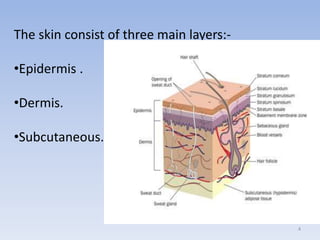
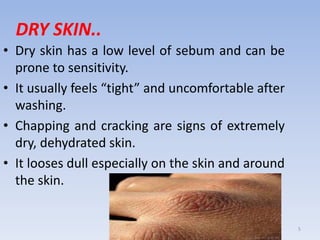
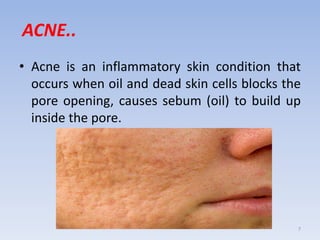
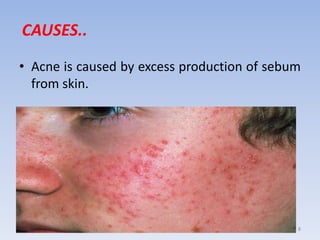
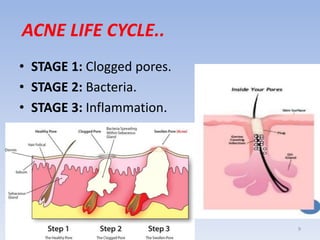
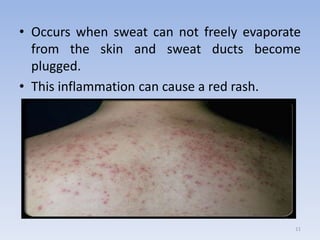
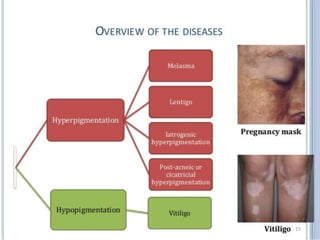
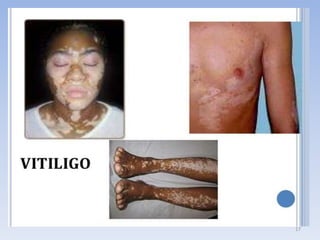
The document discusses various skin-related problems and their causes. It begins by describing the structure of skin and then discusses specific conditions like dry skin, acne, prickly heat, wrinkles, and pigmentation. Dry skin is caused by a lack of oil and can make the skin feel tight. Acne occurs when pores become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. Prickly heat is a rash caused by blocked sweat glands in hot conditions. Wrinkles are lines and creases in the skin that can be caused by age, sun exposure, smoking, and facial expressions. The document also covers moisturizers and their role in hydrating the skin.