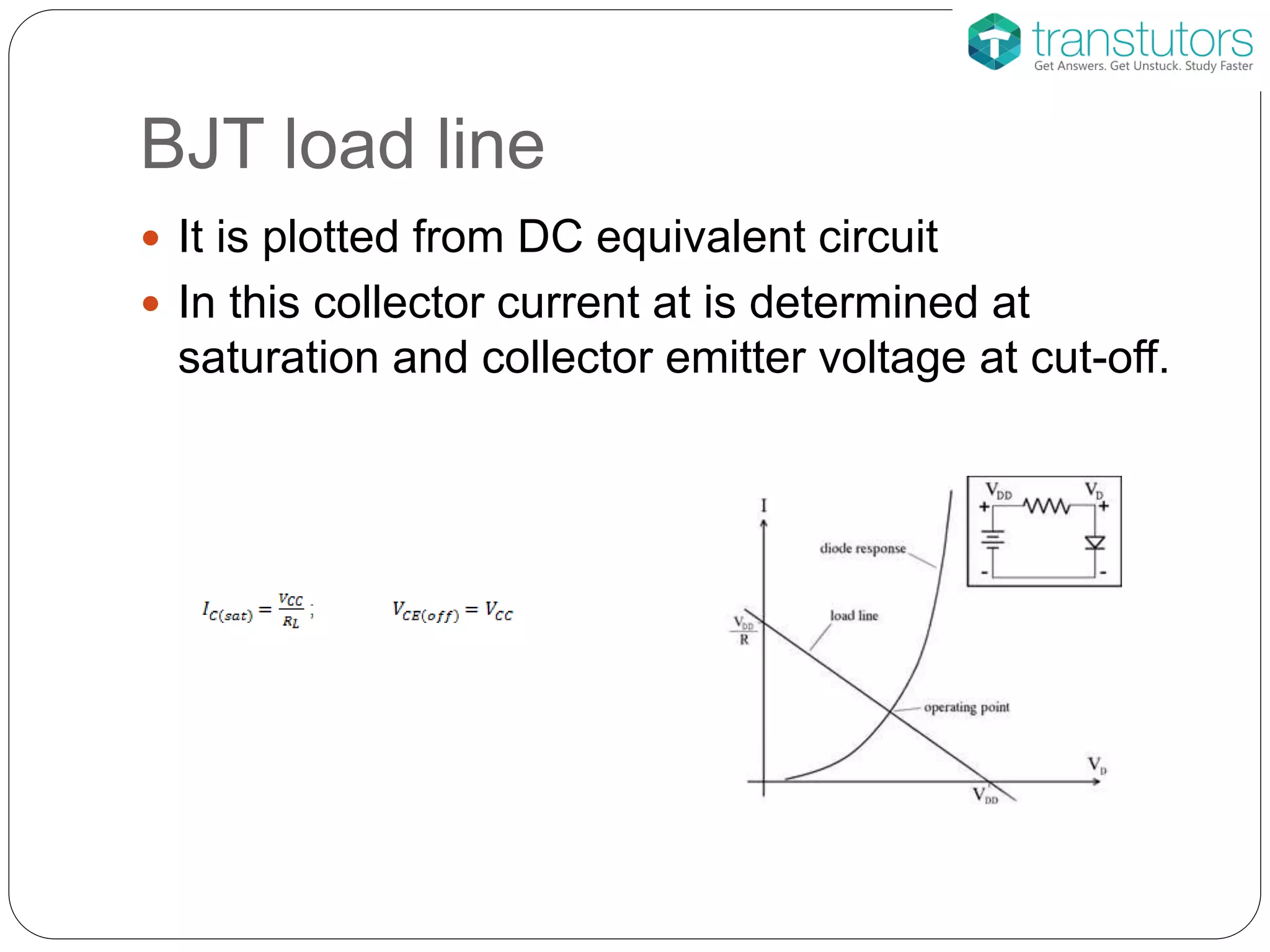
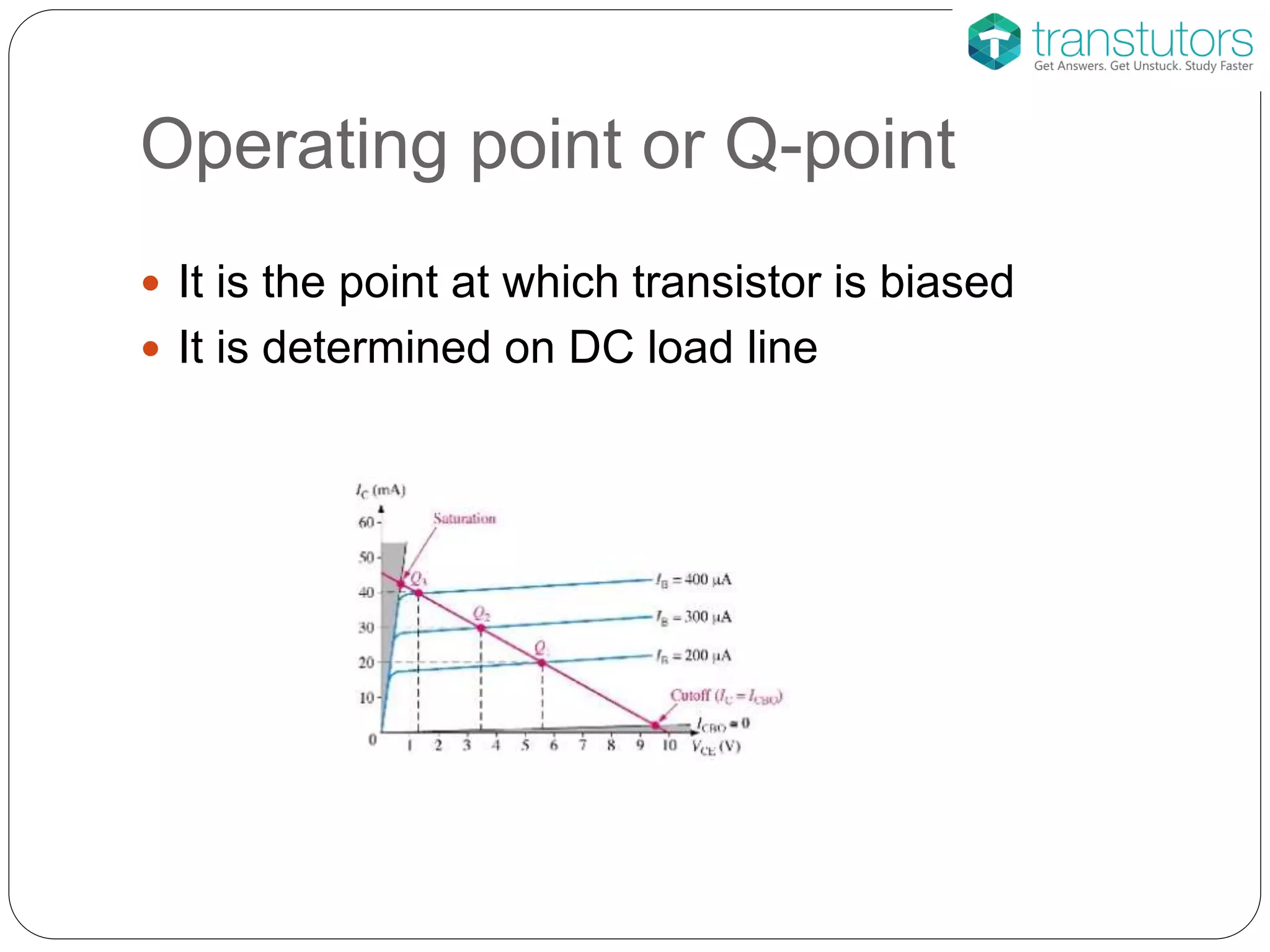
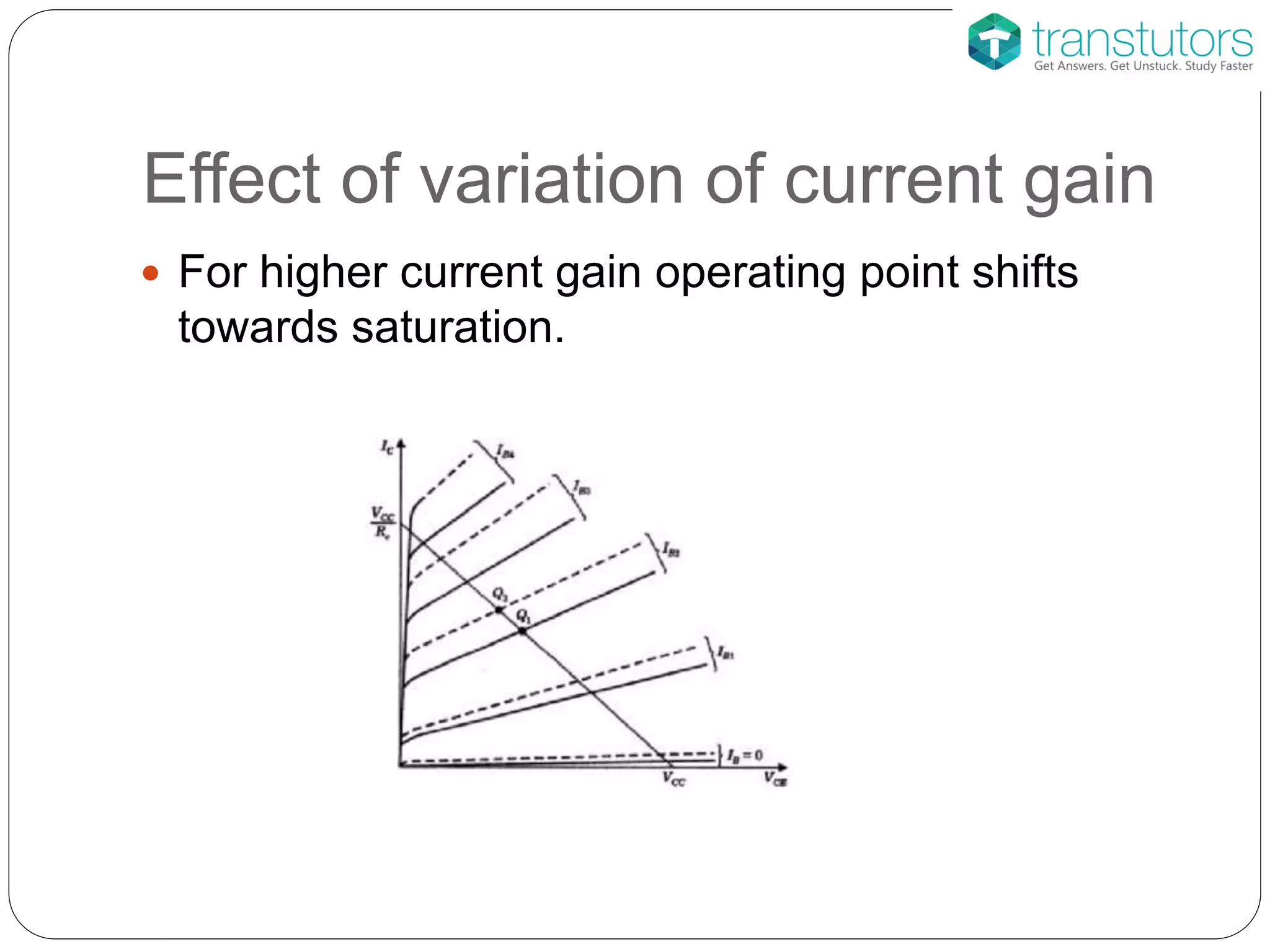
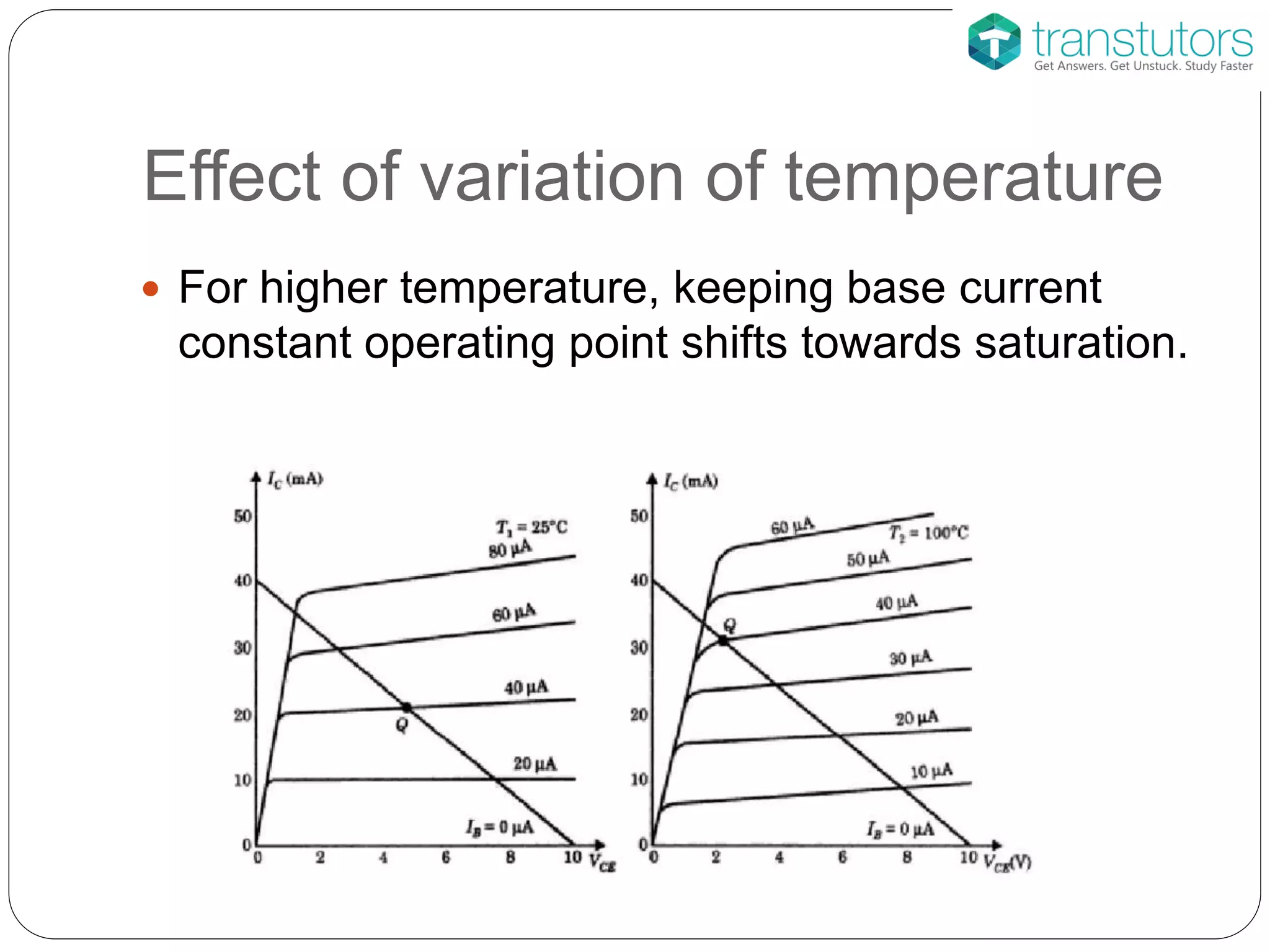
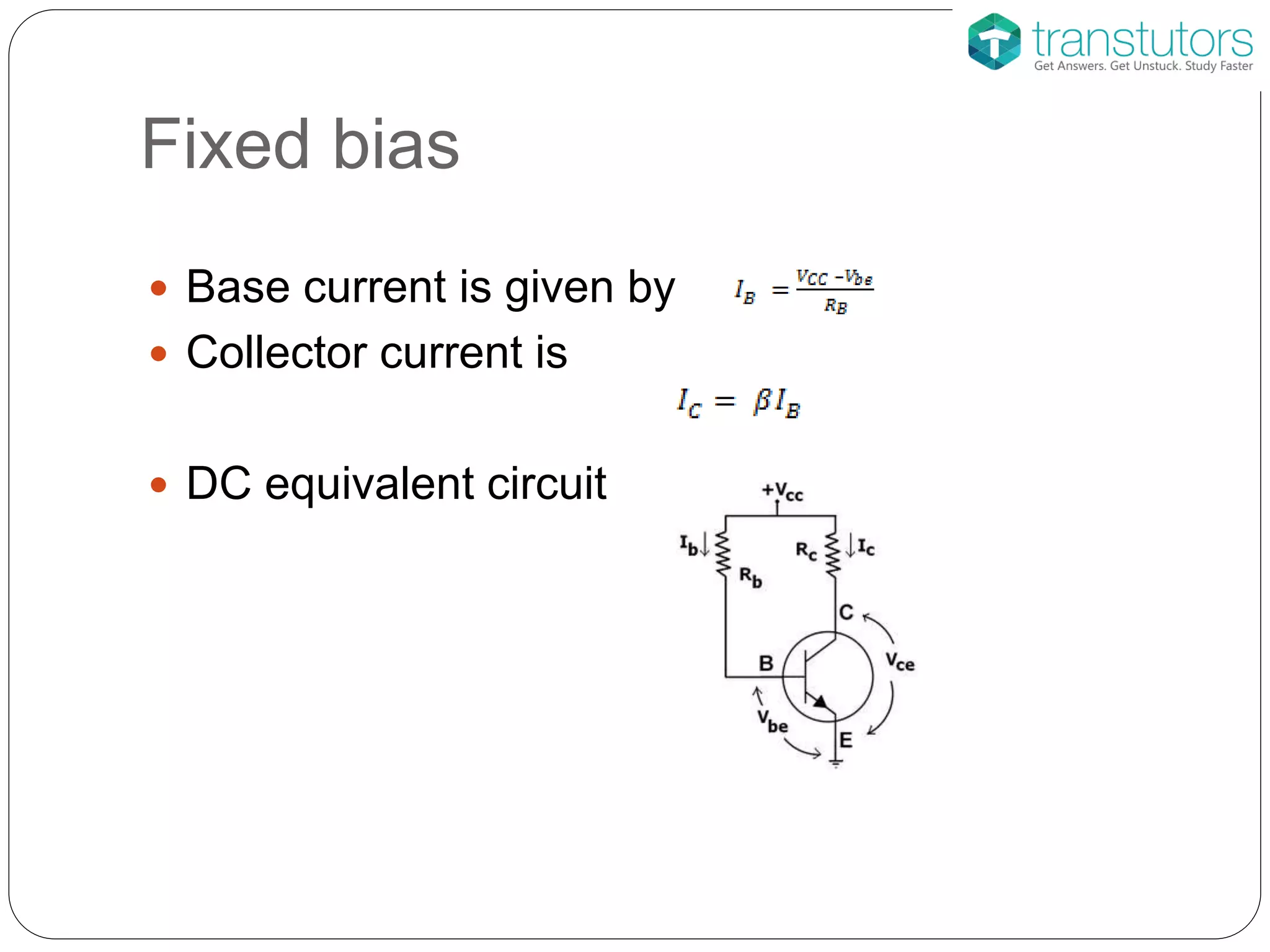
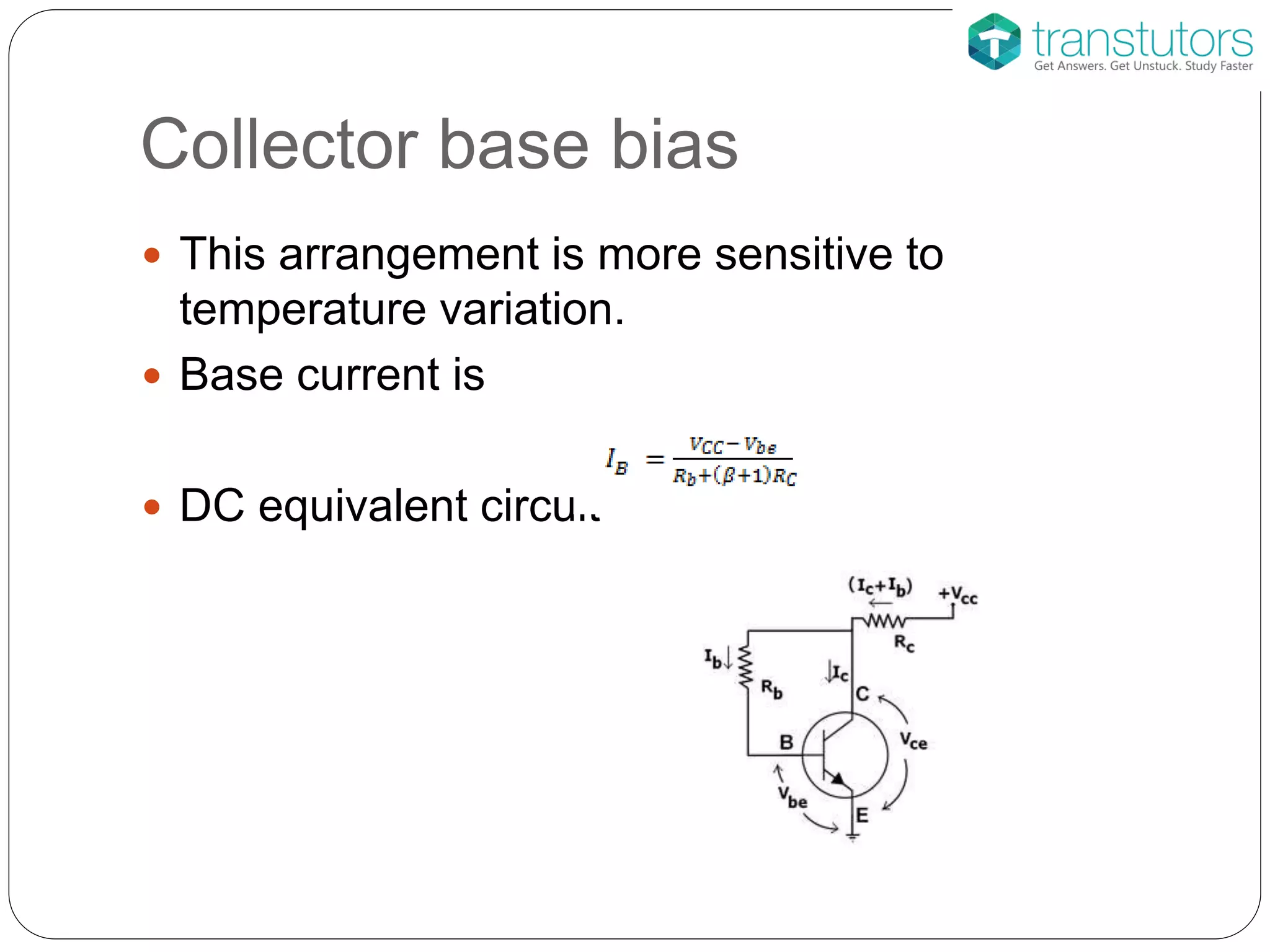
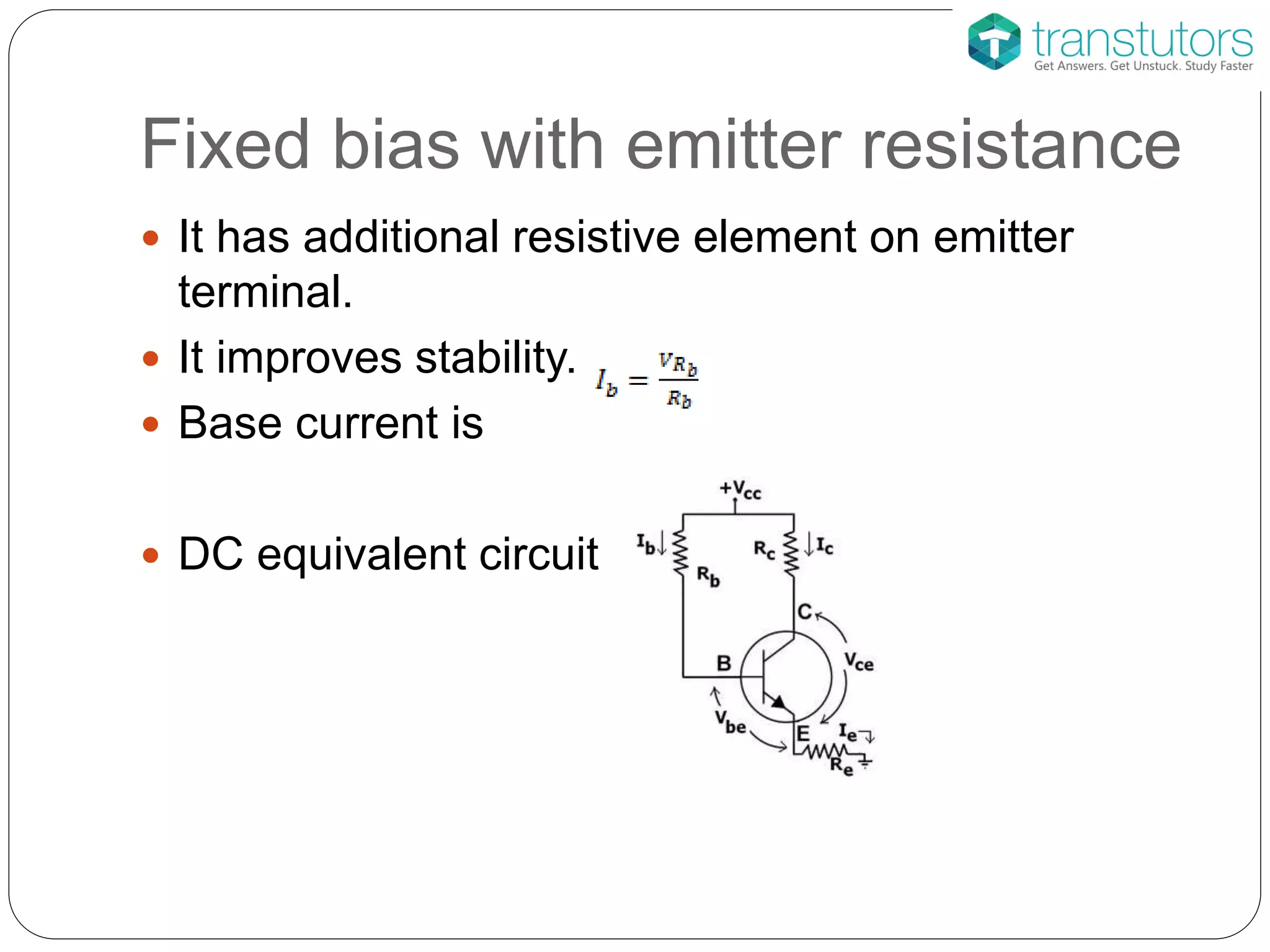
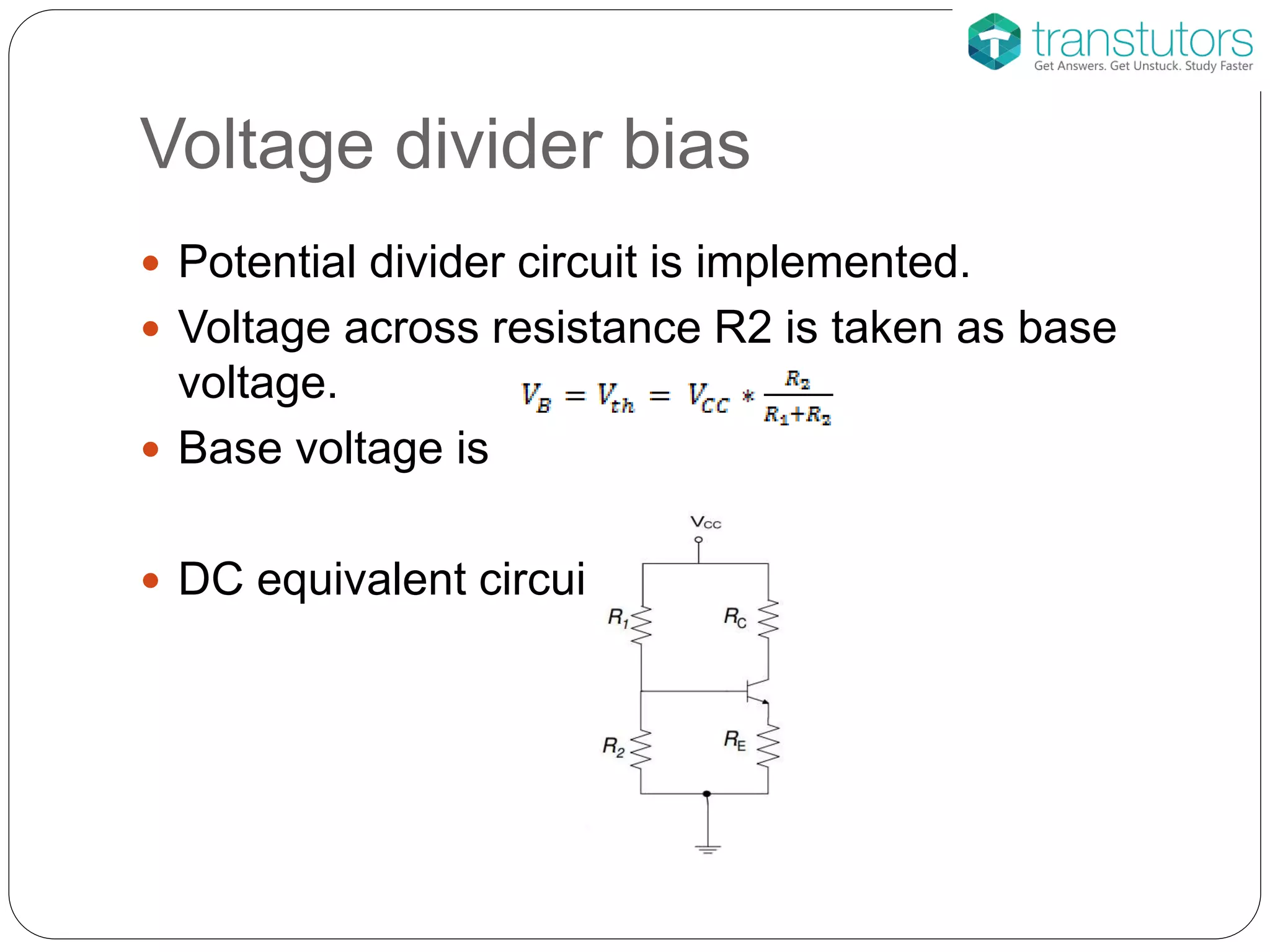
This document discusses the stabilization of operating point in BJTs. It defines the load line and operating point, and explains that the operating point depends on factors like current gain, temperature, and supply voltage variations. An increase in current gain or temperature will shift the operating point towards saturation. It also describes different bias circuit types - fixed bias, collector base bias, fixed bias with emitter resistance, and voltage divider bias - and provides their basic equations.