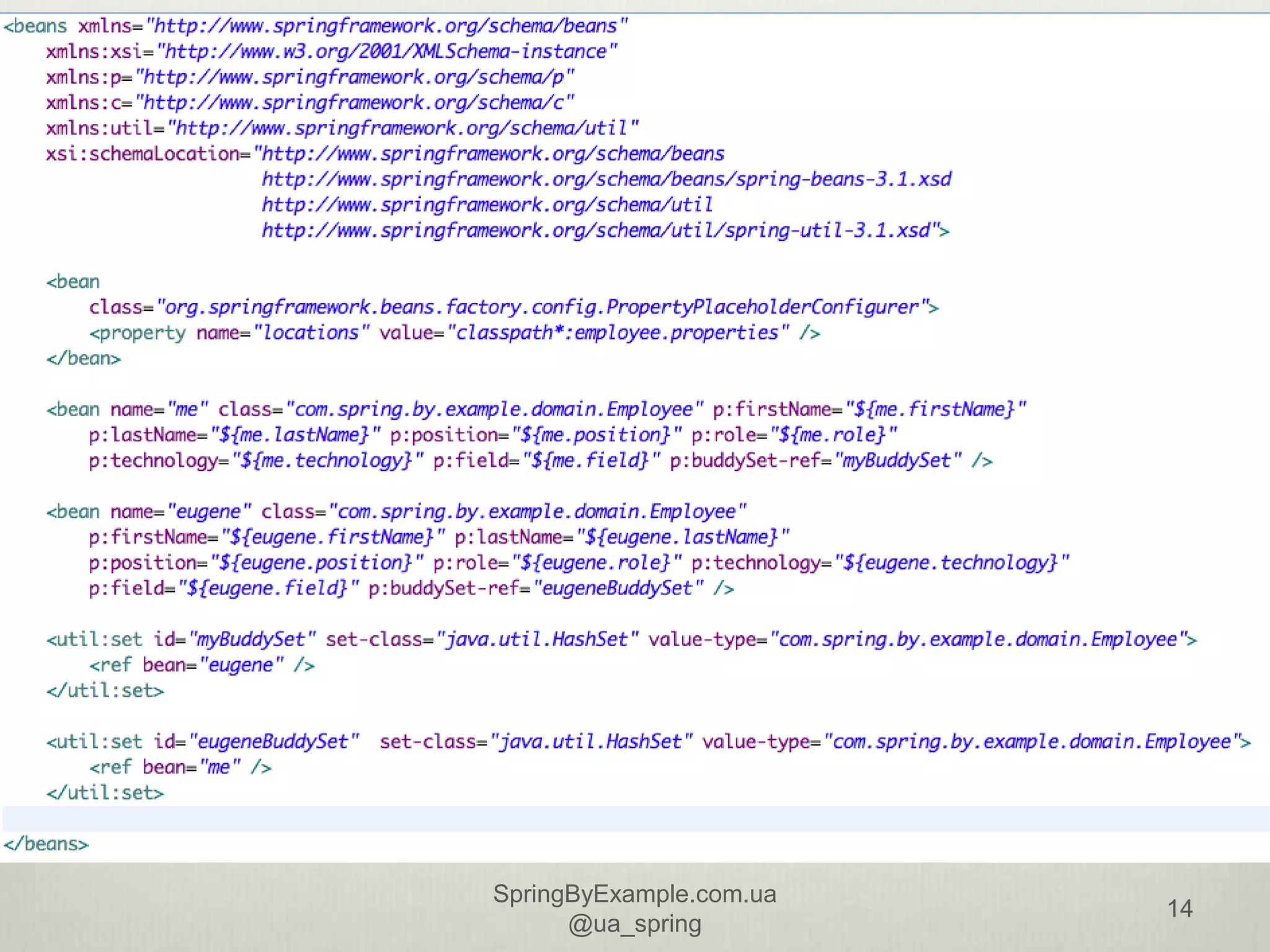
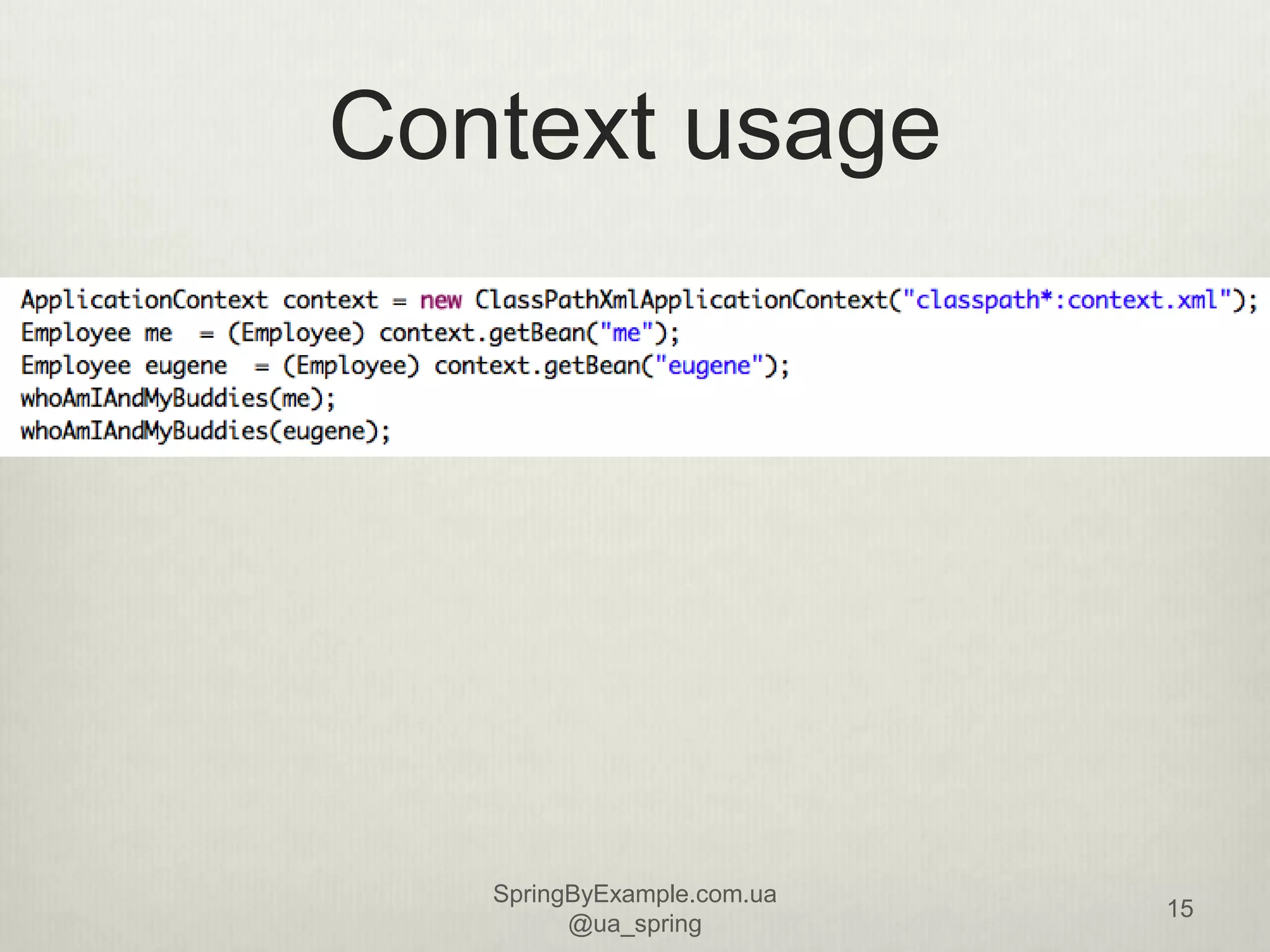
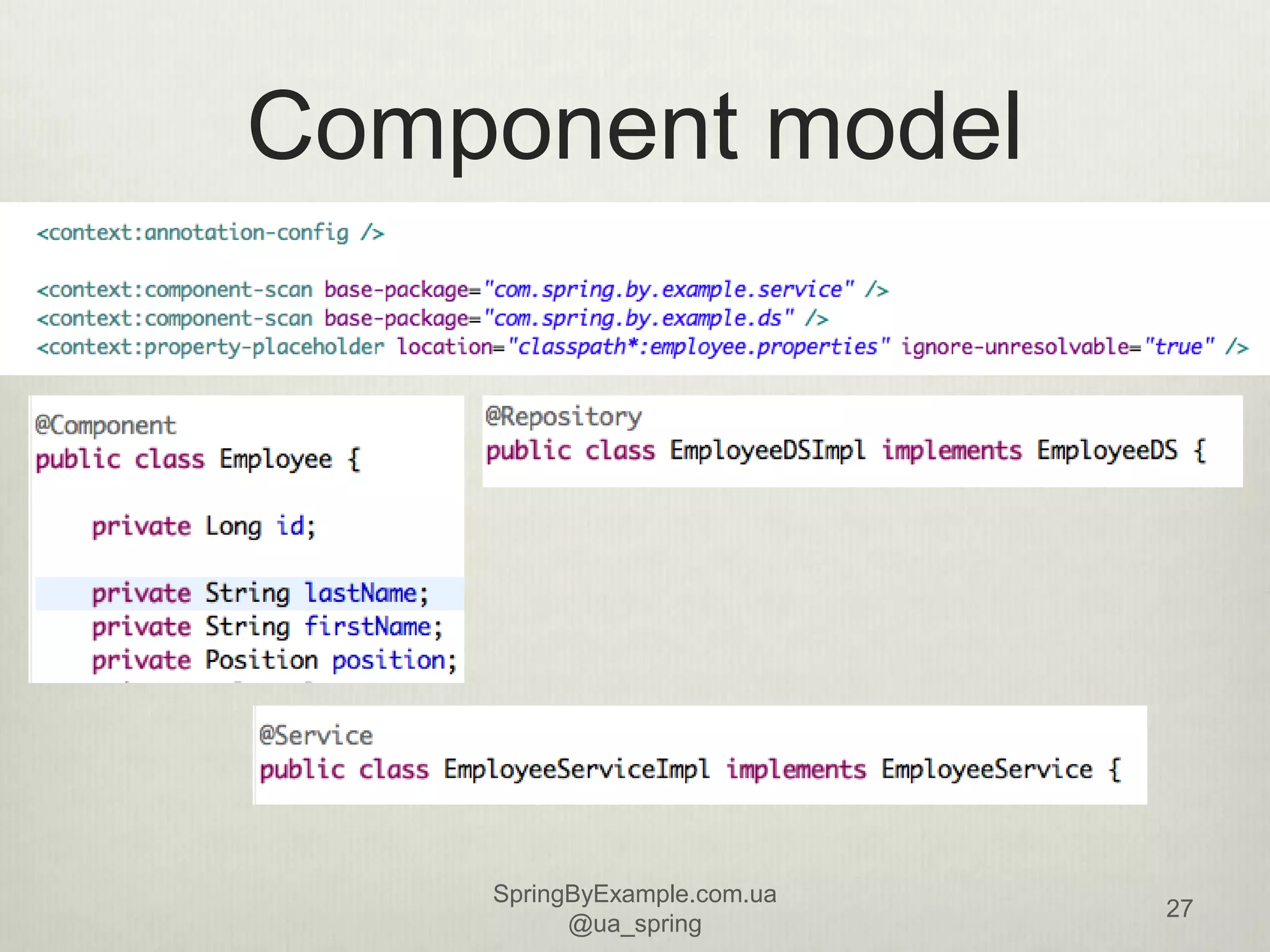
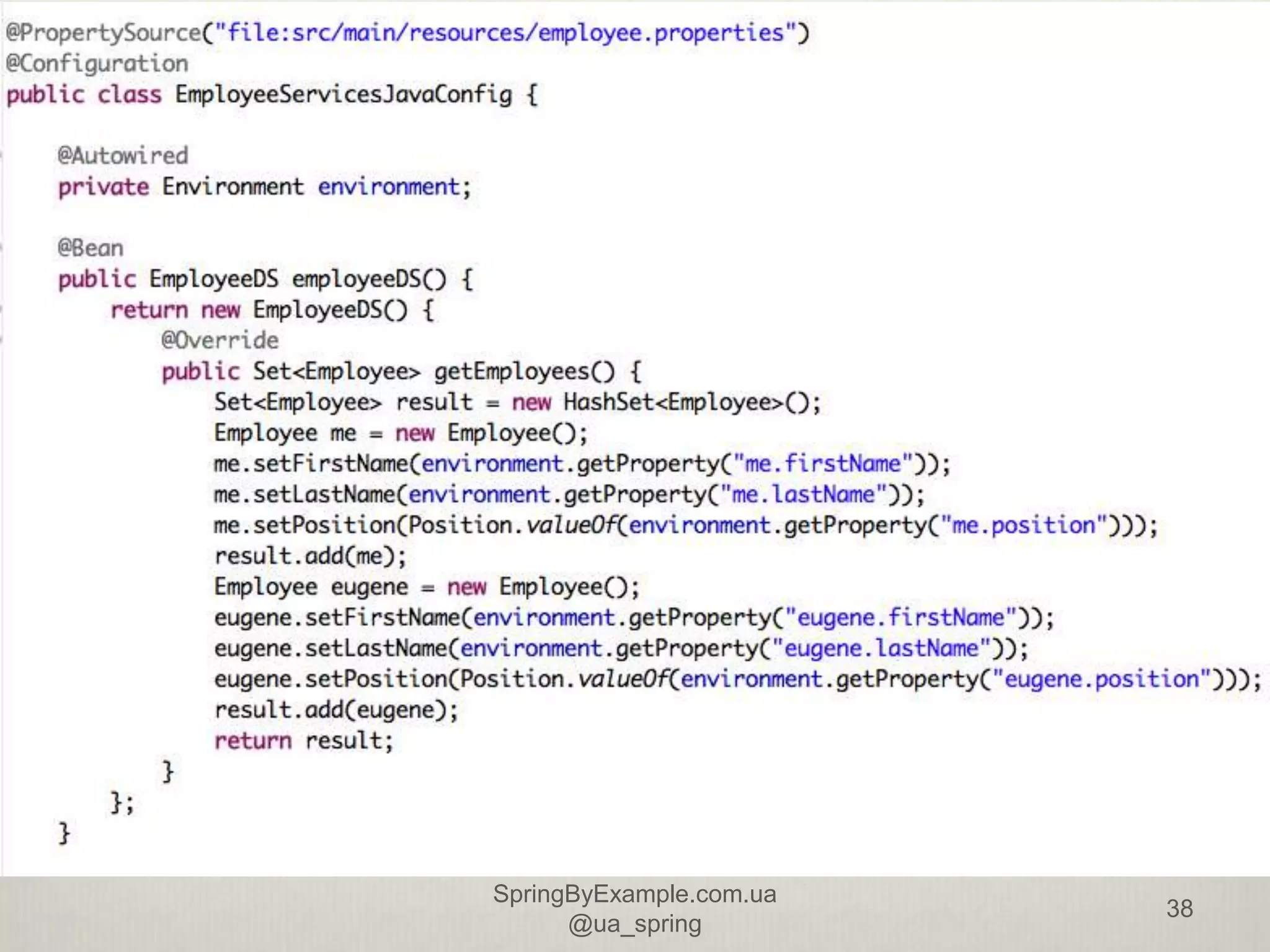
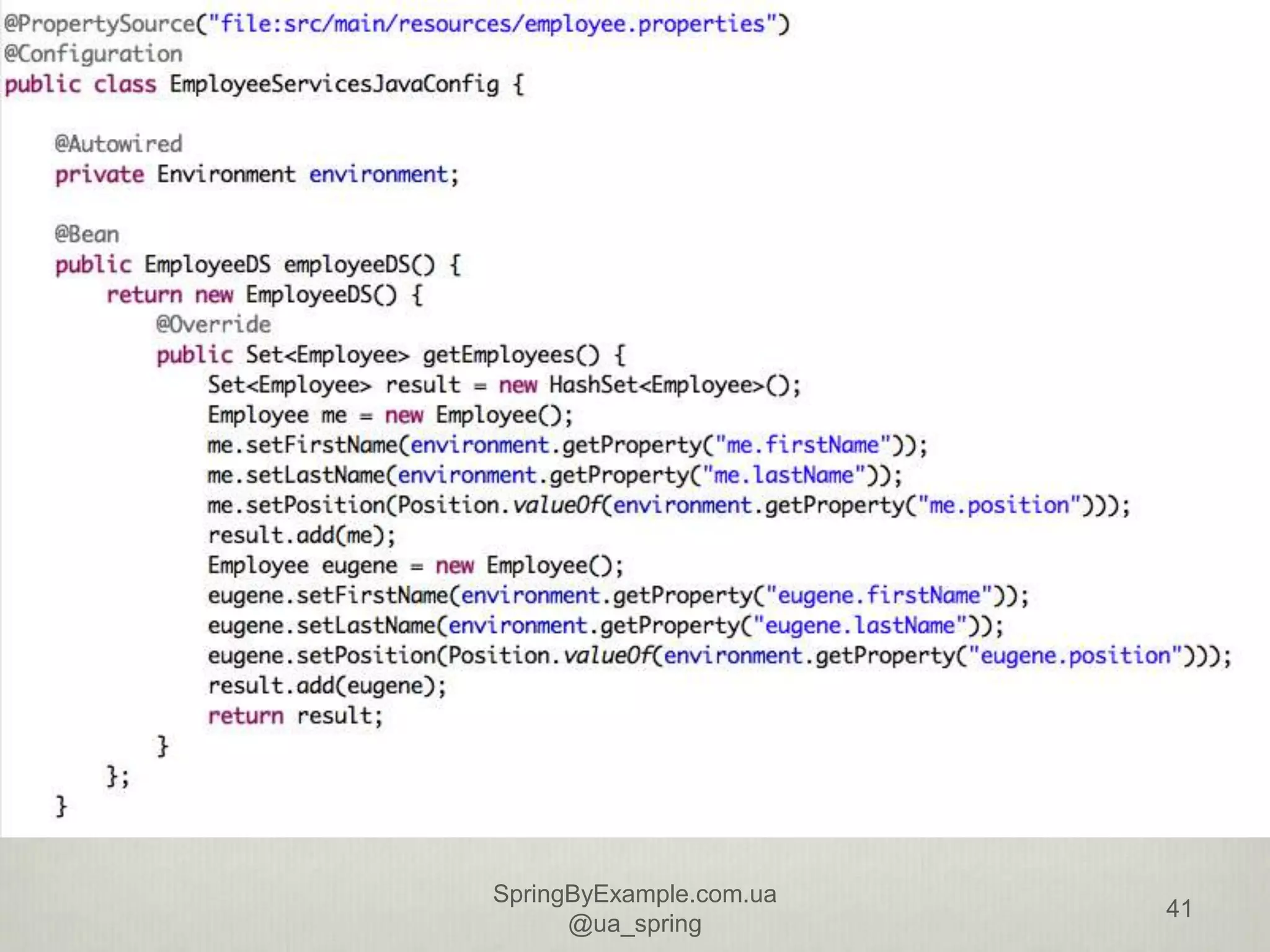
This document provides an overview of a presentation on using the Spring Framework. It discusses the speakers' backgrounds and outlines topics including inversion of control with Spring, dependency injection types, building application contexts, aspect-oriented programming with Spring AOP, and data access with Spring. The presentation aims to teach attendees about core Spring concepts and how to use the framework to build applications.