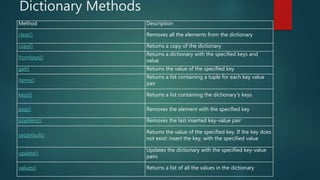
The document discusses arrays in Python. It begins by defining sets and dictionaries. For sets, it explains that they are unordered collections that use curly brackets. It provides examples of creating sets and checking if an item is in a set. It also discusses adding, updating, removing and joining sets. For dictionaries, it defines them as unordered collections that use curly brackets and have keys and values. It provides examples of accessing items, changing values, and looping through a dictionary. It also covers checking for items, adding/removing items, copying dictionaries, and nested dictionaries. Finally, it lists common dictionary methods.




![Change values in sets
Add multiple items to a set, using the update method
Example:
set1 = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
set1.update(["orange", "mango", "grapes"])
print(set1)
Result:
{'grapes', 'orange', 'mongo', 'apple', 'cherry', 'banana'}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seventhsession-200413101957/85/Seventh-session-5-320.jpg)





![Get an item
You can access the items of a dictionary by referring to its key name, inside
square brackets
Example:
x = thisdict["model"]
Print(x)
Result:
Mustang
There is also a method called get() will give the same result
x = thisdict.get(“model”)
Print(x)
Result:
Mustang](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seventhsession-200413101957/85/Seventh-session-11-320.jpg)
![Change values
You can change the value of a specific item by referring to its key name
Example:
thisdict = {
"brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
thisdict["year"] = 2020
This example will change the year to 2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seventhsession-200413101957/85/Seventh-session-12-320.jpg)
![Loops over dictionaries
The following will give all key names in dictionary:
for x in thisdict:
print(x)
The following will give all values names in dictionary:
for x in thisdict:
print(thisdict[x])
We can also use values() function to return values of a dictionary
for x in thisdict.values():
print(x)
To get both of key and values we use items() method:
for x, y in thisdict.items():
print(x, y)
X for the key and y for the value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seventhsession-200413101957/85/Seventh-session-13-320.jpg)
![Check for items in dictionaries
if "model" in thisdict:
print("Yes, 'model' is one of the keys in the thisdict dictionary")
To add item to dictionary we use the following:
thisdict["color"] = "red"
print(thisdict)
Result:
{'brand': 'Ford', 'model': 'Mustang', 'year': 2020, 'color': 'red'}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seventhsession-200413101957/85/Seventh-session-14-320.jpg)