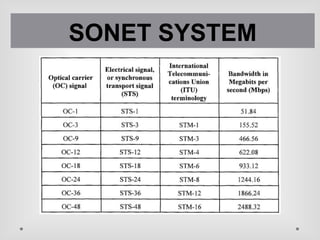
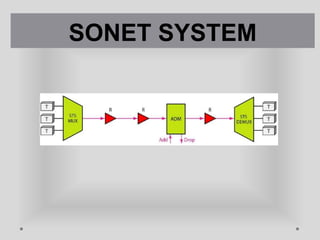
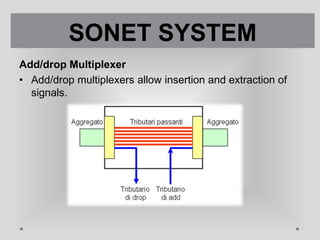
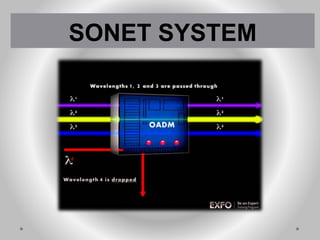
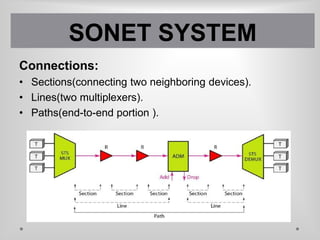
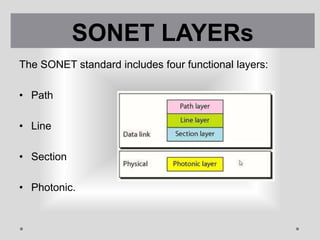
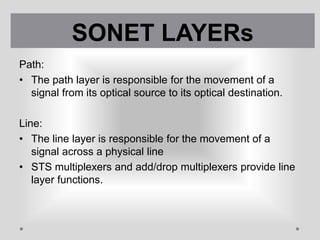
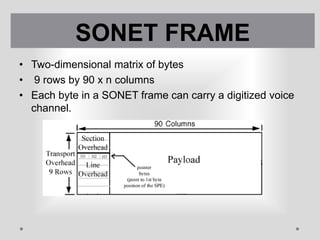
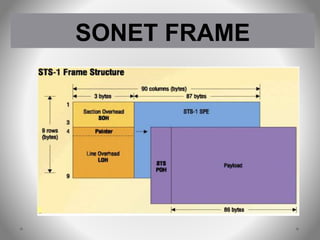
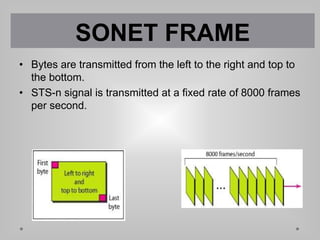
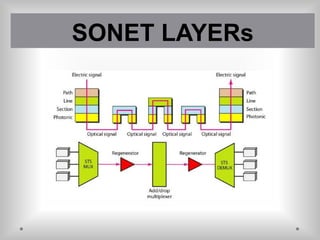
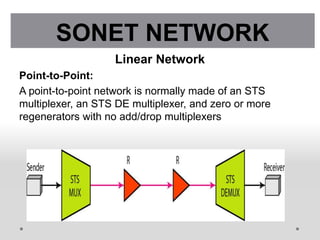
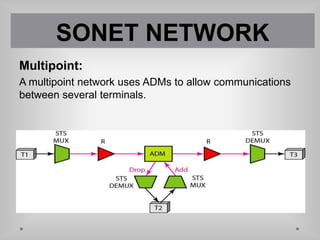
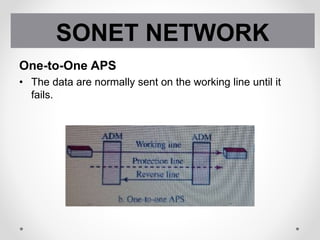
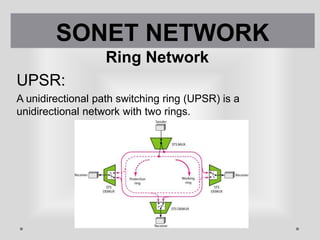
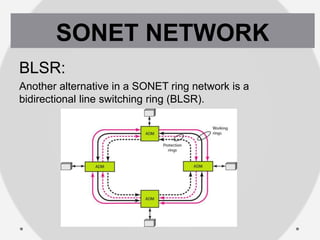
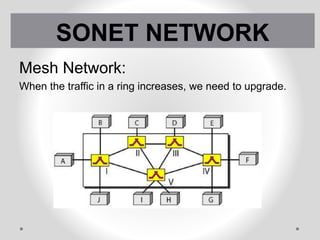
SONET is a standard for optical telecommunication transport that uses optical fiber to send data. It was developed independently in the US as SONET and in Europe as SDH. The SONET standard includes four functional layers - path, line, section, and photonic. It uses a SONET frame that is a 2-dimensional matrix of bytes transmitted at a fixed rate. SONET networks can be created using SONET equipment to form linear, ring or mesh topologies with advantages like protection, high bandwidth, and efficient bandwidth management.