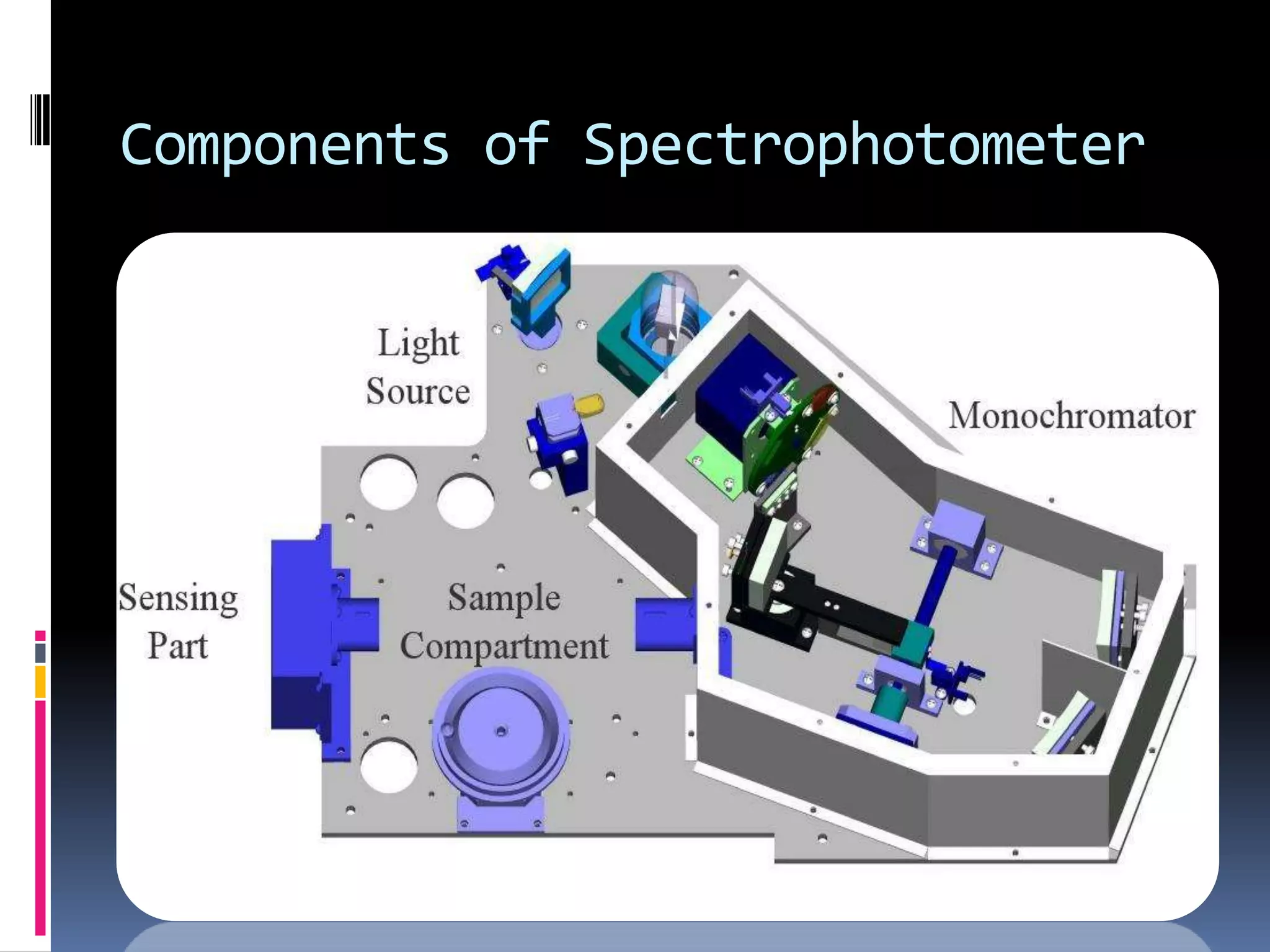
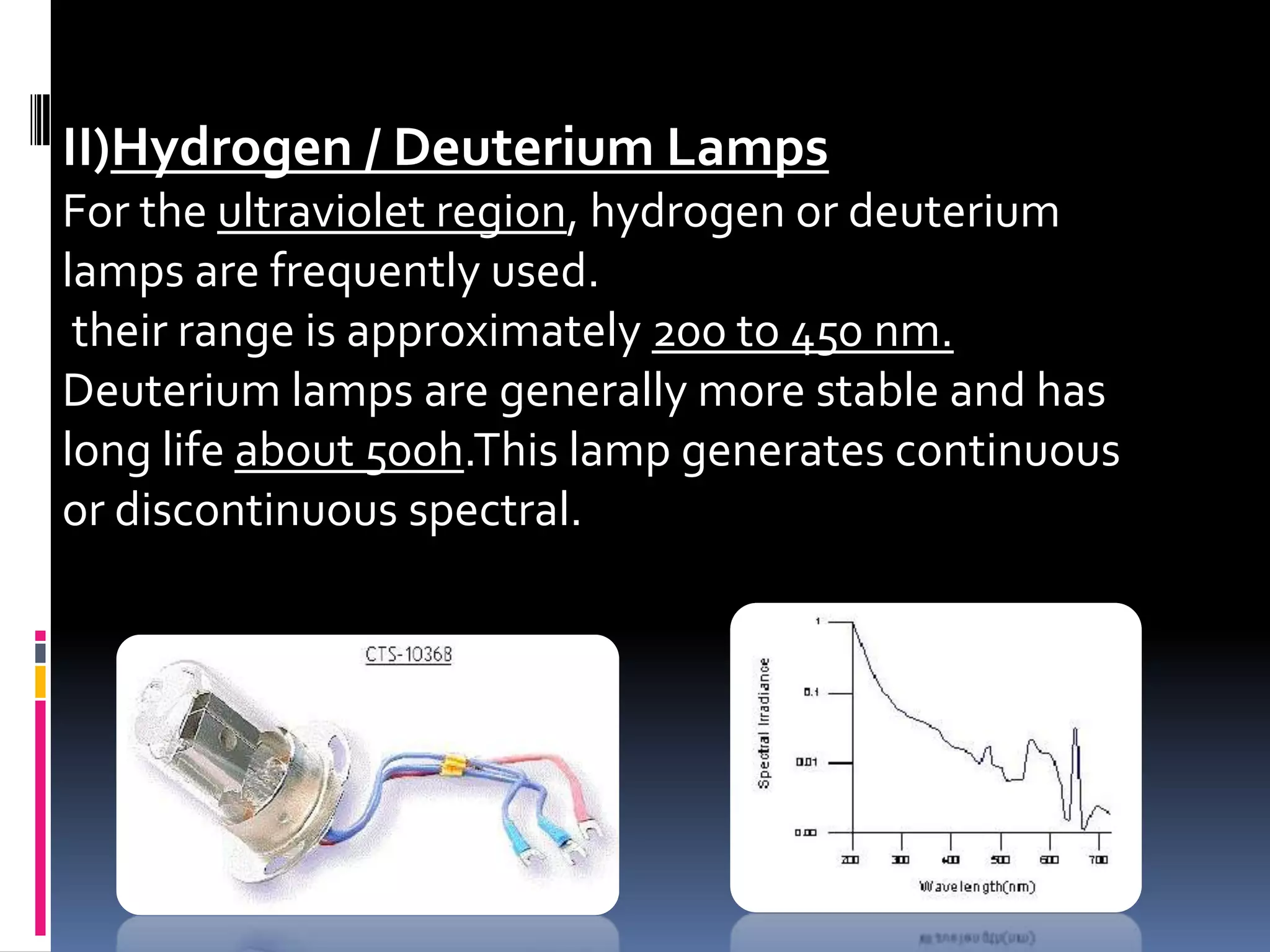
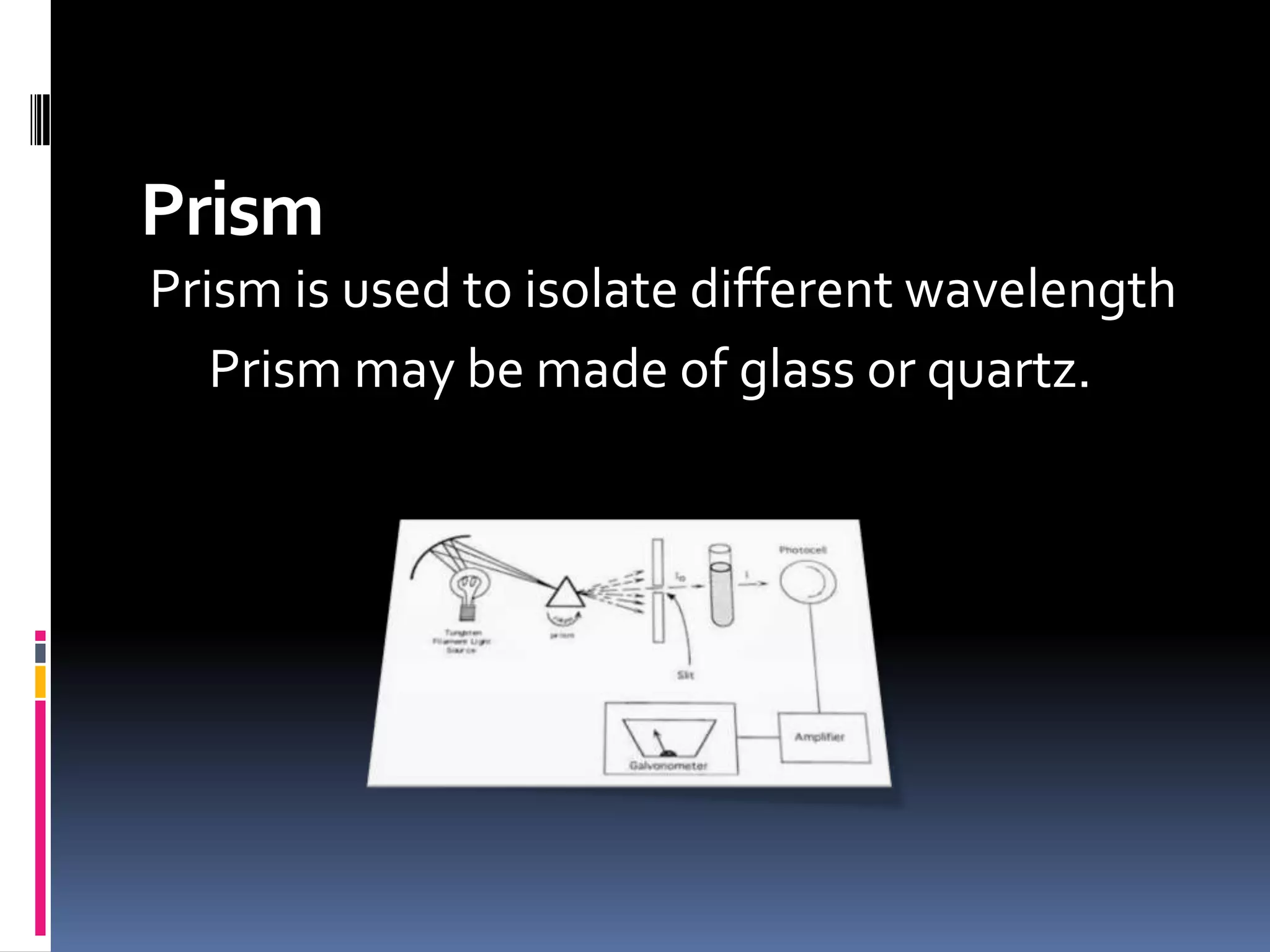
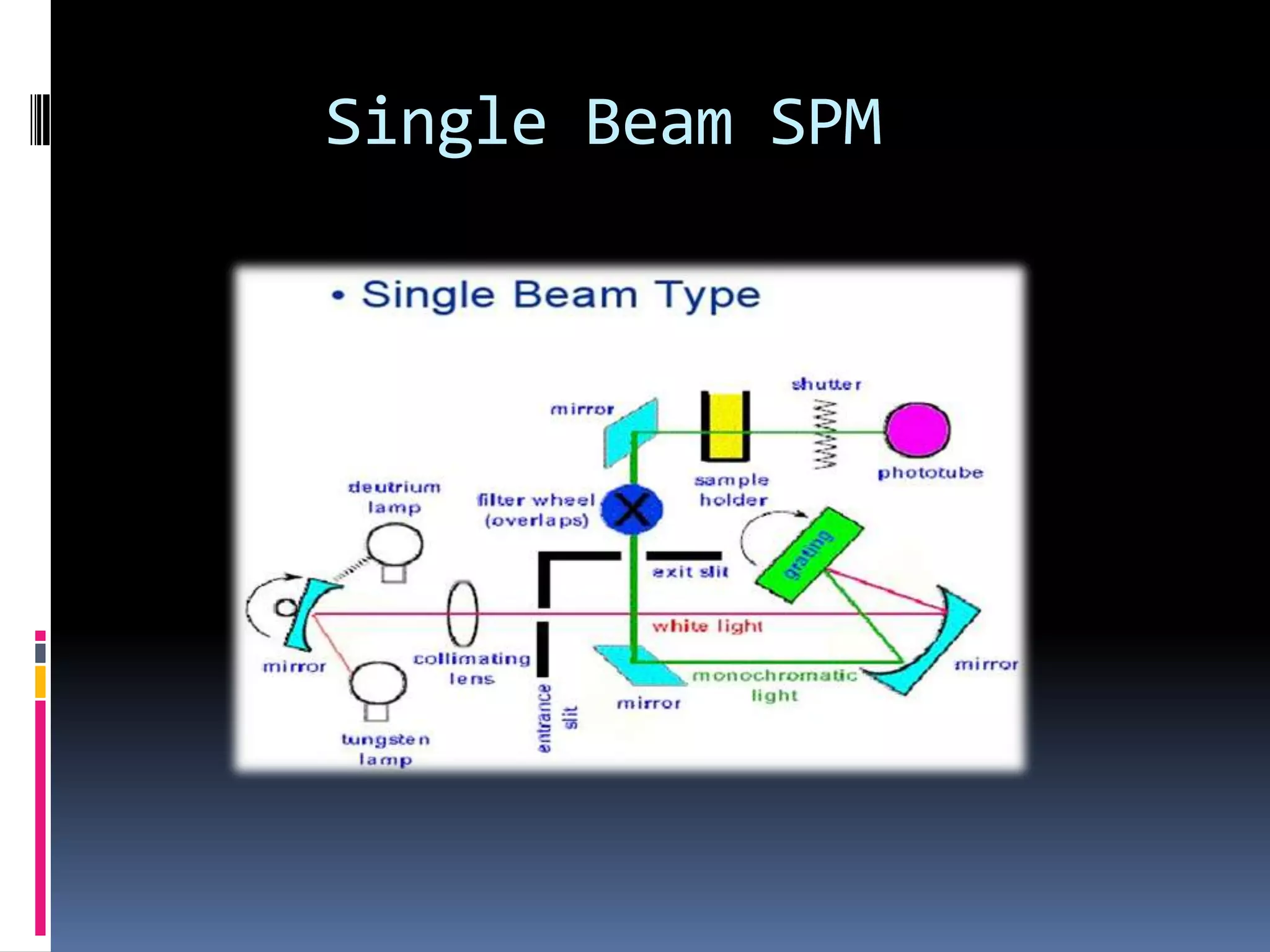
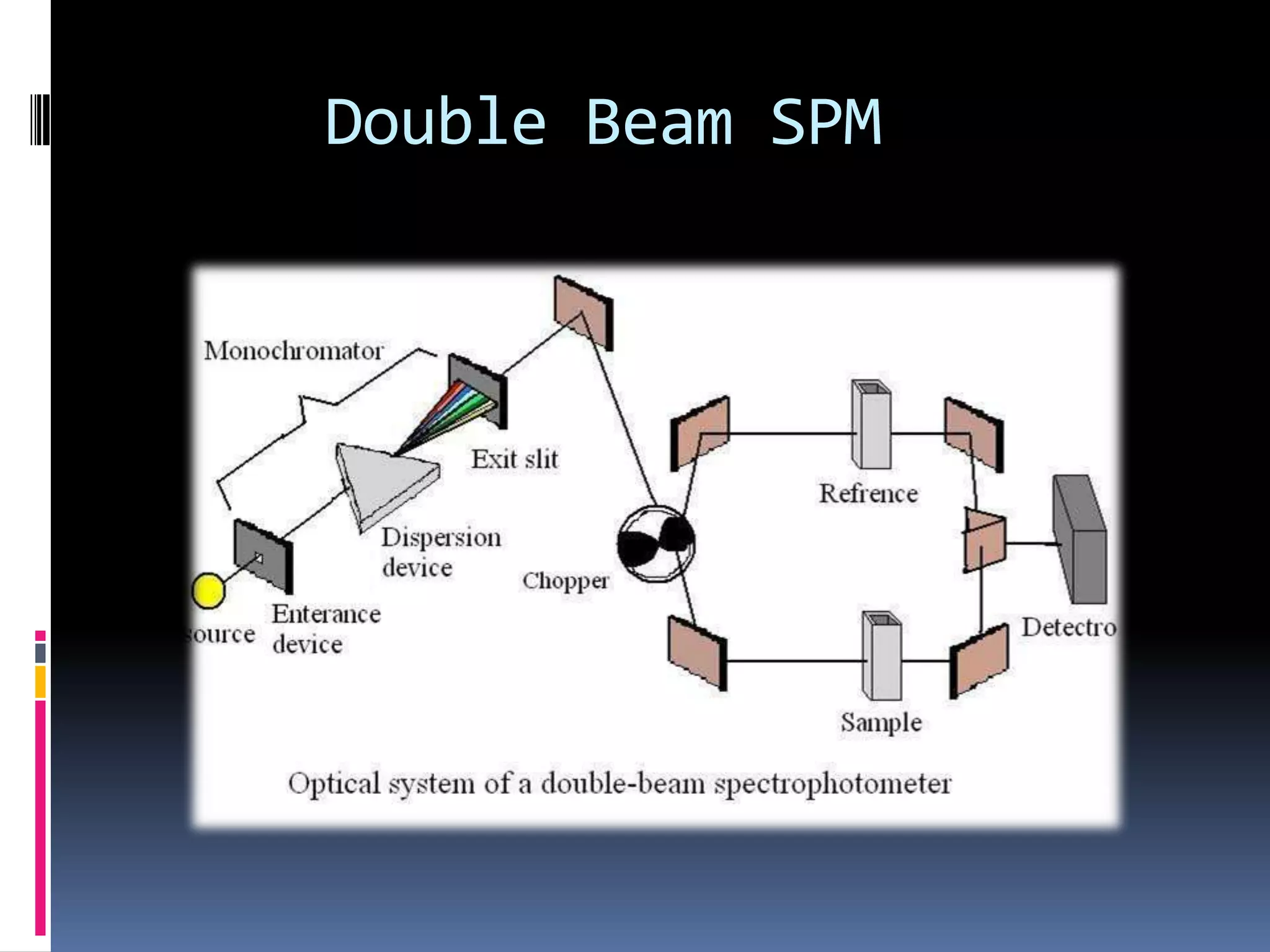
A spectrophotometer measures the amount of light absorbed by a sample. Early models took weeks for results and were only 25% accurate. In 1940, Arnold Beckman invented the first modern spectrophotometer, the Beckman DU, which provided results within minutes that were 99.99% accurate. A spectrophotometer uses a light source, dispersion devices like prisms or filters, sample cells, detectors, and a display. It is used to identify compounds and determine absorbance and transmission of light in chemistry.