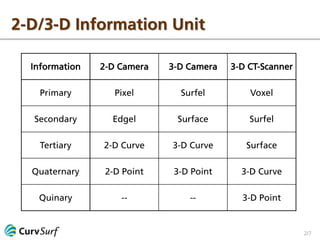
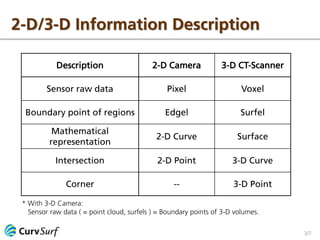
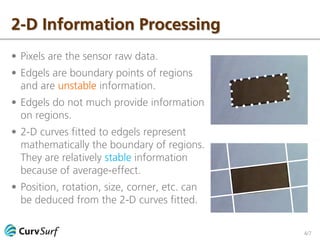
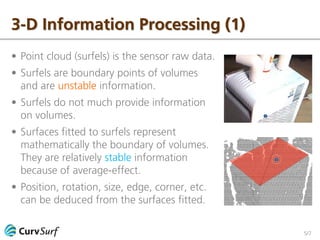
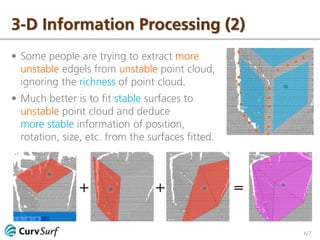
The document discusses 2-D and 3-D information processing, emphasizing the use of cameras and scanners to capture raw data in the form of pixels and point clouds. It highlights the instabilities of edgels and surfels as boundary points and advocates for fitting stable 2-D curves and 3-D surfaces to these elements to derive more reliable information. The author encourages further discussion on the topic.