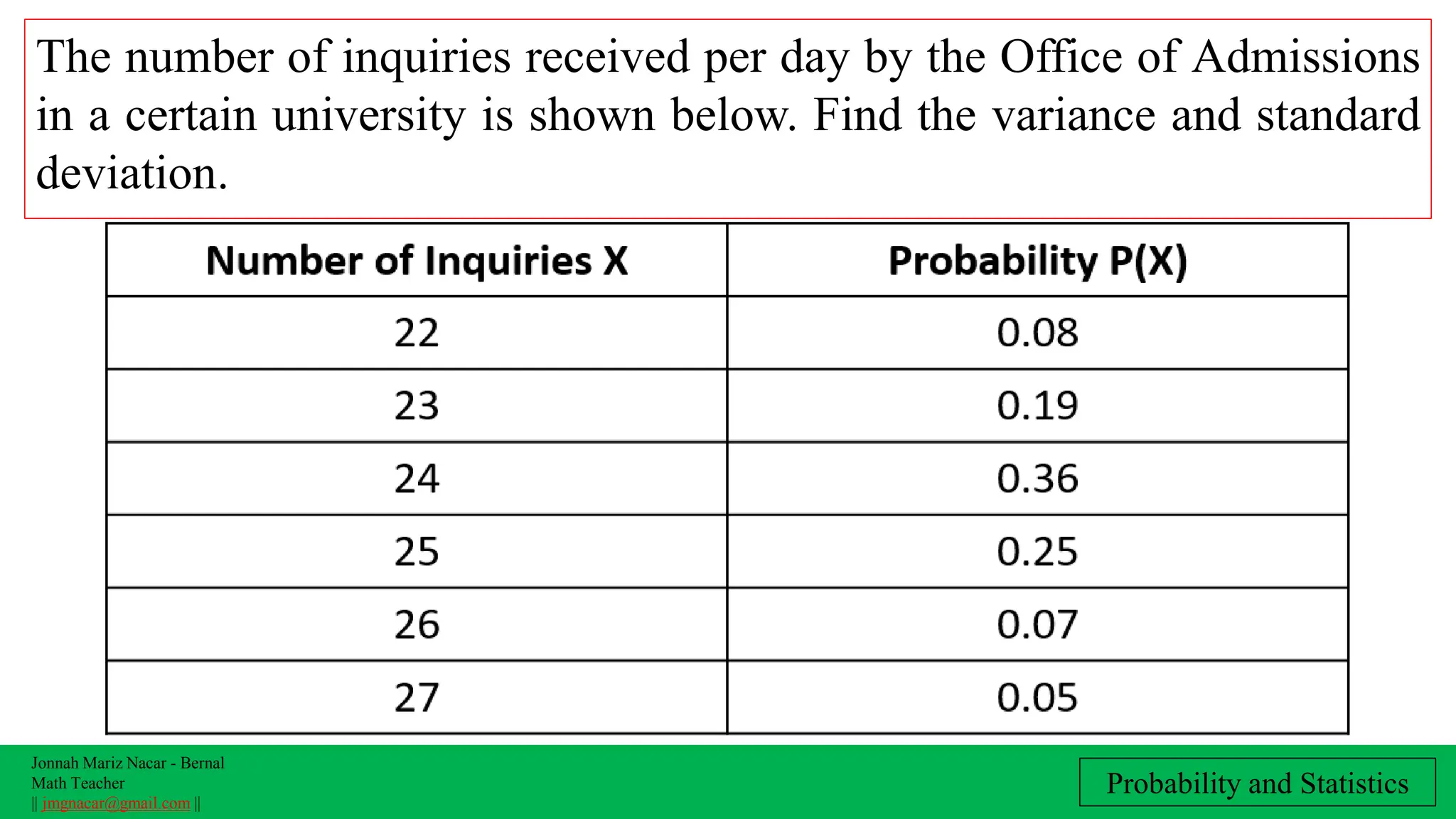
The document outlines a lesson plan on computing variance and standard deviation of discrete probability distributions, aimed at helping students illustrate, calculate, and interpret these statistical measures. It includes step-by-step methods for finding variance and standard deviation using various examples, such as the number of cars sold and machine probabilities. Overall, it provides essential objectives and procedures for teaching and understanding these key statistical concepts.