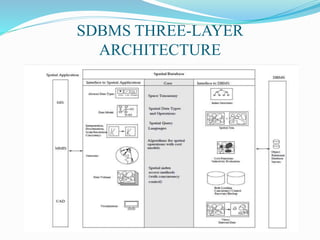
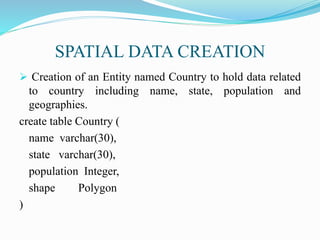
This document provides an overview of spatial data and spatial databases. It discusses key topics like the types of spatial data, properties of spatial data, spatial data types, spatial databases and their characteristics. It also describes spatial database management systems (SDBMS) and their three-layer architecture. Additionally, it covers spatial indices, creation of spatial data, geographic information systems (GIS), advantages and disadvantages of spatial databases, and applications of spatial databases such as urban planning and military operations.