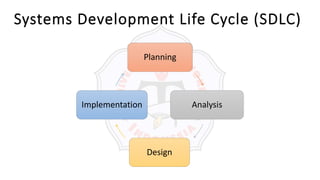
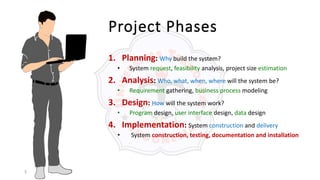
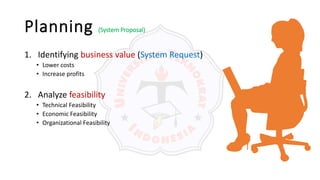
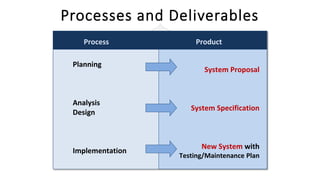
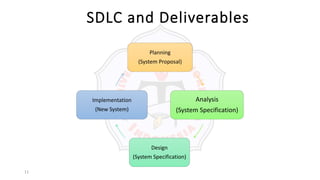
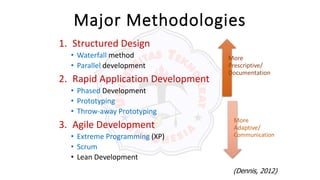
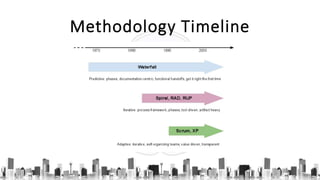
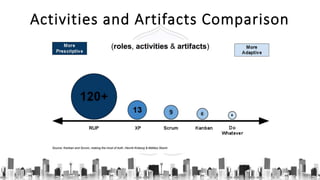
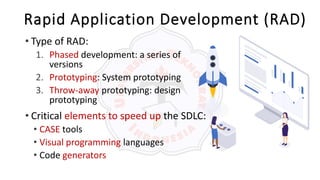
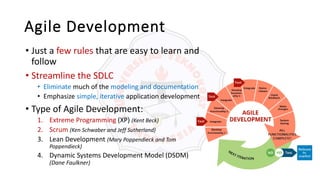
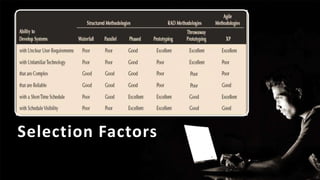
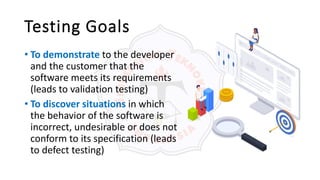
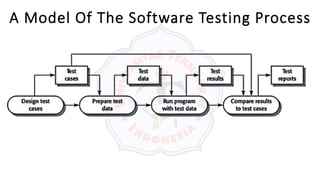
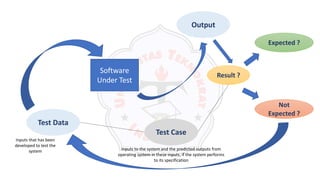
The document describes an introduction to software testing presentation. It discusses the software development life cycle (SDLC) which includes planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance phases. It then explains different software development methodologies like structured design, rapid application development, and agile development. Finally, it provides definitions and goals of software testing, and presents a model of the software testing process.