The word spirometry means
spiro means respiration/breathing
metry means measure
It is derived from latin.
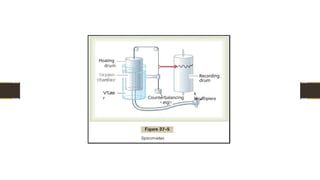
It is a physiological test that measures how an individual inhales & exhales volumes of air as a function of time.
Its assesses the mechanical function of the lung ,chest wall,& respiratory muscles by measuring total vol.of.air exhaled from a full lung [TLC] to maximal expiration [RV].
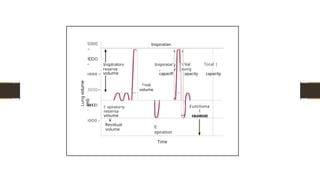
TIDAL VOLUME [TV] : Vol. of. Air inhaled or exhaled with each breath during quite respiration.
400-500 ml [10ml/kg ].
INSPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME [IRV] : Max. vol. of. Air inhaled from the end inspiratory position.
2400-2600 ml.
EXPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME [ERV] : Max. vol. of. Air that can be exhaled after normal expiration.
1200-1500 ml
RESIDUAL VOLUME [RV] : Vol. of. Air remaining in lungs after maximum exhalation.
Indirectly measured [ FRC – ERV ] not by spirometry. 1200-1500 ml.


![DEFINITION
• The word spirometry means
spiro
means respiration/breathing
metry means measure
• It is derived from latin.
• It is a physiological test that measures how an individual inhales
& exhales volumes of air as a function of time.
• Its assesses the mechanical function of the lung ,chest wall,& respiratory
muscles by measuring total vol.of.air exhaled from a full lung [TLC] to
maximal expiration [RV].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spiroetry-260112184851-df74e083/85/Spiroetry-Spirometer-Lung-Function-Test-3-320.jpg)
![LUNG VOLUMES & CAPACITIES
> 4 VOLUMES
• Inspiratory Reserve Volume [IRV]
• Tidal volume [TV]
• Expiratory Reserve Volume [ERV]
• Residual Volume [RV]
o 2 OR More volumes comprise a Capacity
> 4 CAPACITIES
• Vital Capacity [VC]
• Inspiratory Capacity [IC]
• Functional Residual Capacity [FRC]
• Total Lung Capacity [TLC].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spiroetry-260112184851-df74e083/85/Spiroetry-Spirometer-Lung-Function-Test-4-320.jpg)
![LUNG VOLUMES
TIDAL VOLUME [TV] : Vol. of. Air inhaled or exhaled with each breath during
quite respiration.
400-500 ml [10ml/kg ].
> INSPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME [IRV] : Max. vol. of. Air inhaled from the end
inspiratory position.
2400-2600 ml.
> EXPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME [ERV] : Max. vol. of. Air that can be exhaled after
normal expiration.
1200-1500 ml
> RESIDUAL VOLUME [RV] : Vol. of. Air remaining in lungs after maximum
exhalation.
• Indirectly measured [ FRC – ERV ] not by spirometry.
1200-1500 ml.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spiroetry-260112184851-df74e083/85/Spiroetry-Spirometer-Lung-Function-Test-5-320.jpg)
![LUNG CAPACITY
TOTAL LUNG CAPACITY [TLC] : Sum of all volume compartments OR
vol.of.air in the lungs after maximum inspiration.
TLC = TV+IRV+ERV+RV. [5500- 6000ml].
> VITAL CAPACITY [VC] : Max. vol. of air exhaled from maximal inspiratory
level.
VC= TV+IRV+ERV. [4200-4500ml]. 75-80ml/kg.
> INSPIRATORY CAPACITY [IC] : Max. vol. of air that can be inhaled from the
end expiratory position.
IC= TV+IRV. [3000ml].
> FUNCTIONAL RESIDUAL CAPACITY [FRC] : Vol. of.air in the lungs at the
end expiration.
FRC= ERV+RV. [2400-2600ml].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spiroetry-260112184851-df74e083/85/Spiroetry-Spirometer-Lung-Function-Test-6-320.jpg)





![> PHASE OF EXHALATION
• Subject should be prompted to BLAST not just to BLOW,the air from their lungs .
• Exhalation should be forced & sustained
> Subject should try to exhale for
ADULT >= 6 sec [ age > 10 yrs ]
CHILDREN >= 3sec [ age < 10 yrs ]
D TWO IMPORTANT PARAMETERS :
FORCED VITAL CAPACITY ( FVC ) – Vol.of.air that can be forcefully exhaled after a maximal
inhalation.
• Majority of FVC can be exhaled in < 3sec of exhalation in normal people, whereas it is
prolonged in people vth Obstructive lung diseases.
FORCED EXPIRATORY VOLUME in 1 Sec ( FEV 1) vol. of. Air exhaled in first second
of FVC.
> NORMAL subject can exhale 75-80%of their FVC in 1st second
FEV1/FVC ratio is an important determinant in assessing lung disease.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spiroetry-260112184851-df74e083/85/Spiroetry-Spirometer-Lung-Function-Test-14-320.jpg)



