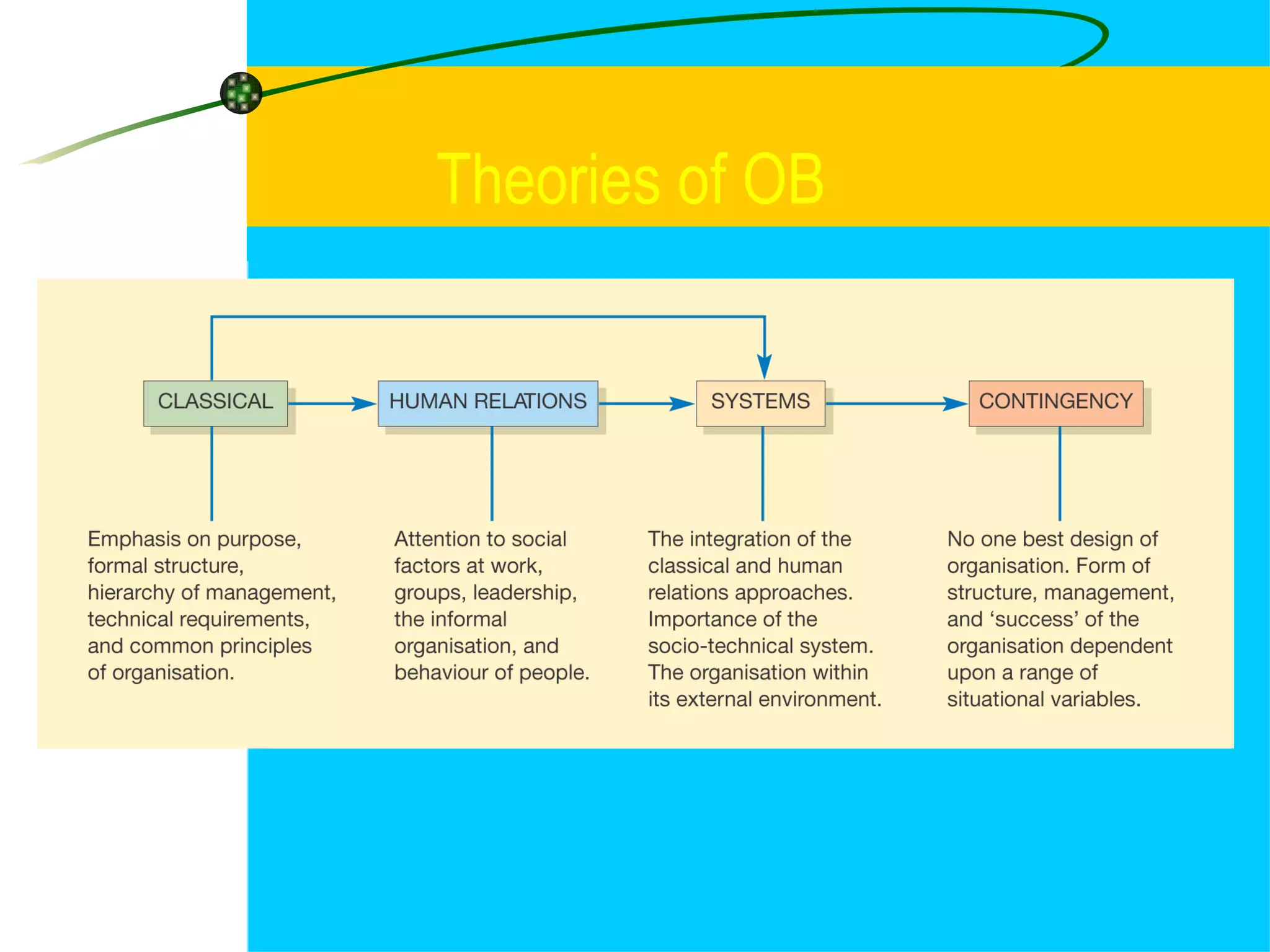
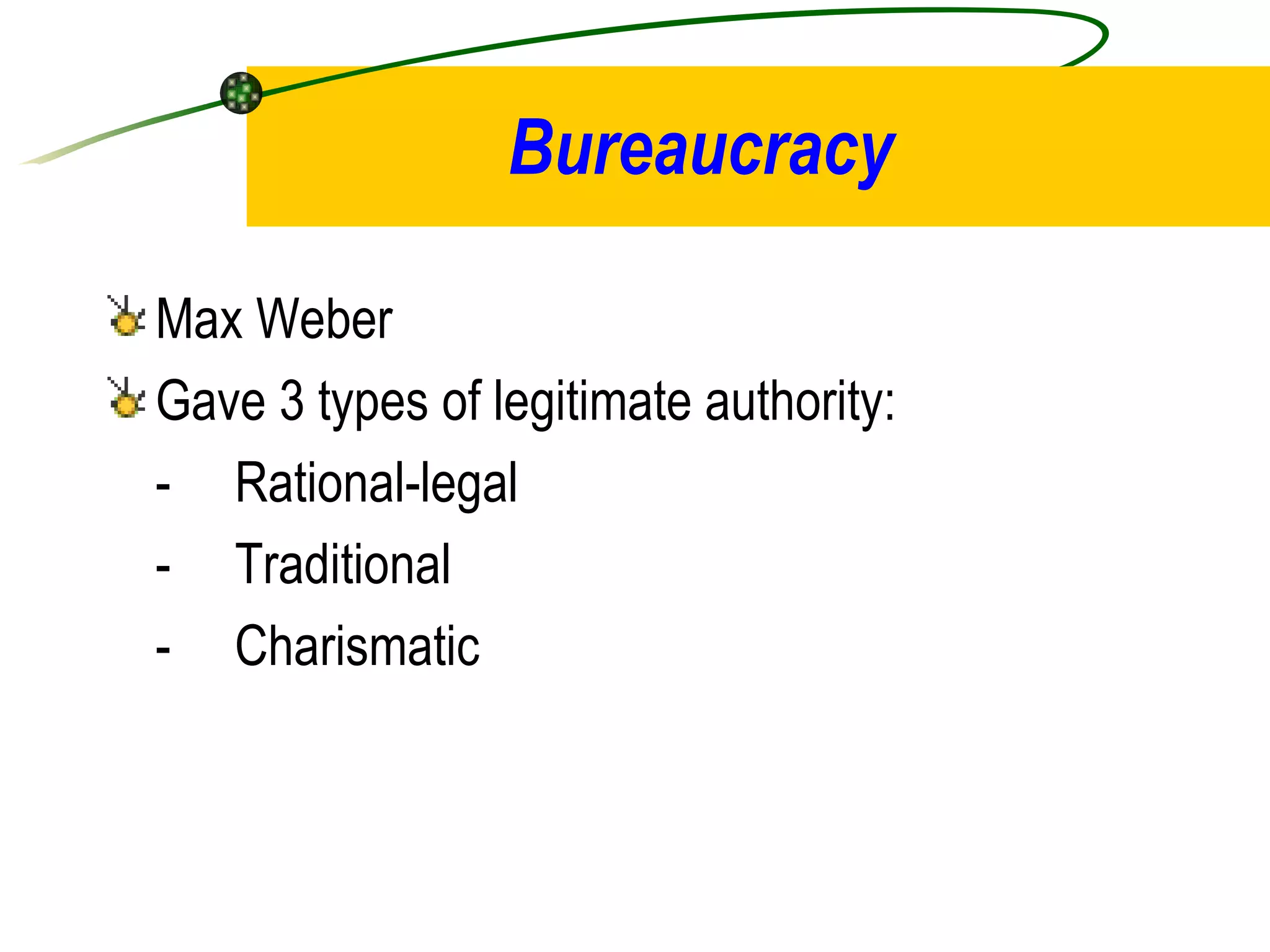
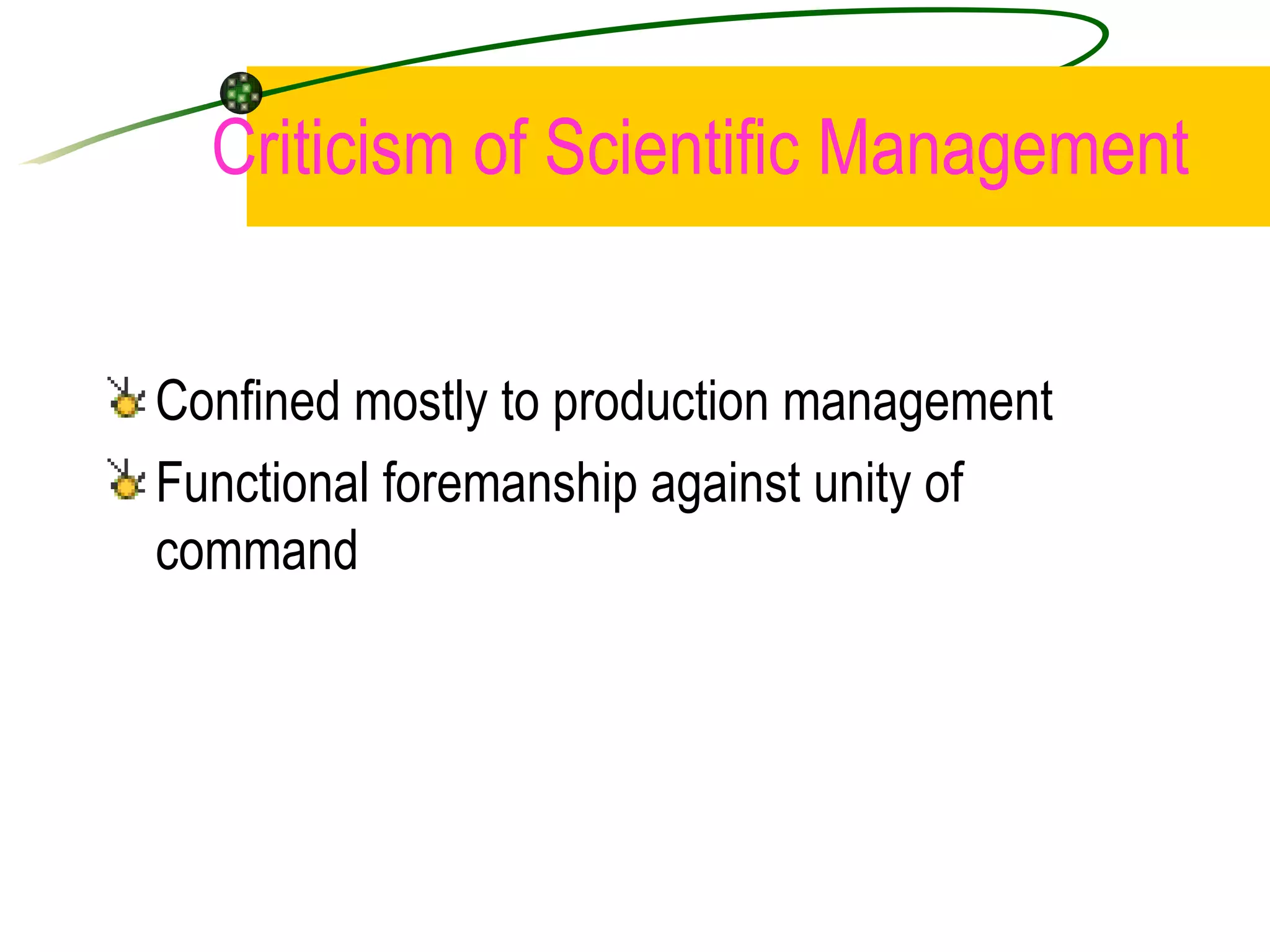
1. Classical management theories include scientific management, bureaucracy, and administrative management. Scientific management focused on efficiency through time and motion studies while bureaucracy emphasized standardized rules and procedures.
2. Neo-classical theories took a human relations approach exemplified by the Hawthorne studies, which found that social and psychological factors influenced productivity more than physical conditions alone.
3. Systems theory views organizations as open systems that must adapt to their external environment. The McKinsey 7S framework also analyzed internal factors like strategy, structure, and staff that influence organizational effectiveness.