Recommended
PDF
PDF
An Overview of Different PWM Techniques to Reduce Total Harmonic Distortion o...
PDF
A Comparative Analysis of MPWM & SPWM Techniques to Reduce Harmonic Distortio...
POTX
PDF
IRJET- Analysis of Sine Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM) and Third Harmonic Puls...
PDF
IRJET- Simulation and Analysis of Five Level SPWM Inverter
PDF
Study of Different Types of Inverters and FFT Analysis of Output of SPWM Inve...
PDF
Multilevel Inverter and Multipliers
PDF
Study of single pulse width modulated inverter and sinusoidal pulse width mod...
PDF
Matlab Simulink Model of Sinusoidal PWM For Three-Phase Voltage Source Inverter
PPT
PDF
PDF
differentmethodsofpwmforinvertercontrol-171103170201.pdf
PPTX
Different methods of pwm for inverter control
PDF
Carrier based hybrid pwm algorithm with reduced common mode voltage
PPTX
Simulation of sinosoidal pulse width modulation
PDF
Design and implementation of carrier based sinusoidal pwm (bipolar) inverter
PPT
ghbhgcngcbhdggddgfdgtfgdfggdfgtdetfgdrtfgdtfgdg
PDF
Common Mode Voltage reduction in Diode Clamped MLI using Alternative Phase Op...
DOC
PDF
Lecture slides_Ch 8 power electronics daniel hart.pdf
PDF
Implementation of d space controlled dpwm based
PDF
Harmonic reduction of cascaded mli fed induction
PDF
THD analysis of SPWM & THPWM Controlled Three phase Voltage Source Inverter
PDF
THD analysis of SPWM & THPWM Controlled Three phase Voltage Source Inverter
PDF
THD analysis of SPWM & THPWM Controlled Three phase Voltage Source Inverter
PPTX
Pwm techniques for converters
PDF
Design and Simulation of Low Pass Filter for Single phase full bridge Inverte...
PPTX
BE Probnmvlnmlvnmlmnlgmnlmdfb,ndf;,dgram.pptx
PPT
PPT-ghgkjgkjgkjjkgkjgjkgjkbjbjkgSeminar.ppt
More Related Content
PDF
PDF
An Overview of Different PWM Techniques to Reduce Total Harmonic Distortion o...
PDF
A Comparative Analysis of MPWM & SPWM Techniques to Reduce Harmonic Distortio...
POTX
PDF
IRJET- Analysis of Sine Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM) and Third Harmonic Puls...
PDF
IRJET- Simulation and Analysis of Five Level SPWM Inverter
PDF
Study of Different Types of Inverters and FFT Analysis of Output of SPWM Inve...
PDF
Multilevel Inverter and Multipliers
Similar to Sinusoidal_PWM_Modulation_Index_lecture.pptx
PDF
Study of single pulse width modulated inverter and sinusoidal pulse width mod...
PDF
Matlab Simulink Model of Sinusoidal PWM For Three-Phase Voltage Source Inverter
PPT
PDF
PDF
differentmethodsofpwmforinvertercontrol-171103170201.pdf
PPTX
Different methods of pwm for inverter control
PDF
Carrier based hybrid pwm algorithm with reduced common mode voltage
PPTX
Simulation of sinosoidal pulse width modulation
PDF
Design and implementation of carrier based sinusoidal pwm (bipolar) inverter
PPT
ghbhgcngcbhdggddgfdgtfgdfggdfgtdetfgdrtfgdtfgdg
PDF
Common Mode Voltage reduction in Diode Clamped MLI using Alternative Phase Op...
DOC
PDF
Lecture slides_Ch 8 power electronics daniel hart.pdf
PDF
Implementation of d space controlled dpwm based
PDF
Harmonic reduction of cascaded mli fed induction
PDF
THD analysis of SPWM & THPWM Controlled Three phase Voltage Source Inverter
PDF
THD analysis of SPWM & THPWM Controlled Three phase Voltage Source Inverter
PDF
THD analysis of SPWM & THPWM Controlled Three phase Voltage Source Inverter
PPTX
Pwm techniques for converters
PDF
Design and Simulation of Low Pass Filter for Single phase full bridge Inverte...
More from JITENDER773791
PPTX
BE Probnmvlnmlvnmlmnlgmnlmdfb,ndf;,dgram.pptx
PPT
PPT-ghgkjgkjgkjjkgkjgjkgjkbjbjkgSeminar.ppt
PPTX
Principle Of A Single-phase VSI To Draw Its Power Circuit And Explain Square ...
PPTX
jkthsjlfd lectsdfdsfdsfdsfsdfdssfsure.pptx
PPTX
Lectureerdjkldfgjkkjkjkjdfgjlmfdgdfgker.pptx
PPTX
Lecturekjkljkljlkjknklnjkghvblkbbkbkjb.pptx
PPTX
Lecturedsfndskfjdsklfjldsdsfdsgmjdflgmdflmg.pptx
PPTX
Lecture (Additional)sdfjksjfkldsfsdf.pptx
PPTX
Lecture (Additional)fghgfhdfghgfhgfhgfh.pptx
PPTX
Analysdsdsdfgdfgdfgdfsgdfis of Data_2.pptx
PPTX
Analysis of hgfhgfhgfjgfjmghjghjghData_1.pptx
PPT
VR_Unit-1_Lec(9)_B_3D_sdfdsfsdfScanner.ppt
PPT
nkllml;m;llkmlmljkjiuhihkjnklnjkhjgjk.ppt
PDF
Unit-4.-Chi-squjkljl;jj;ljl;jlm;lml;mare.pdf
PPT
15hjkljklj'jklj'kljkjkljkljkljkl95867.ppt
PPTX
Lecture dsfgidsjfhjknflkdnkldnklnfklfndls.pptx
PPT
Chghjgkgyhbygukbhyvuhbbubnubuyuvyyvivlh06.ppt
PPT
1328cvkdlgkdgjfdkjgjdfgdfkgdflgkgdfglkjgld8679 - Copy.ppt
PPT
lghjghgggkgjhgjghhjgjhgkhjghjghjghjghect1.ppt
PPT
inmlk;lklkjlk;lklkjlklkojhhkljkbjlkjhbtroDM.ppt
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Limpitlaw "Licensing: From Mindset to Milestones"
PPTX
How to Manage Line Discounts in Odoo 18 POS
PDF
DHA/HAAD/MOH/DOH OPTOMETRY MCQ PYQ. .pdf
PPTX
Accounting Skills Paper-II (Registers of PACs and Credit Co-operative Societies)
PPTX
Semester 6 unit 2 Atopic dermatitis.pptx
PDF
Digital Wellness in University Communities: Libraries as Guardians of Healthy...
PPTX
Unit I — Introduction to Anatomical Terms and Organization of the Human Body
PDF
The Tale of Melon City poem ppt by Sahasra
PDF
UKSG Forum 2025 - They asked for everything - The Case of the Systematic Revi...
PDF
NAVIGATE PHARMACY CAREER OPPORTUNITIES.pdf
PDF
The Drift Principle: When Information Accelerates Faster Than Minds Can Compress
PPTX
ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION (UNIT 2) .pptx
PPTX
Cost of Capital - Cost of Equity, Cost of debenture, Cost of Preference share...
PDF
APM Wessex Network: DEIB Policy into Practice
PPTX
CHAPTER NO.08 HCP BY GG CLINICAL PHARMACY
PPTX
The Cell & Cell Cycle-detailed structure and function of organelles.pptx
PDF
Models of Teaching - TNTEU - B.Ed I Semester - Teaching and Learning - BD1TL ...
PPTX
TAMIS & TEMS - HOW, WHY and THE STEPS IN PROCTOLOGY
PPTX
How to use search_read method in Odoo 18
PPTX
15 December 2025 Education for human flourishing Michael Stevenson .pptx
Sinusoidal_PWM_Modulation_Index_lecture.pptx 1. Sinusoidal PWM and Modulation
Index in Voltage Source Inverters
• PWM is a technique used to control output
voltage and harmonics in inverters.
• It compares a reference sine signal with a
high-frequency triangular carrier.
• Applications: motor drives, UPS, renewable
converters.
2. Sinusoidal PWM (SPWM) Principle
• A sinusoidal reference is compared with a
triangular carrier.
• Switch turns ON when reference > carrier.
• Average output voltage follows a sine pattern.
• Key parameters: carrier frequency (f_c),
modulating frequency (f_m), ratio N=f_c/f_m.
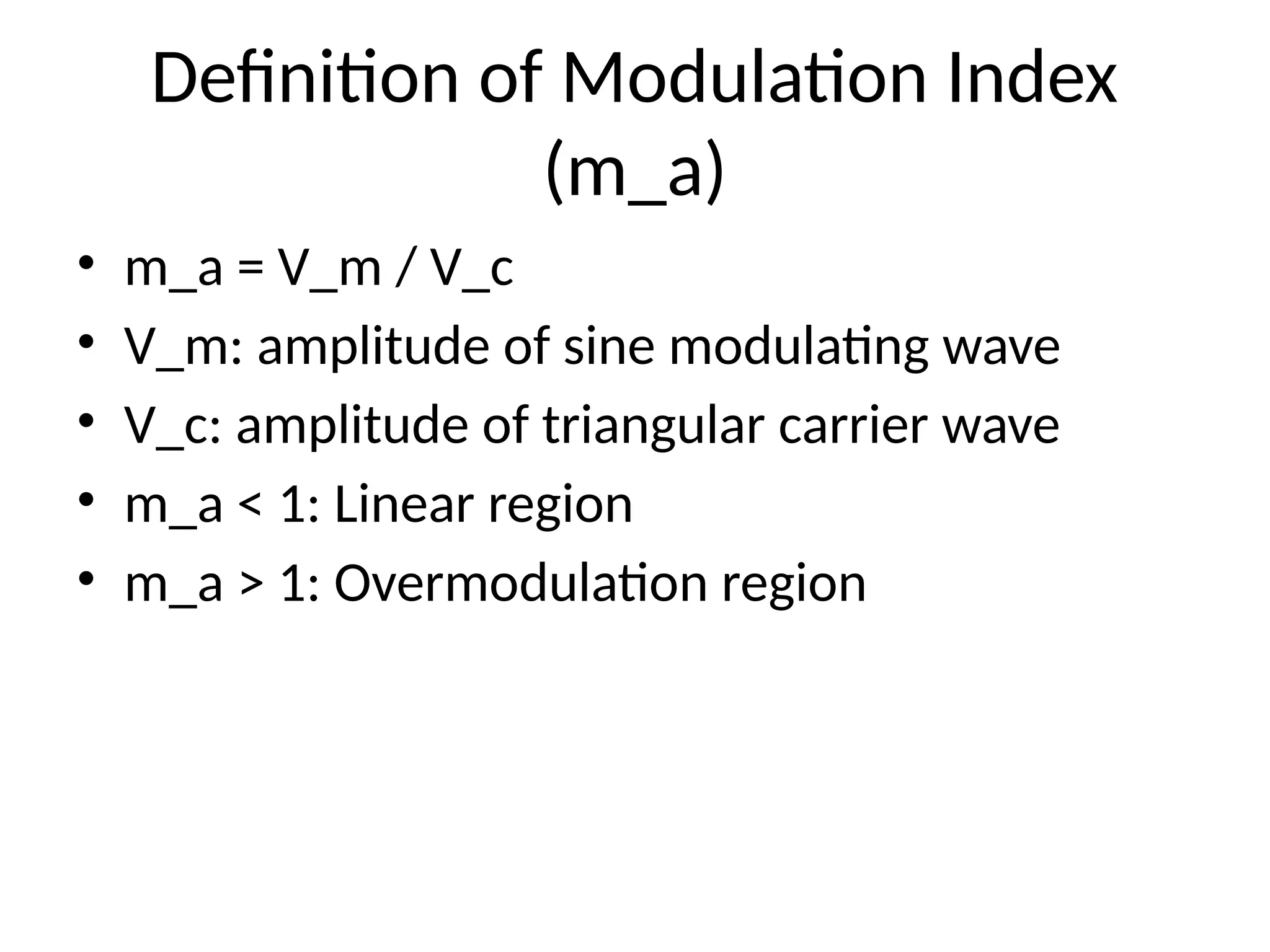
3. Definition of Modulation Index
(m_a)
• m_a = V_m / V_c
• V_m: amplitude of sine modulating wave
• V_c: amplitude of triangular carrier wave
• m_a < 1: Linear region
• m_a > 1: Overmodulation region
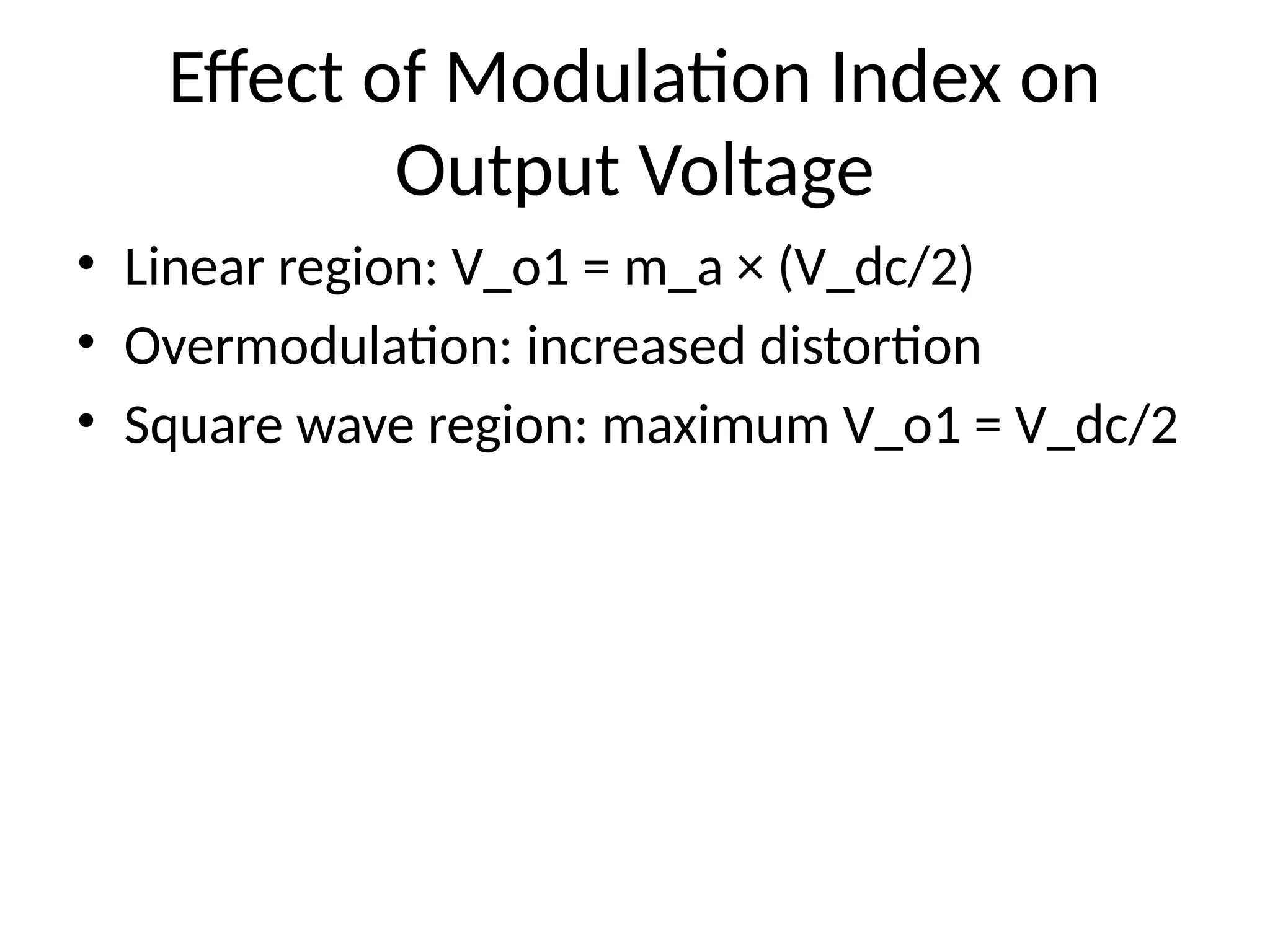
4. Effect of Modulation Index on
Output Voltage
• Linear region: V_o1 = m_a × (V_dc/2)
• Overmodulation: increased distortion
• Square wave region: maximum V_o1 = V_dc/2
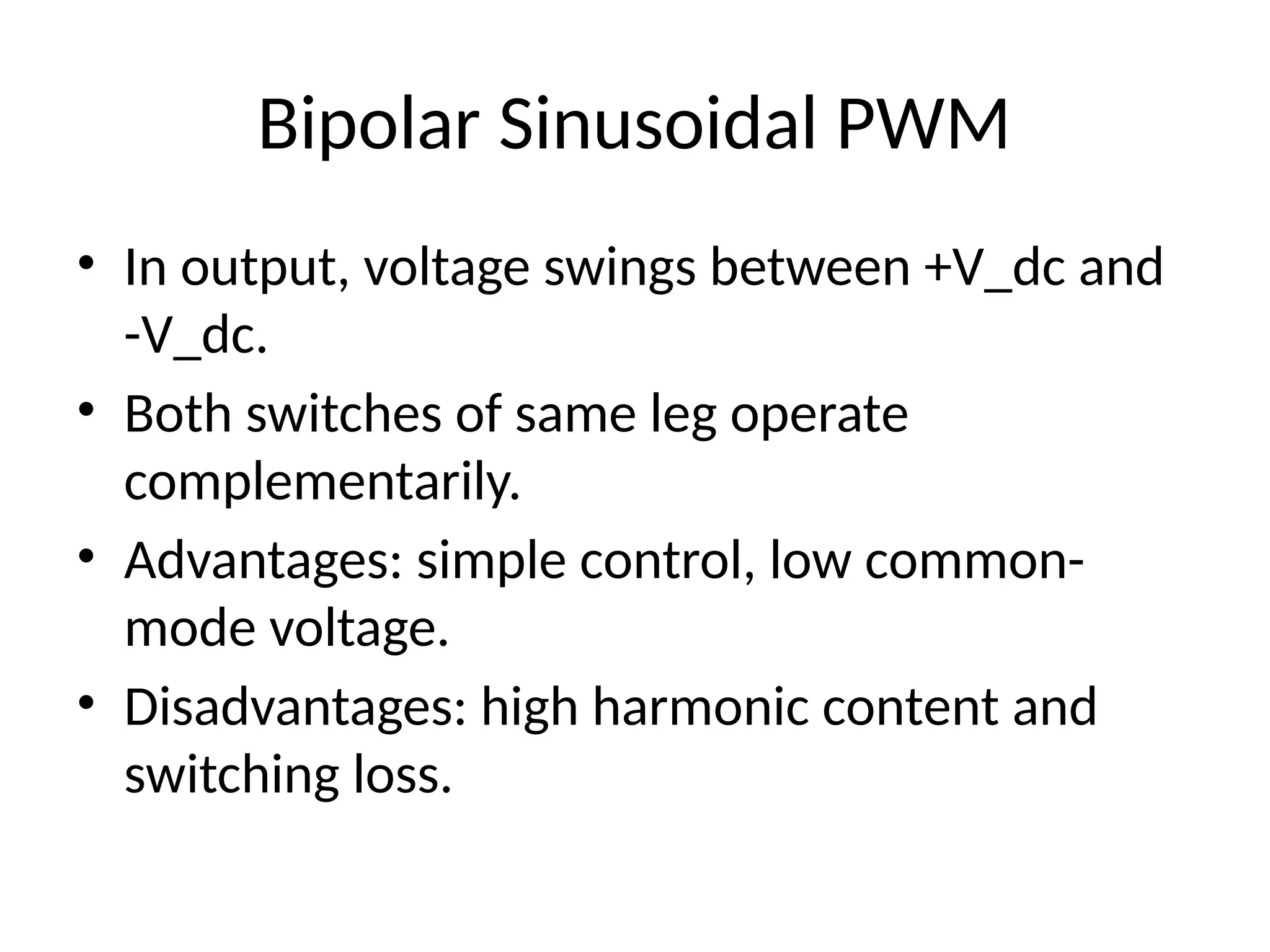
5. Bipolar Sinusoidal PWM
• In output, voltage swings between +V_dc and
-V_dc.
• Both switches of same leg operate
complementarily.
• Advantages: simple control, low common-
mode voltage.
• Disadvantages: high harmonic content and
switching loss.
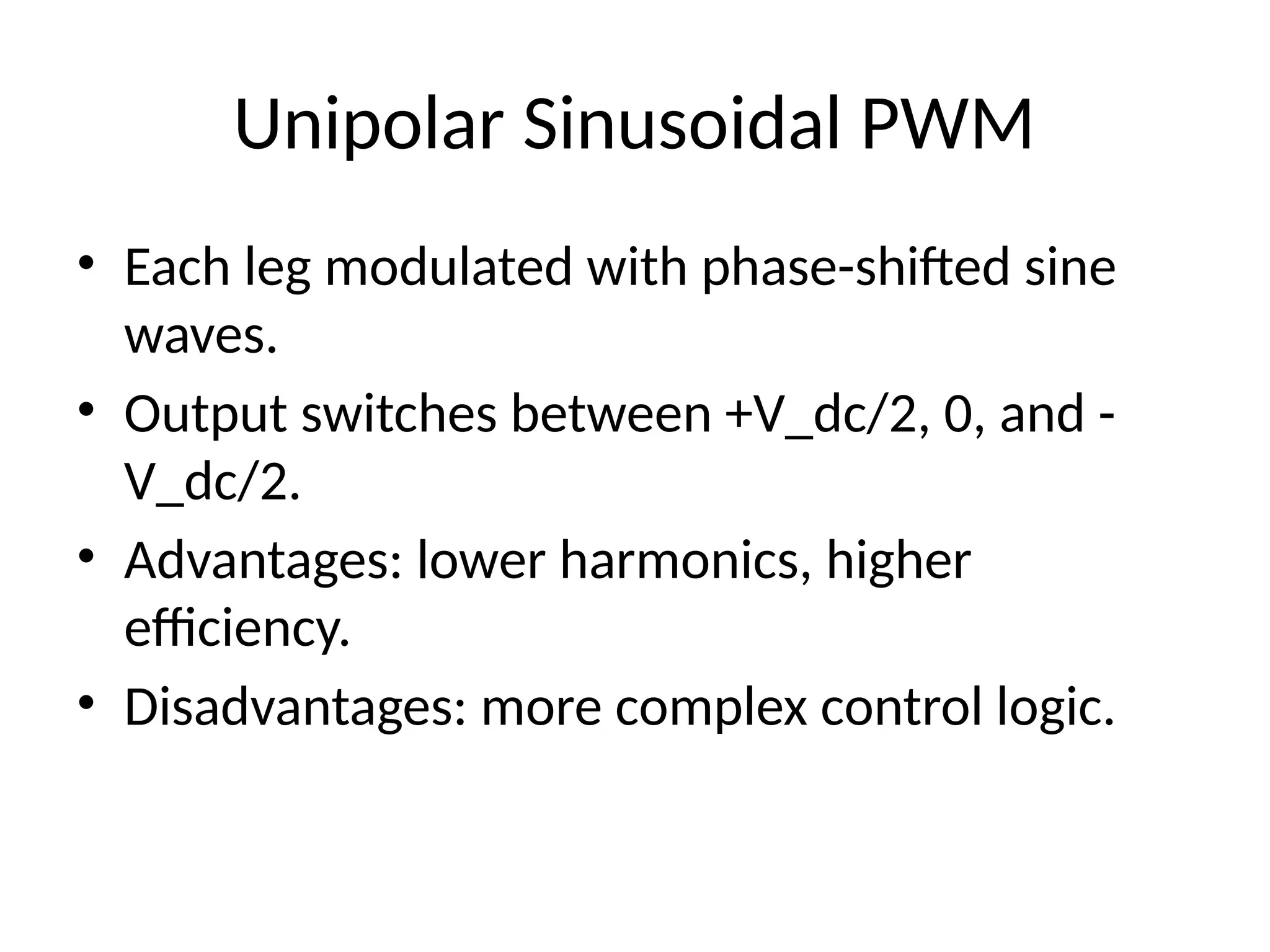
6. Unipolar Sinusoidal PWM
• Each leg modulated with phase-shifted sine
waves.
• Output switches between +V_dc/2, 0, and -
V_dc/2.
• Advantages: lower harmonics, higher
efficiency.
• Disadvantages: more complex control logic.
7. Comparison Between Bipolar and
Unipolar PWM
• Bipolar: two-level (+Vdc, -Vdc) output, higher
THD, simpler.
• Unipolar: three-level (+Vdc/2, 0, -Vdc/2),
lower THD, efficient but complex.
• Unipolar preferred in high-performance
inverters.
8. Summary
• • Modulation index (m_a) controls output
voltage amplitude.
• • m_a > 1 leads to overmodulation and
distortion.
• • Unipolar SPWM gives superior harmonic
performance and efficiency.