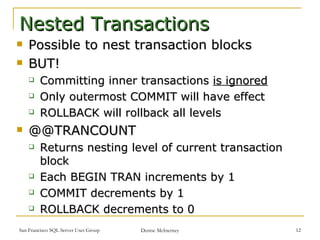
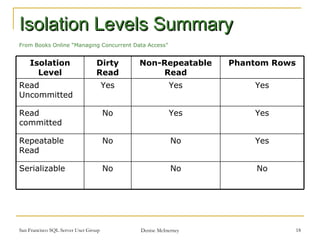
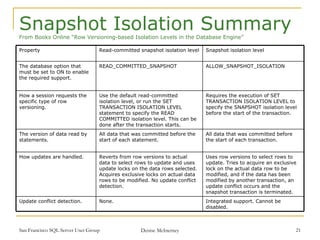
Transactions are used to ensure data integrity and manage concurrent access in SQL Server. There are two types of transactions: implicit, which automatically commit after each statement, and explicit, which require BEGIN, COMMIT, or ROLLBACK statements. Transactions have ACID properties including atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. Isolation levels like read committed and serializable control how transactions see concurrent data modifications. Snapshot isolation is an alternative to locking that uses row versioning to provide consistency.