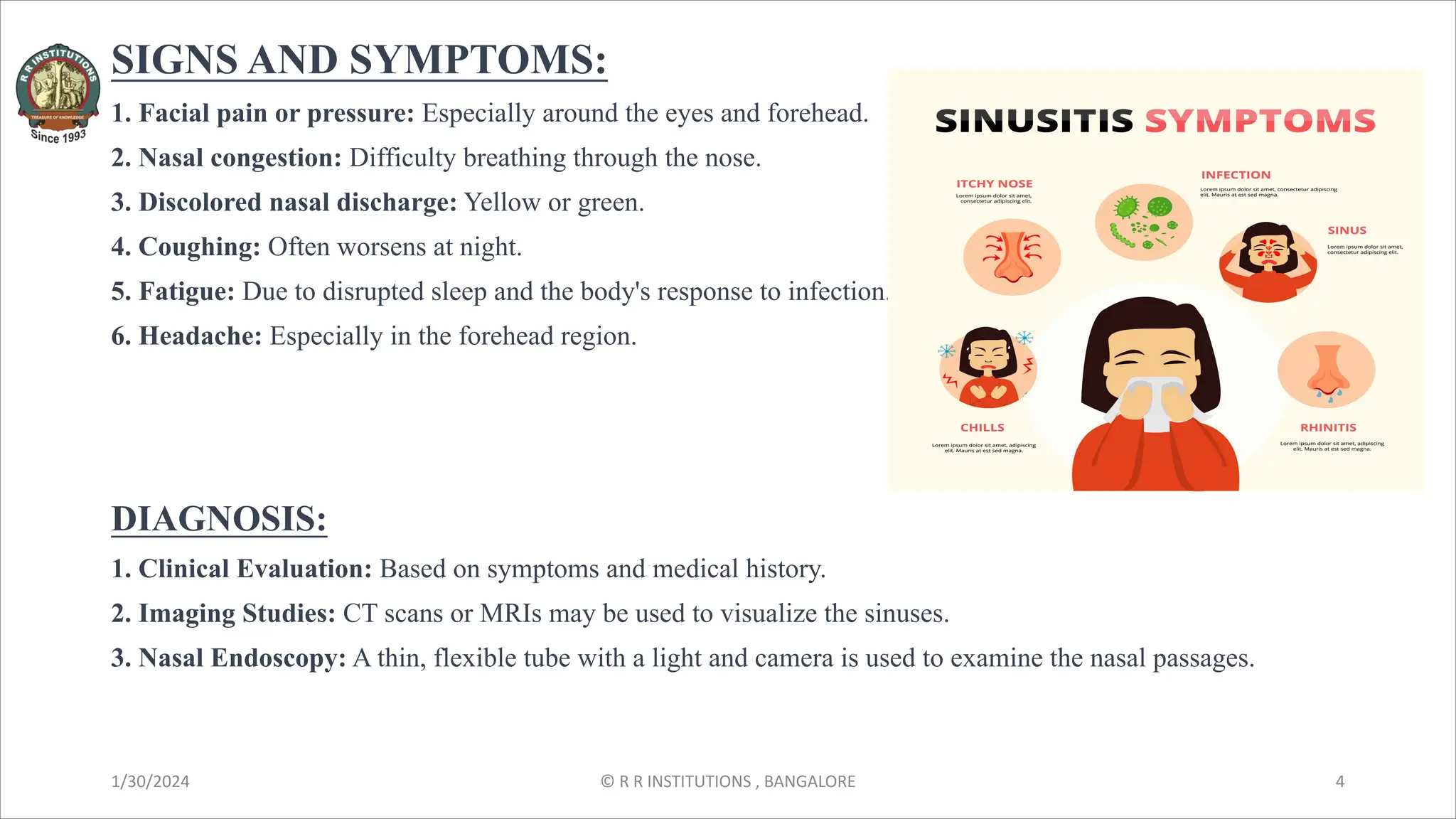
Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses that can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, allergies, or nasal polyps. It is characterized by facial pain, nasal congestion, discolored discharge, coughing, fatigue, and headaches. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, imaging tests, and nasal endoscopy. Treatment consists of home remedies, medications like decongestants, antibiotics, and pain relievers, nasal irrigation, and corticosteroids. Nursing management focuses on patient education, monitoring for symptoms, providing comfort, promoting hygiene, and ensuring compliance with treatment.