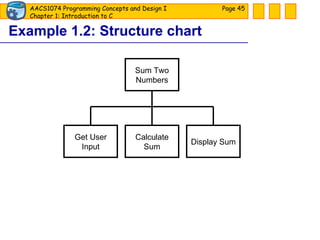
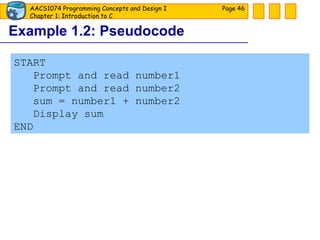
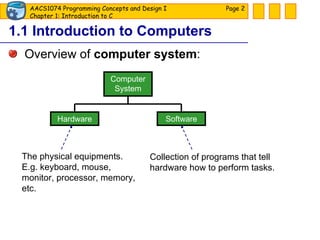
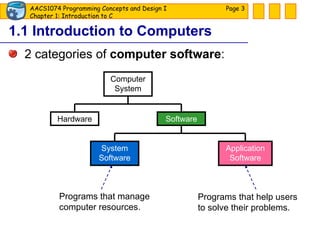
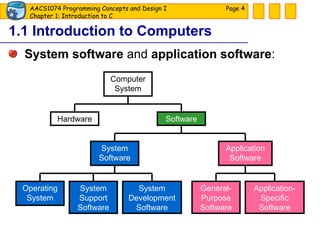
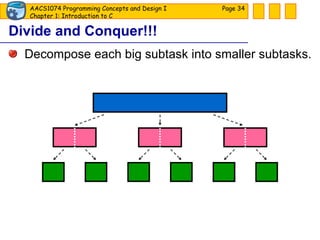
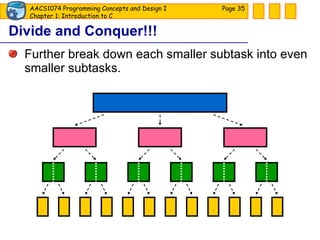
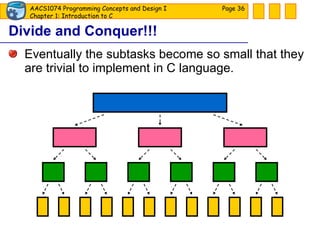
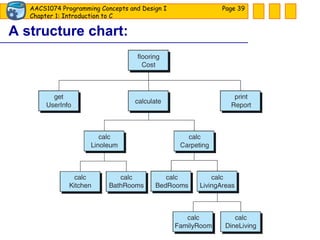
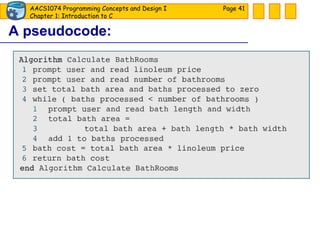
The document discusses introduction to computers and computer programming languages. It covers the basics of computer hardware and software, different types of computer languages like machine language, assembly language, high-level languages and their evolution. It also discusses the program development process which involves understanding the problem, developing a solution design, writing the program code, and testing. As an example, it shows how to approach designing a flooring cost calculation program using techniques like top-down design, structure charts, pseudocode and flowcharts.











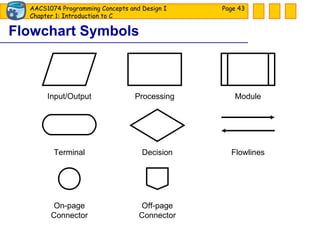
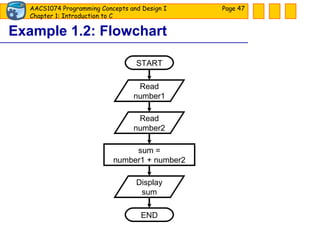
![Tool: Flowchart Use standard graphical symbols to represent the logical flow of data through a program. [ show flowchart ] Page](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slide01-090805052850-phpapp01/85/Slide-01-42-320.jpg)