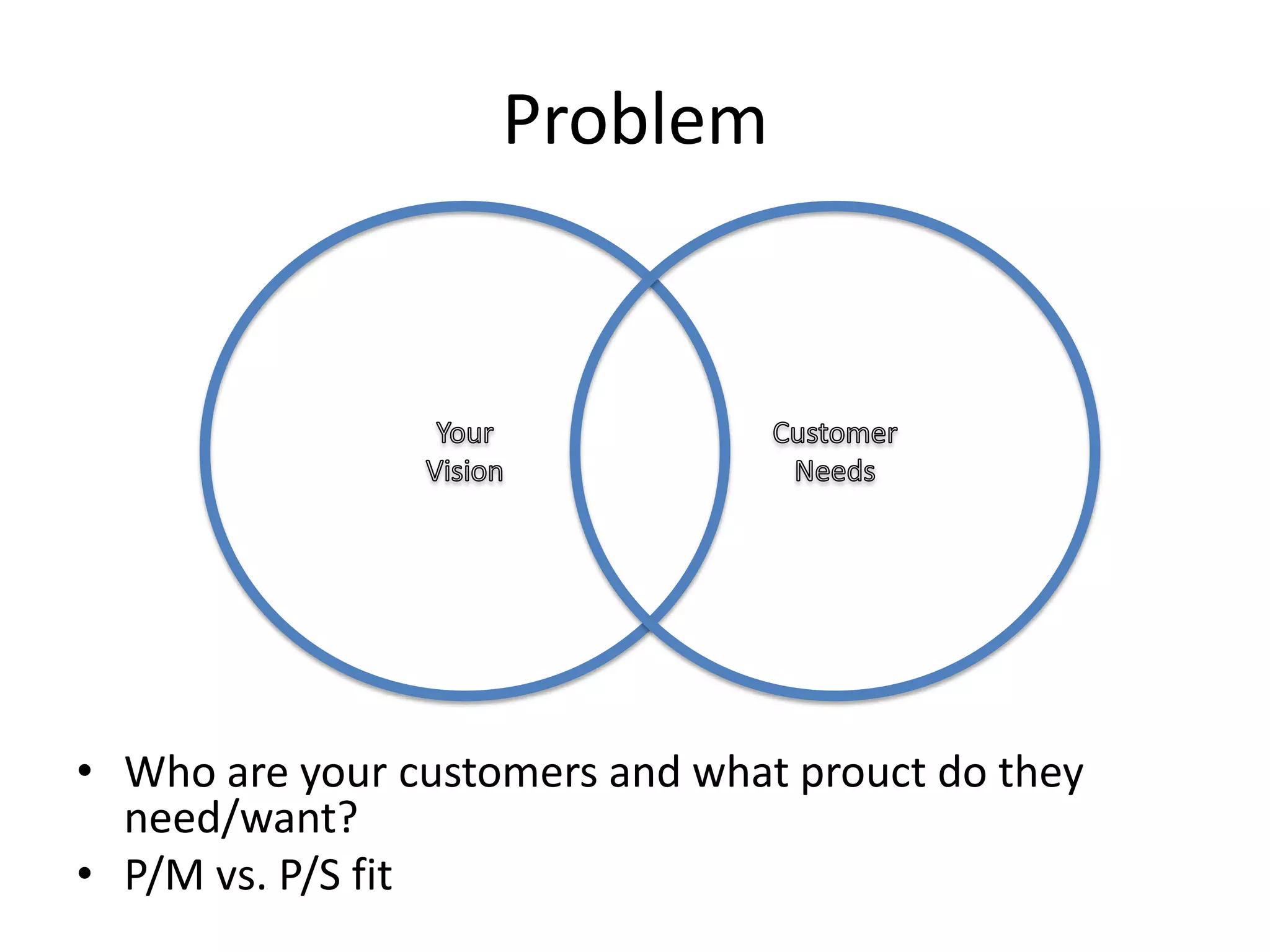
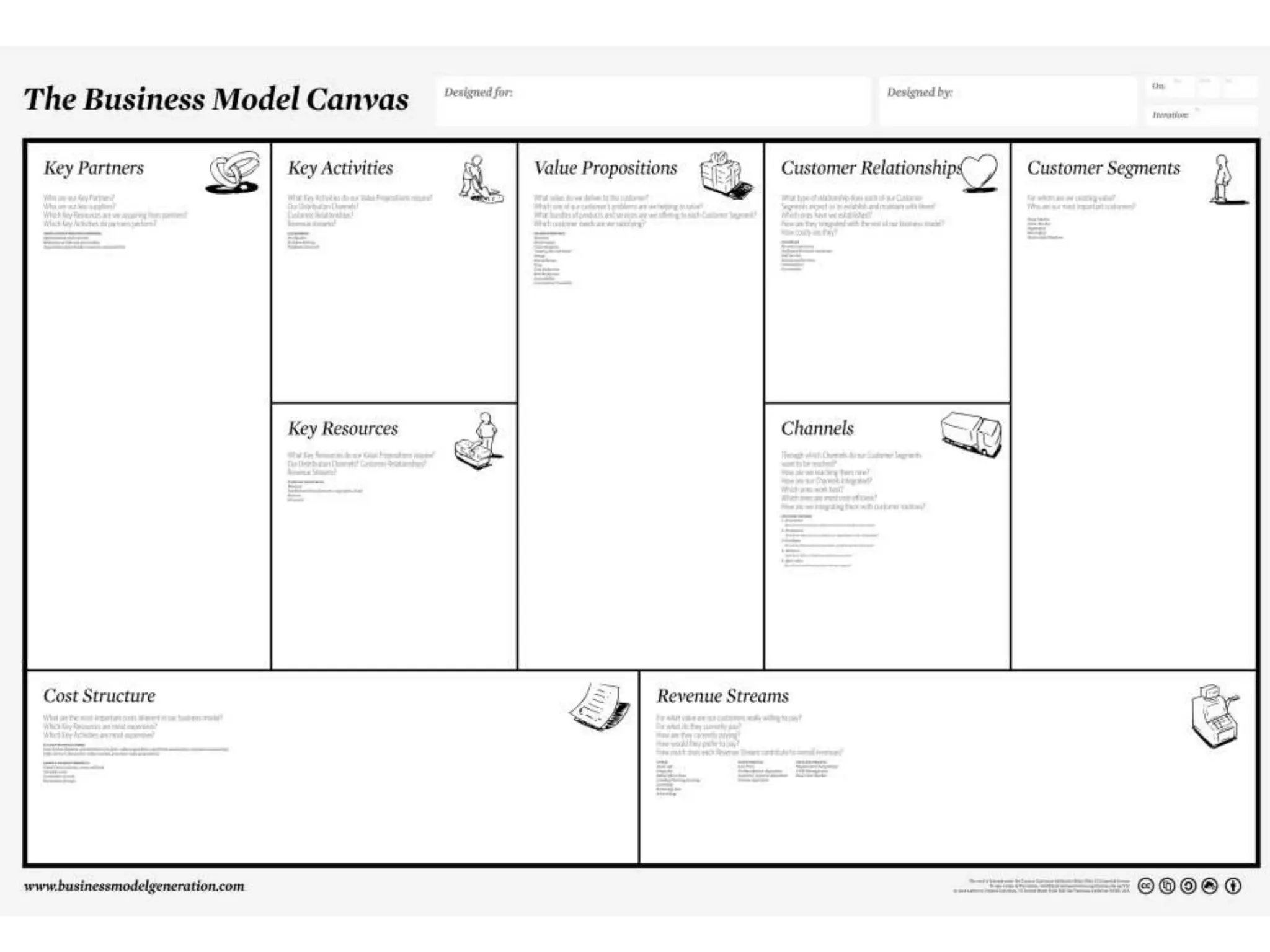
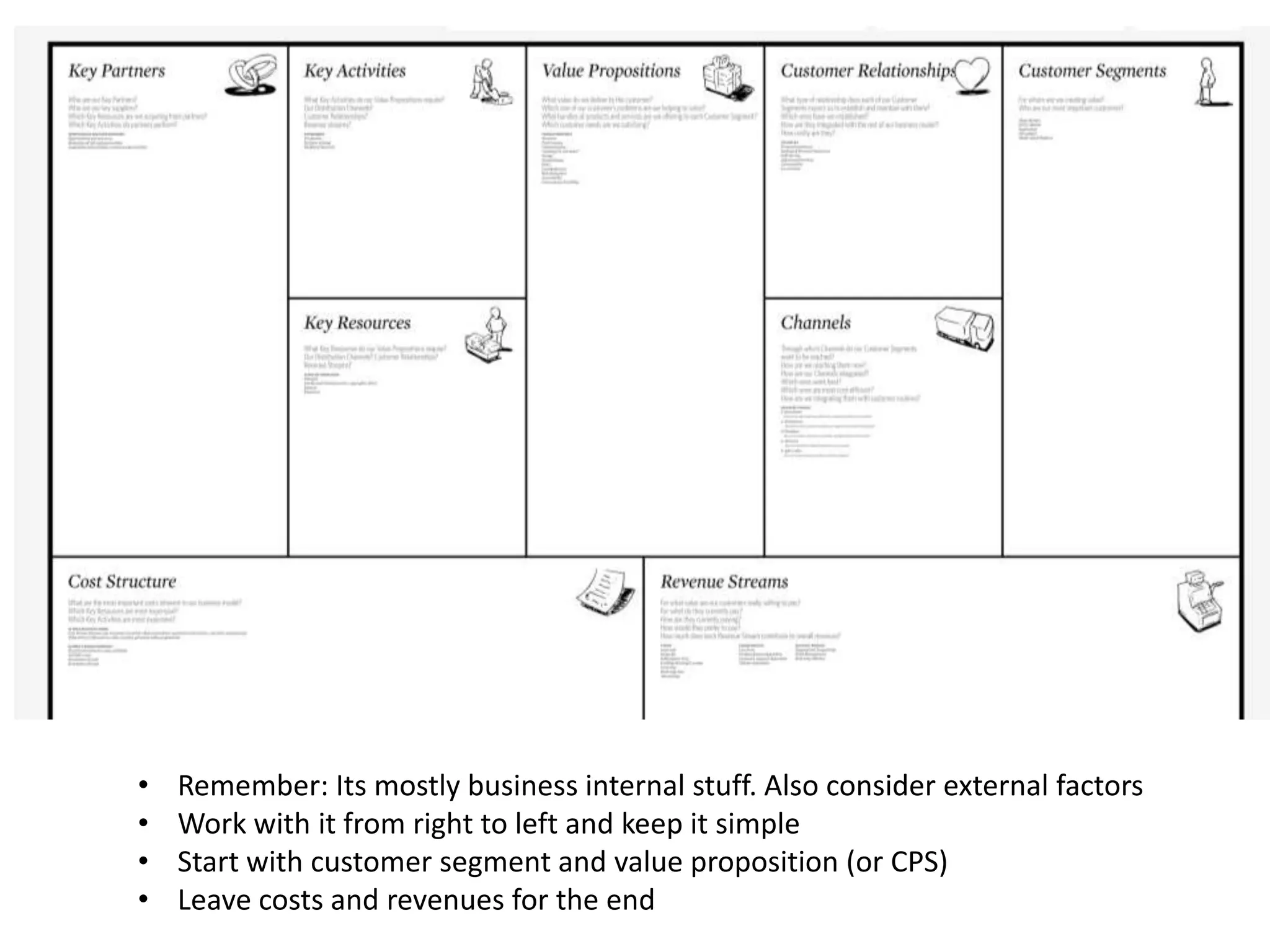
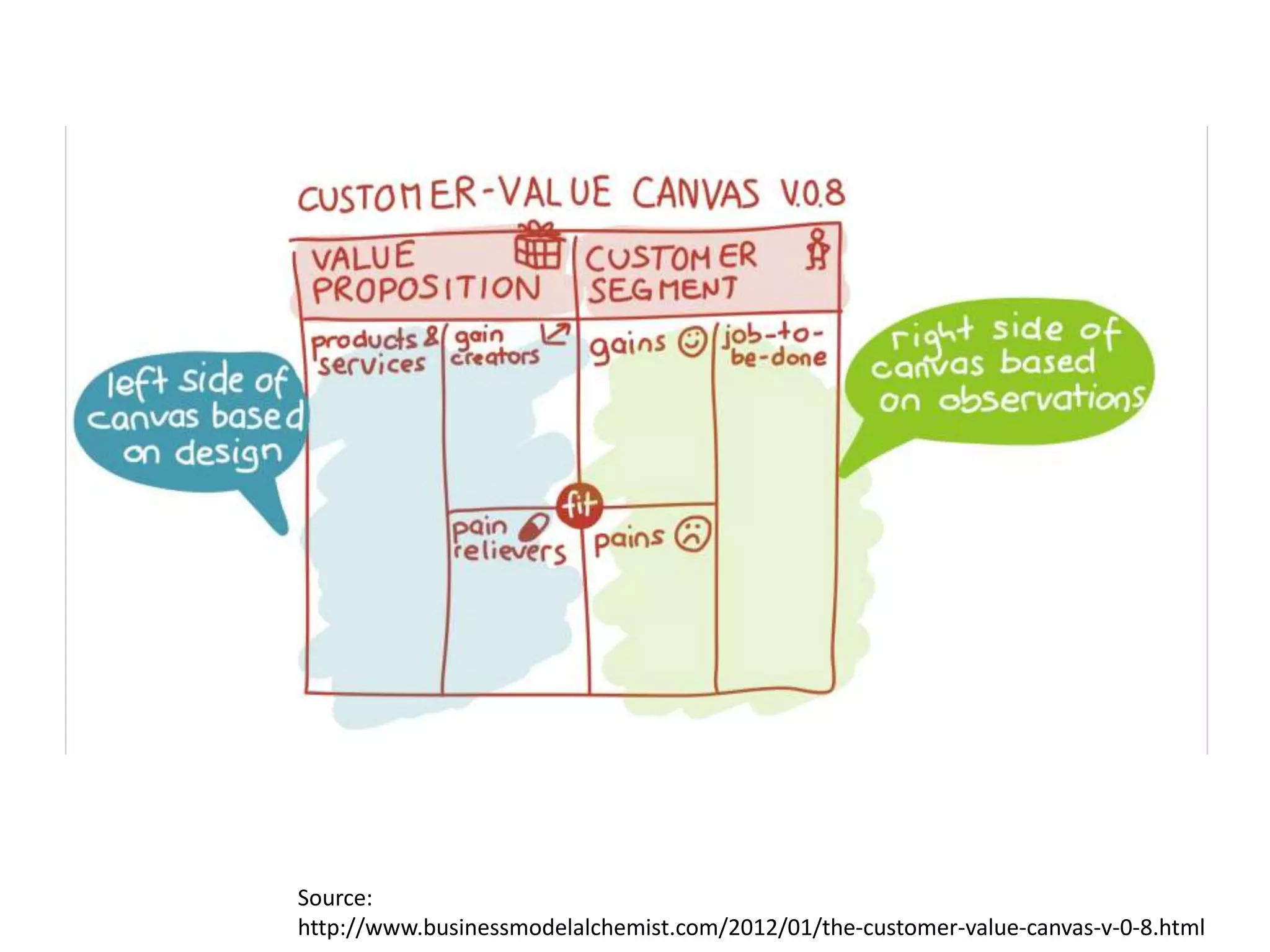
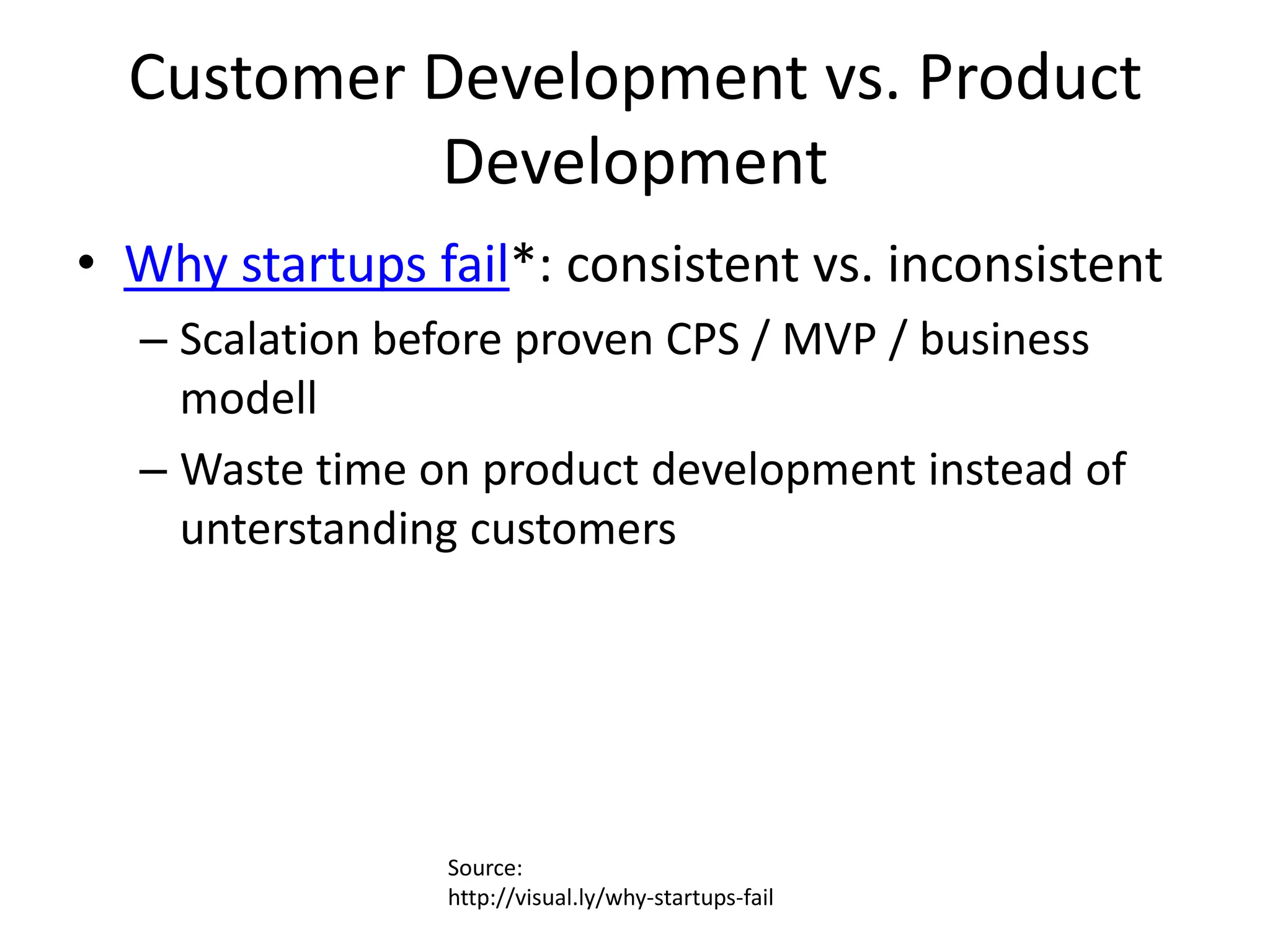
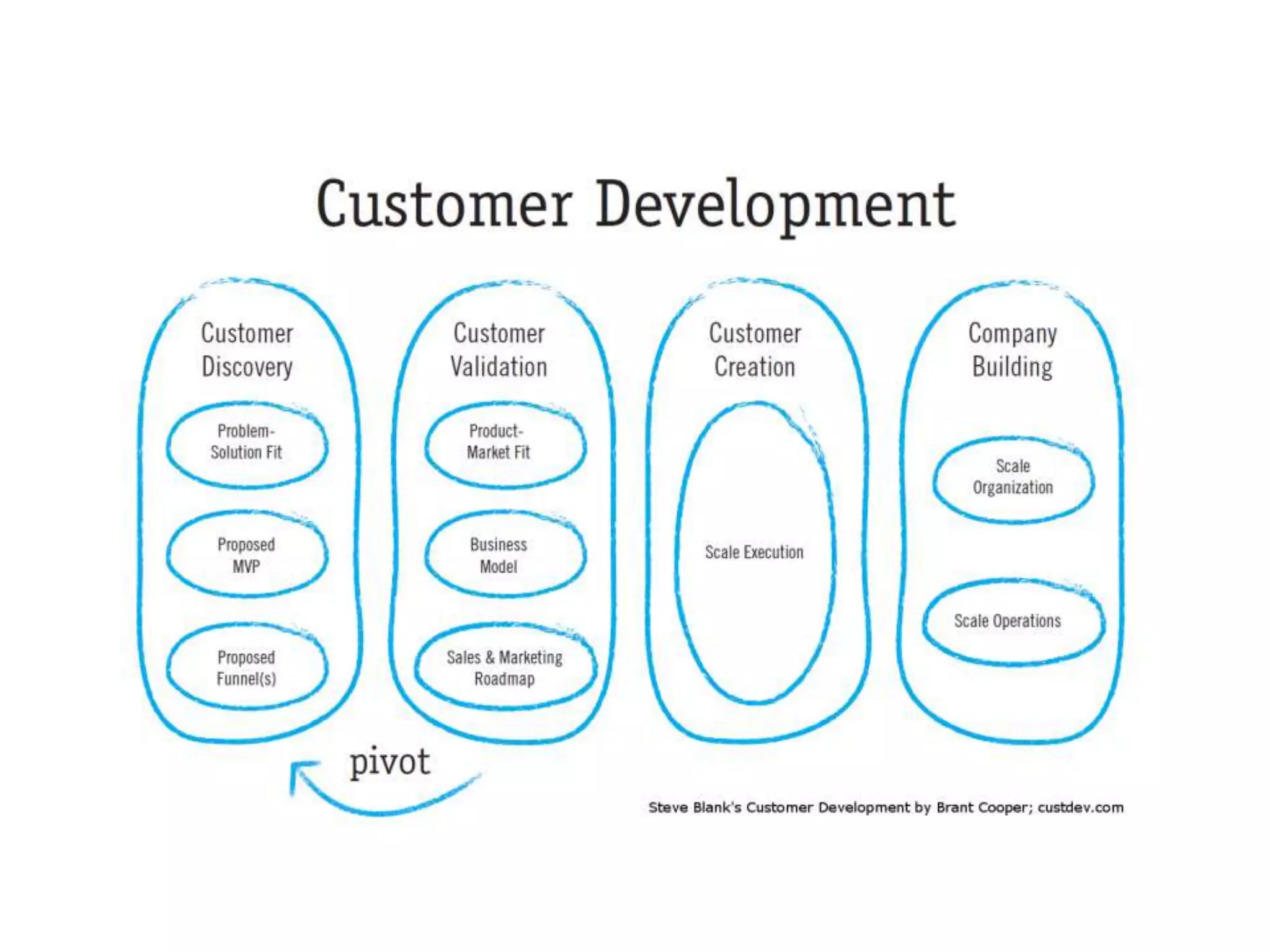
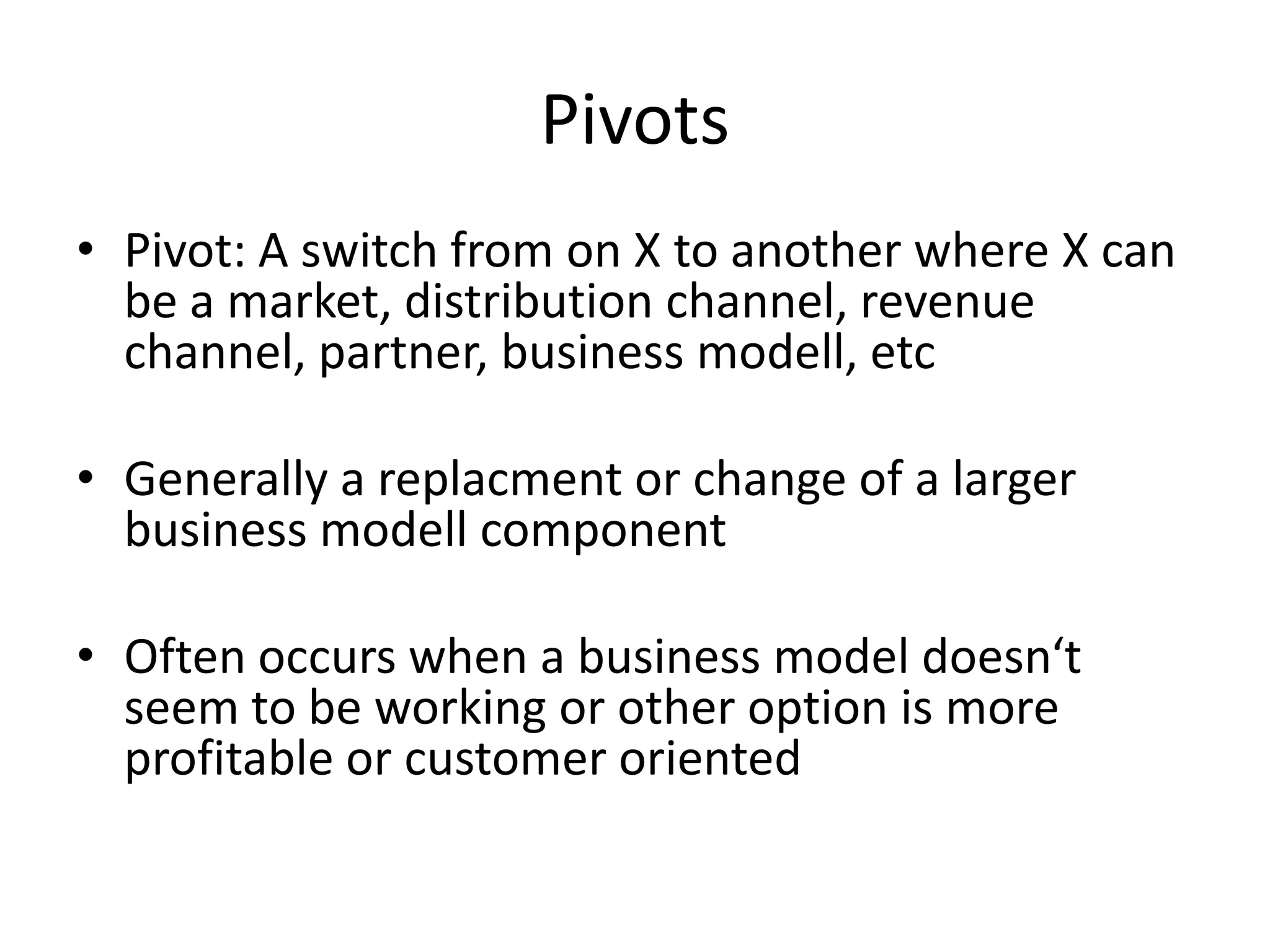
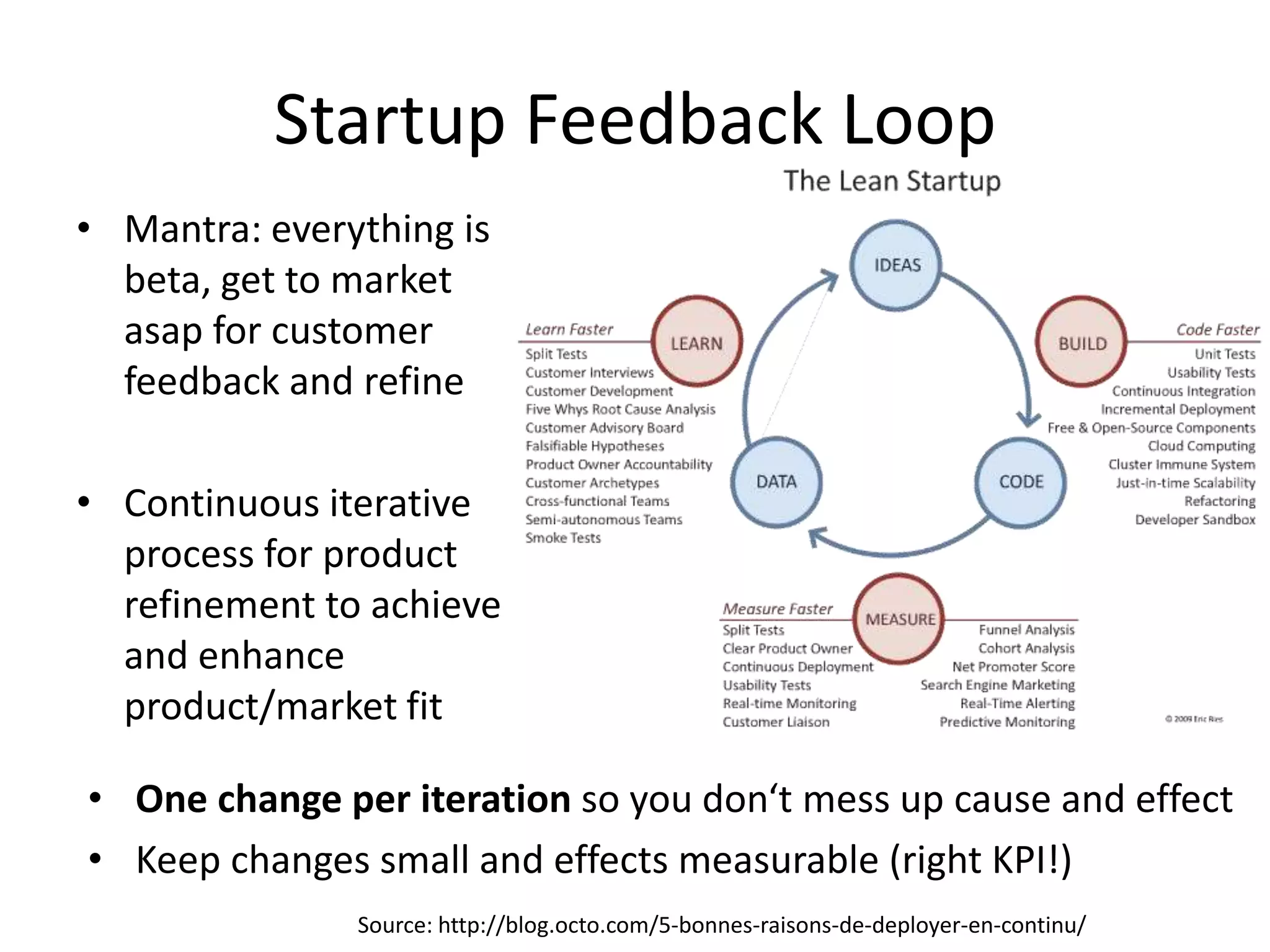
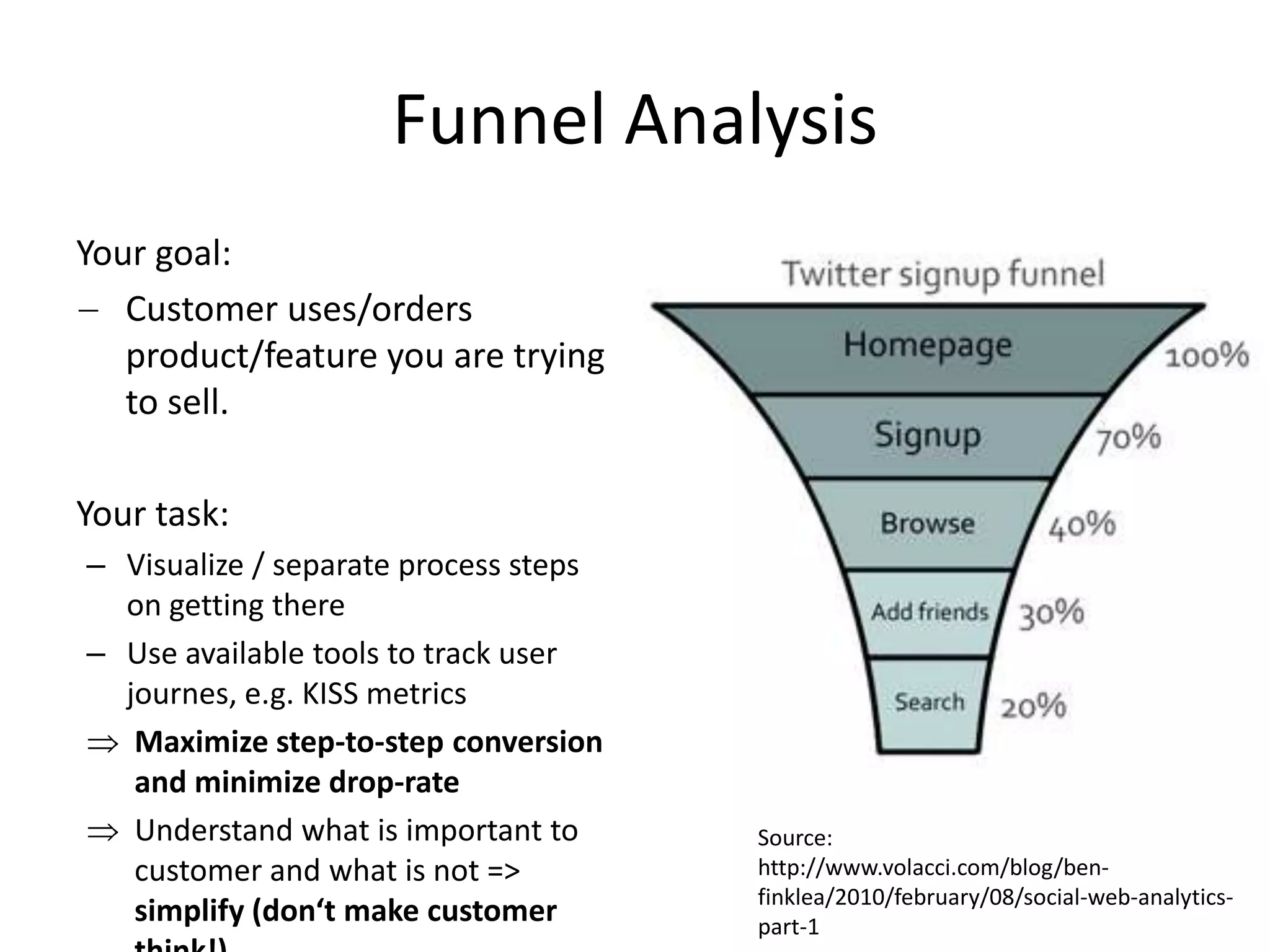
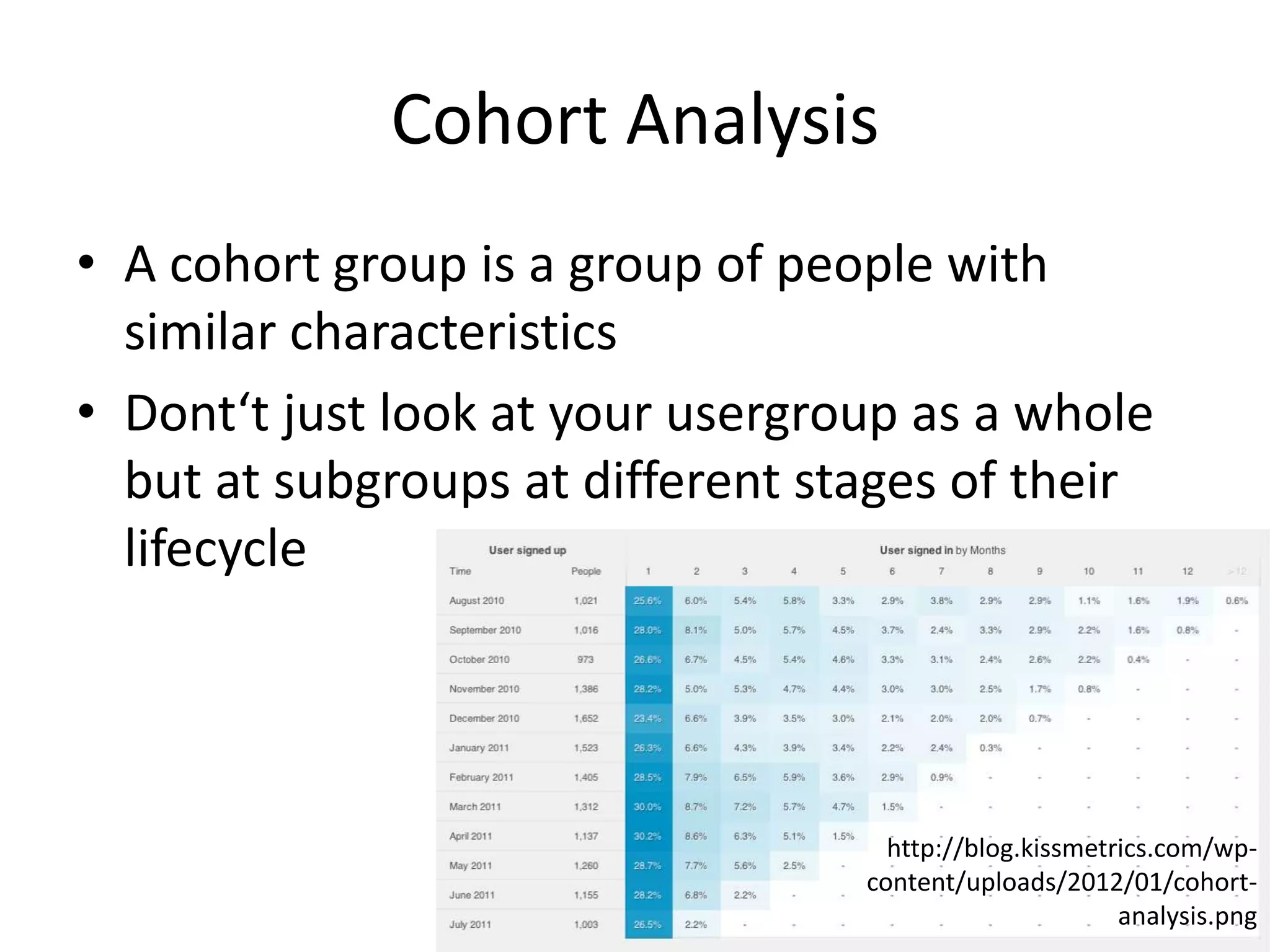
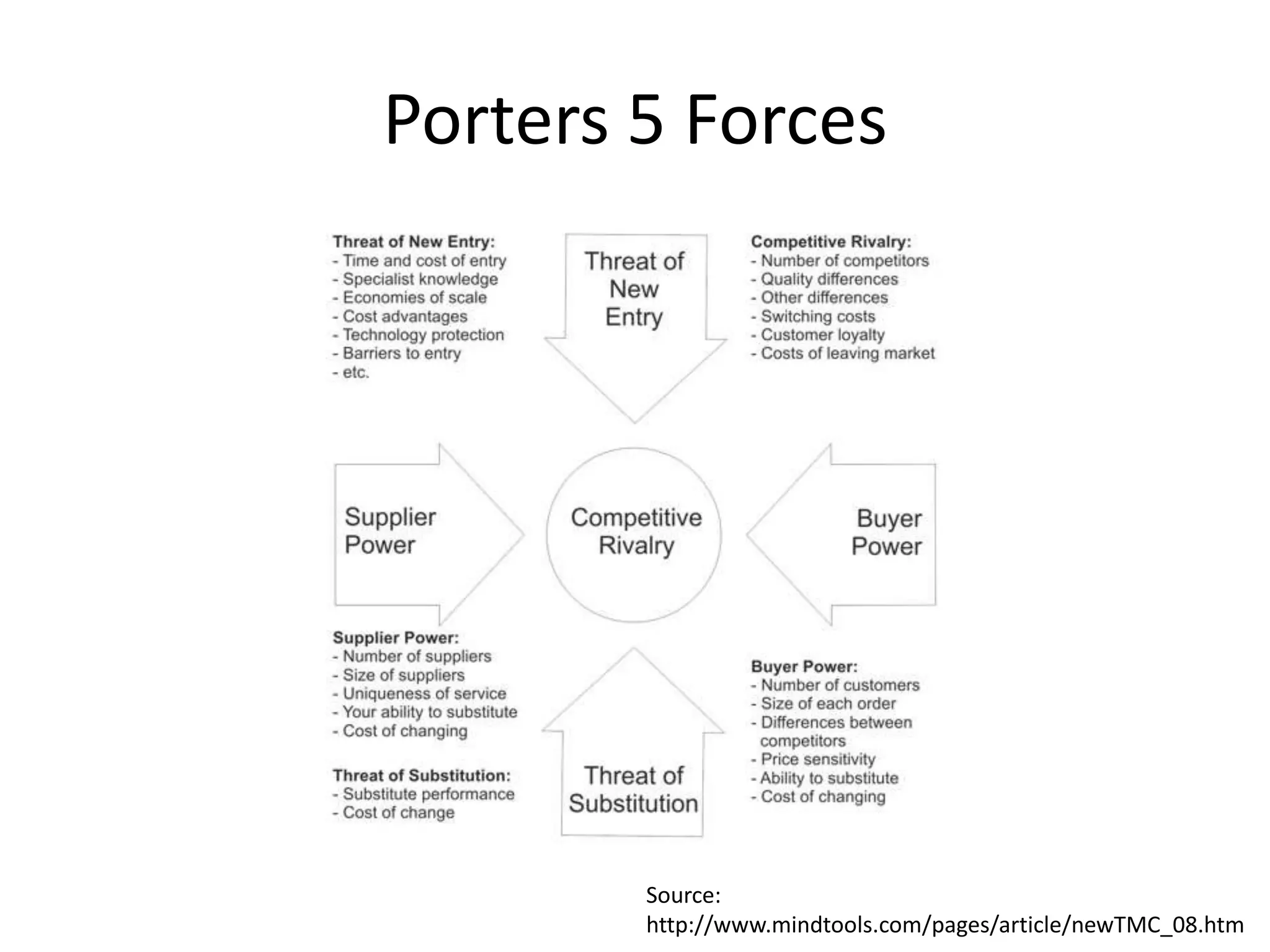
This document provides an overview of frameworks and strategies for startups, including Lean Startup, Business Model Canvas, Customer Development, and Service Design. It discusses validating problems and solutions with customers through iterative testing of minimum viable products and pivoting based on feedback. Key aspects of startups mentioned include achieving product-market fit, lowering costs and churn while growing new customers over time through compelling products people love. Revenue streams and costs are also briefly covered.