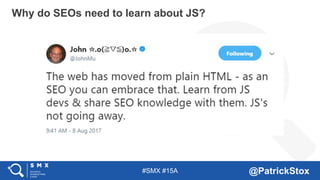
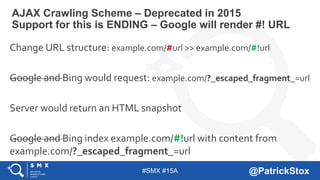
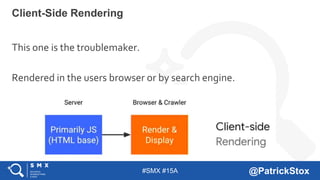
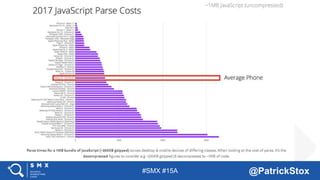
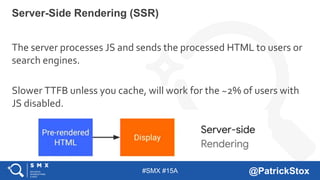
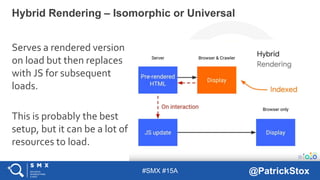
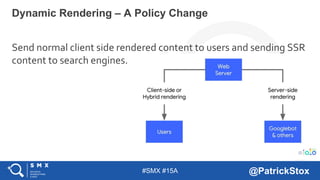
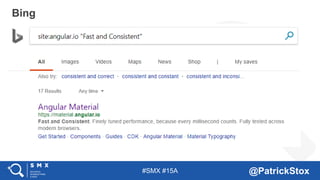
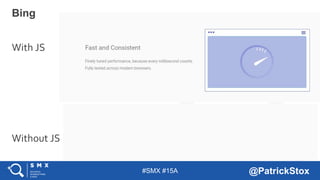
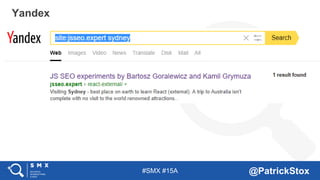
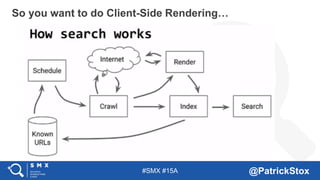
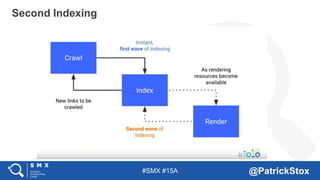
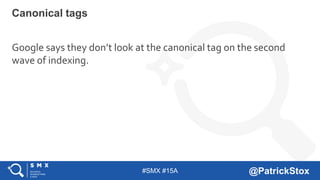
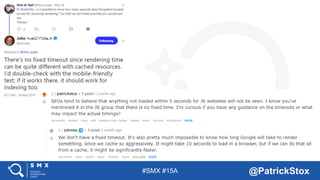
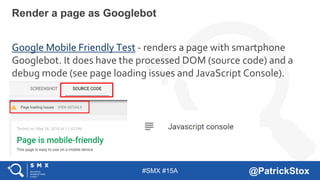
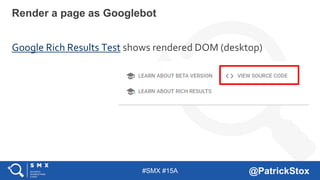
The document discusses SEO considerations for JavaScript frameworks. It notes that SEOs need to understand how JavaScript works and how search engines handle it, as many developers are not familiar with SEO. It provides tips for SEOs, including that search engines don't interact with the page content in the same way users do, and content should be loaded by default without user interaction. It also discusses different approaches to rendering pages for search engines like server-side rendering versus client-side rendering.