This document provides an overview of a branding course, including session topics, assigned readings, and course objectives. Some key points:
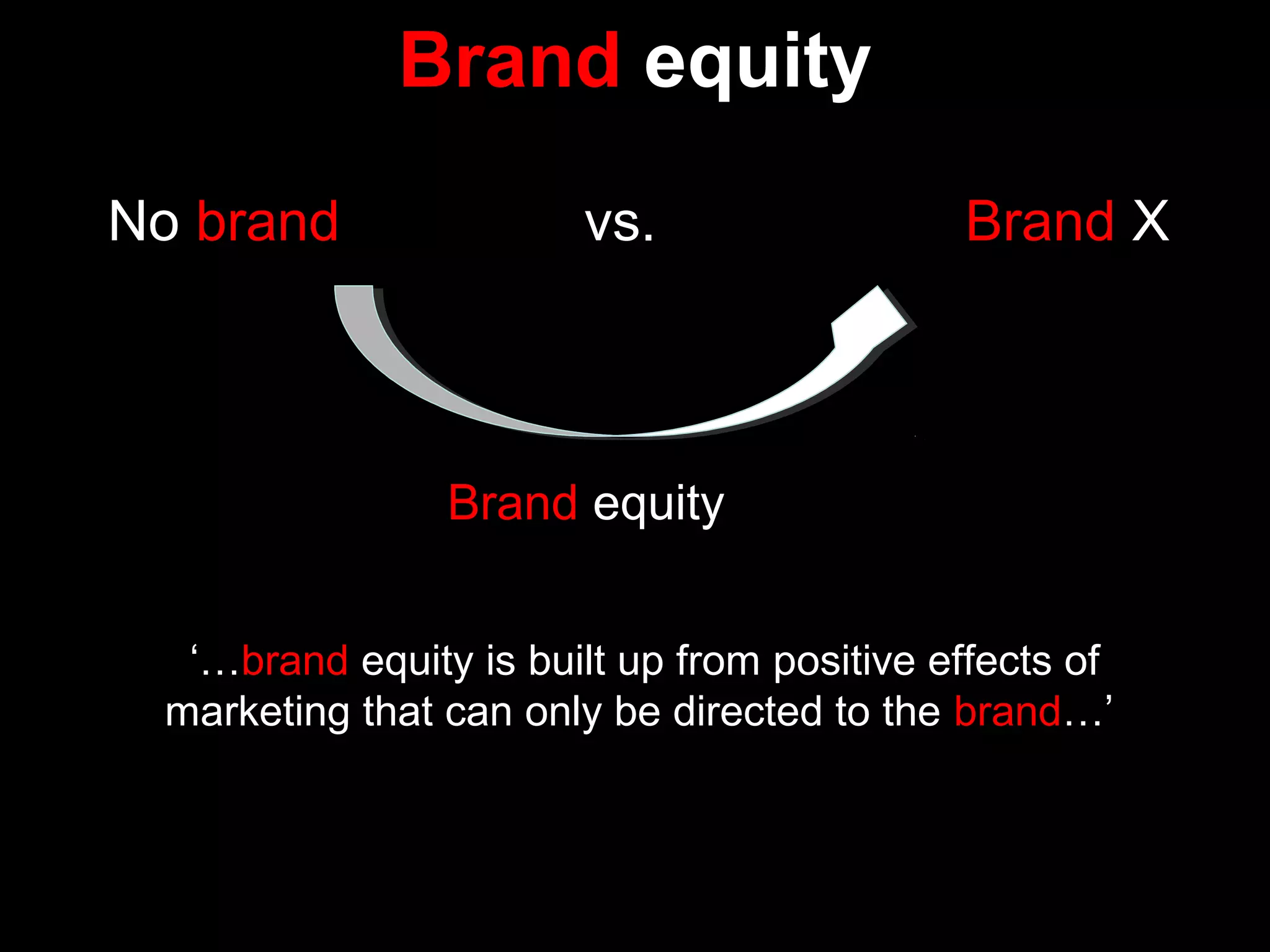
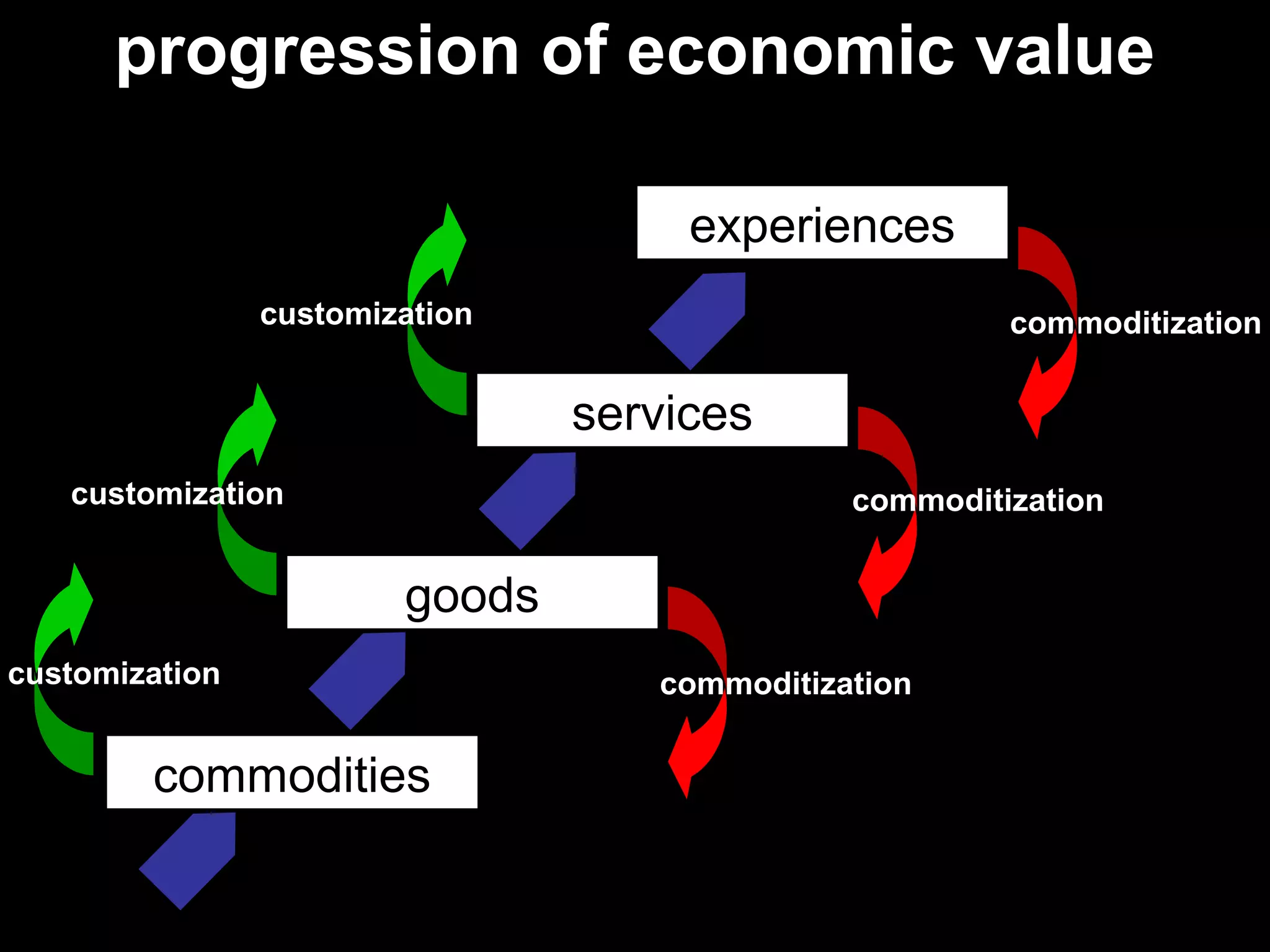
- The course covers topics like creating brand value, brand positioning, building brand equity, and brand research methods.
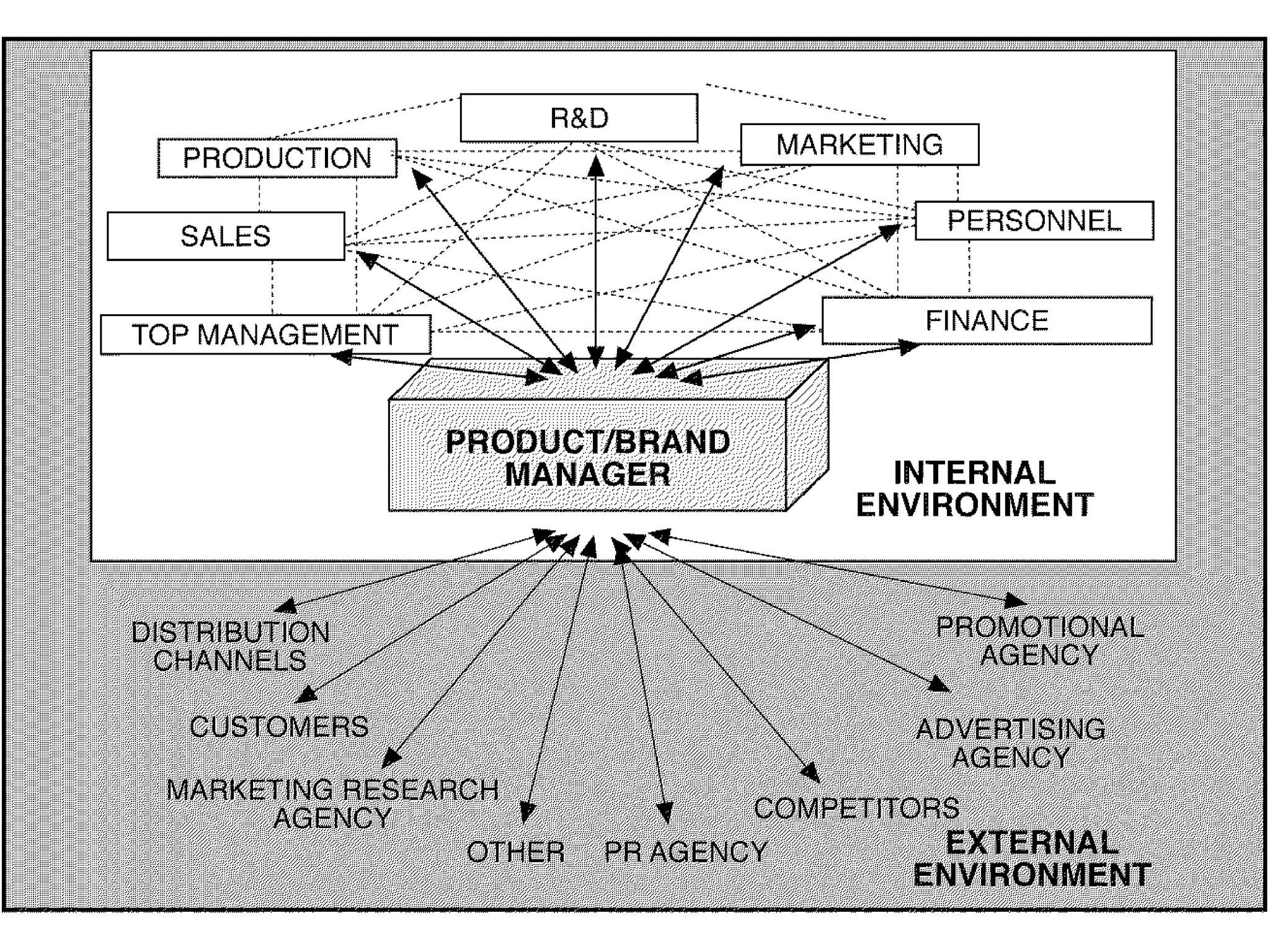
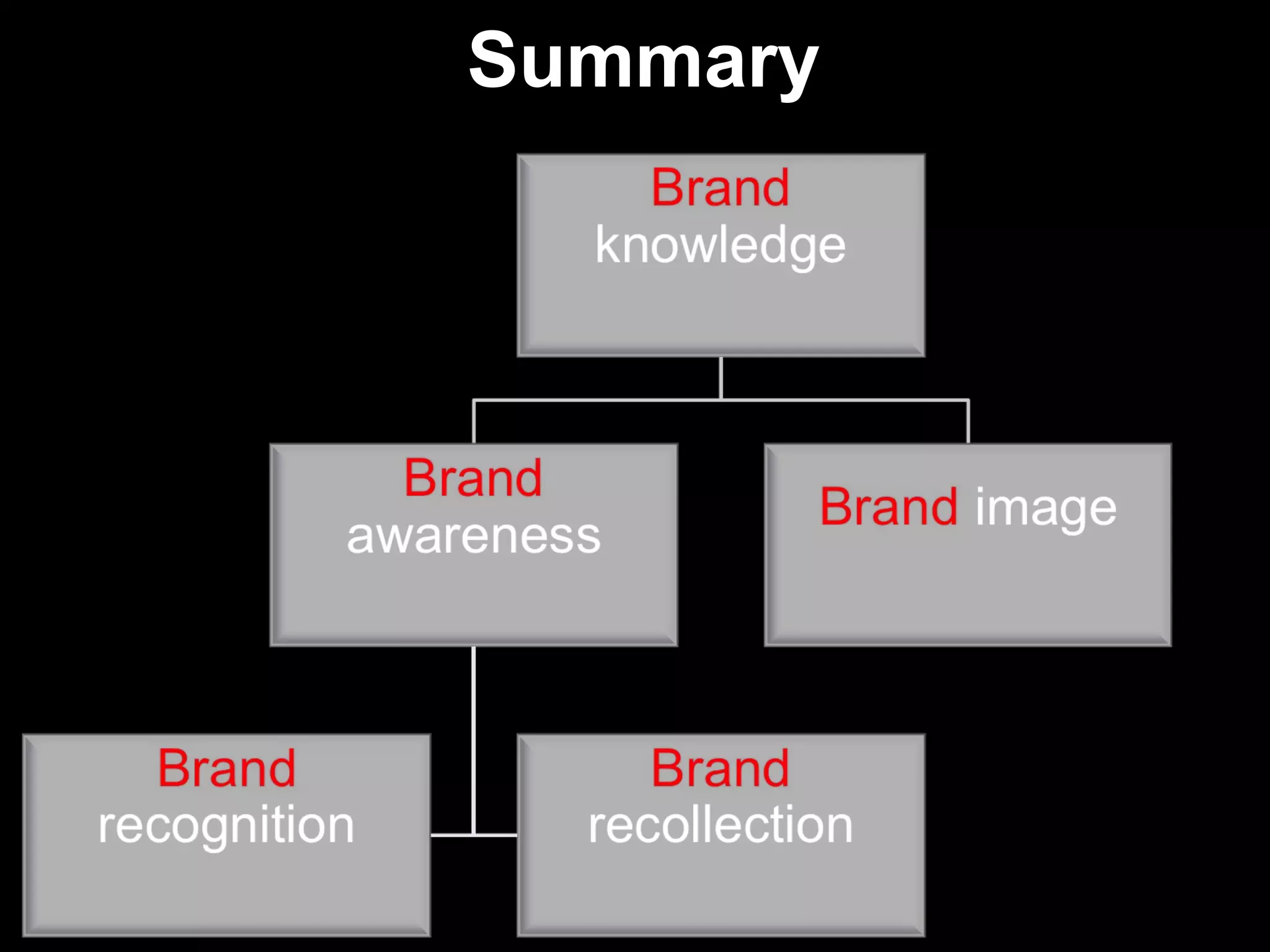
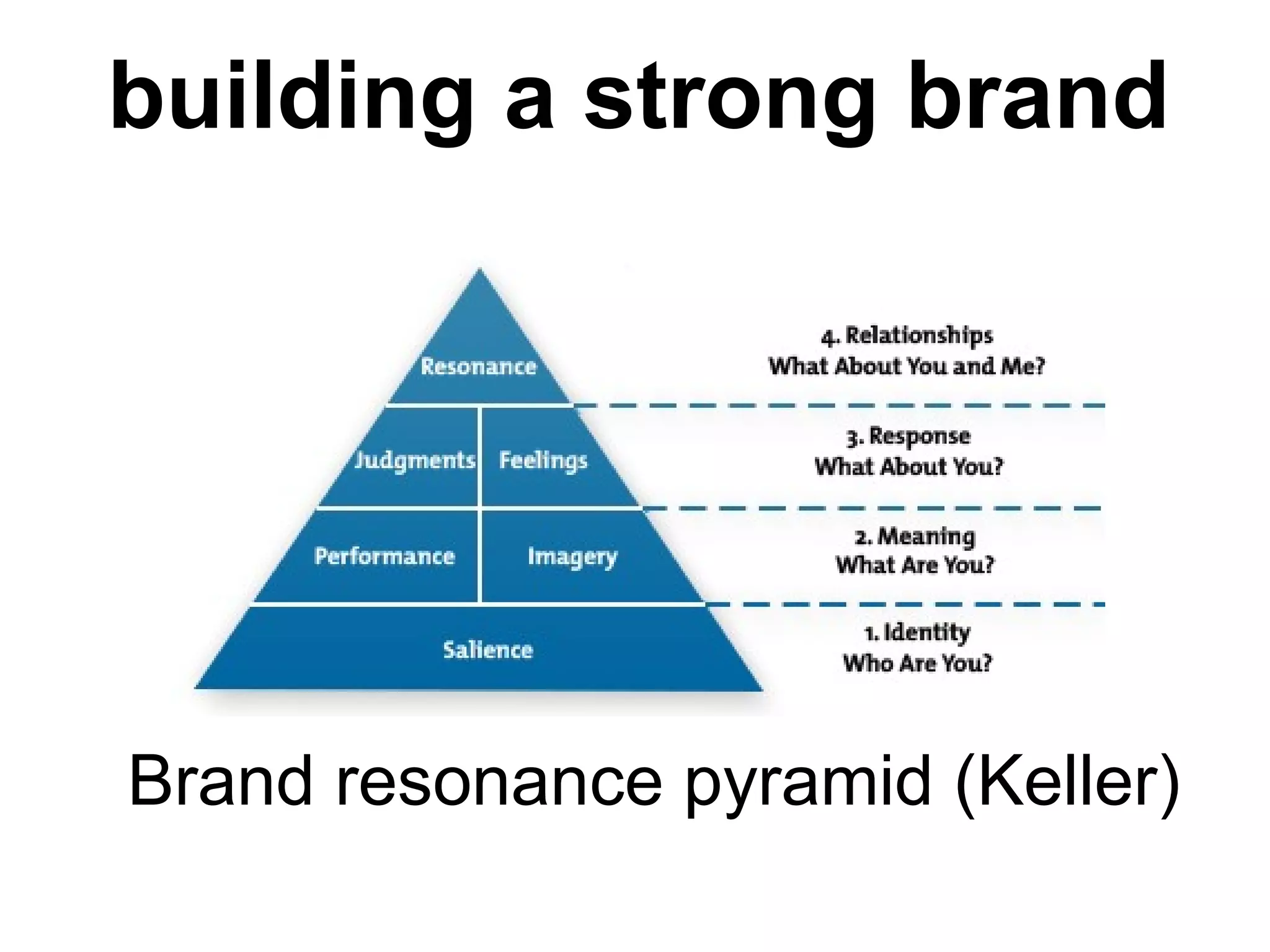
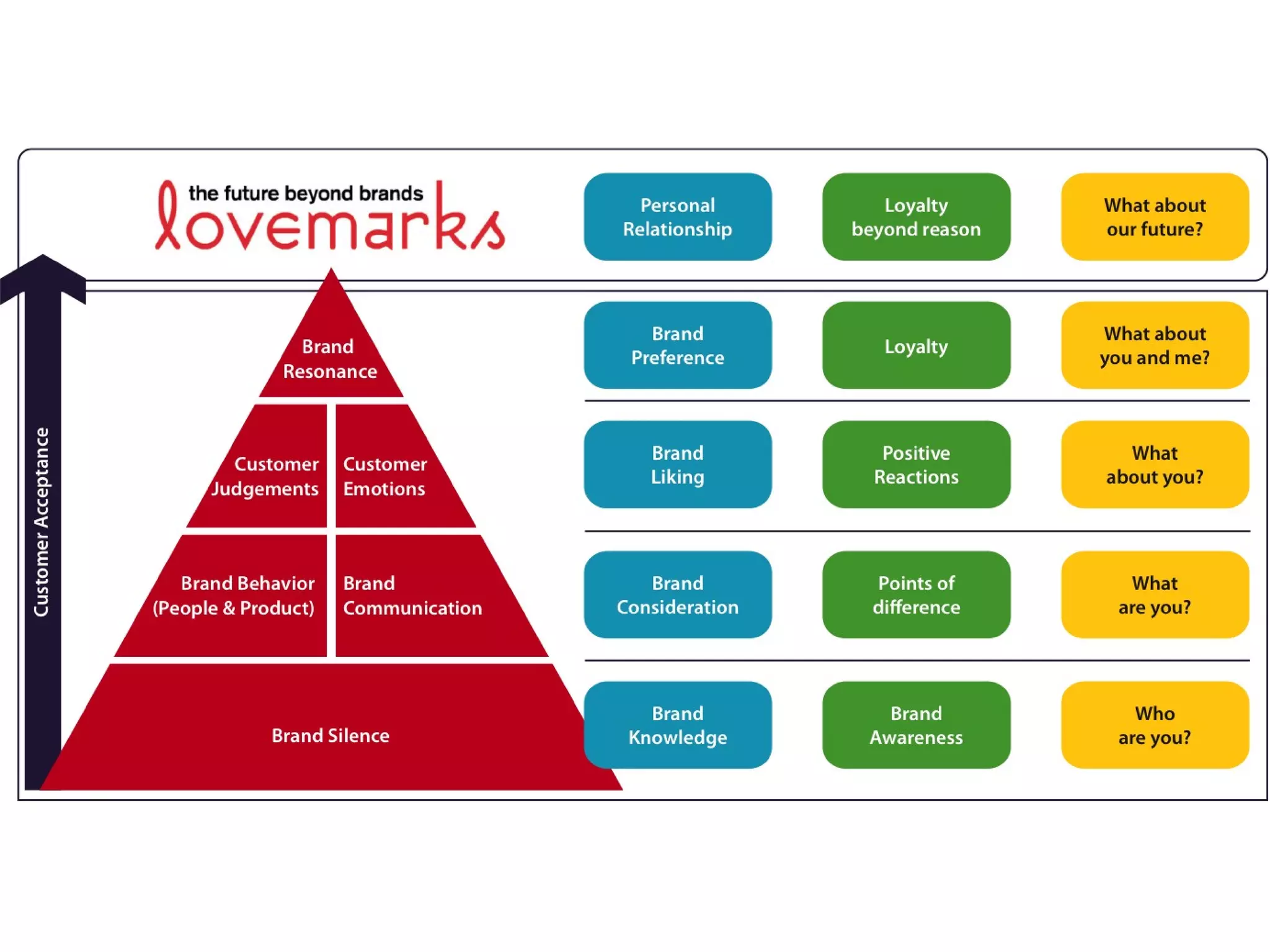
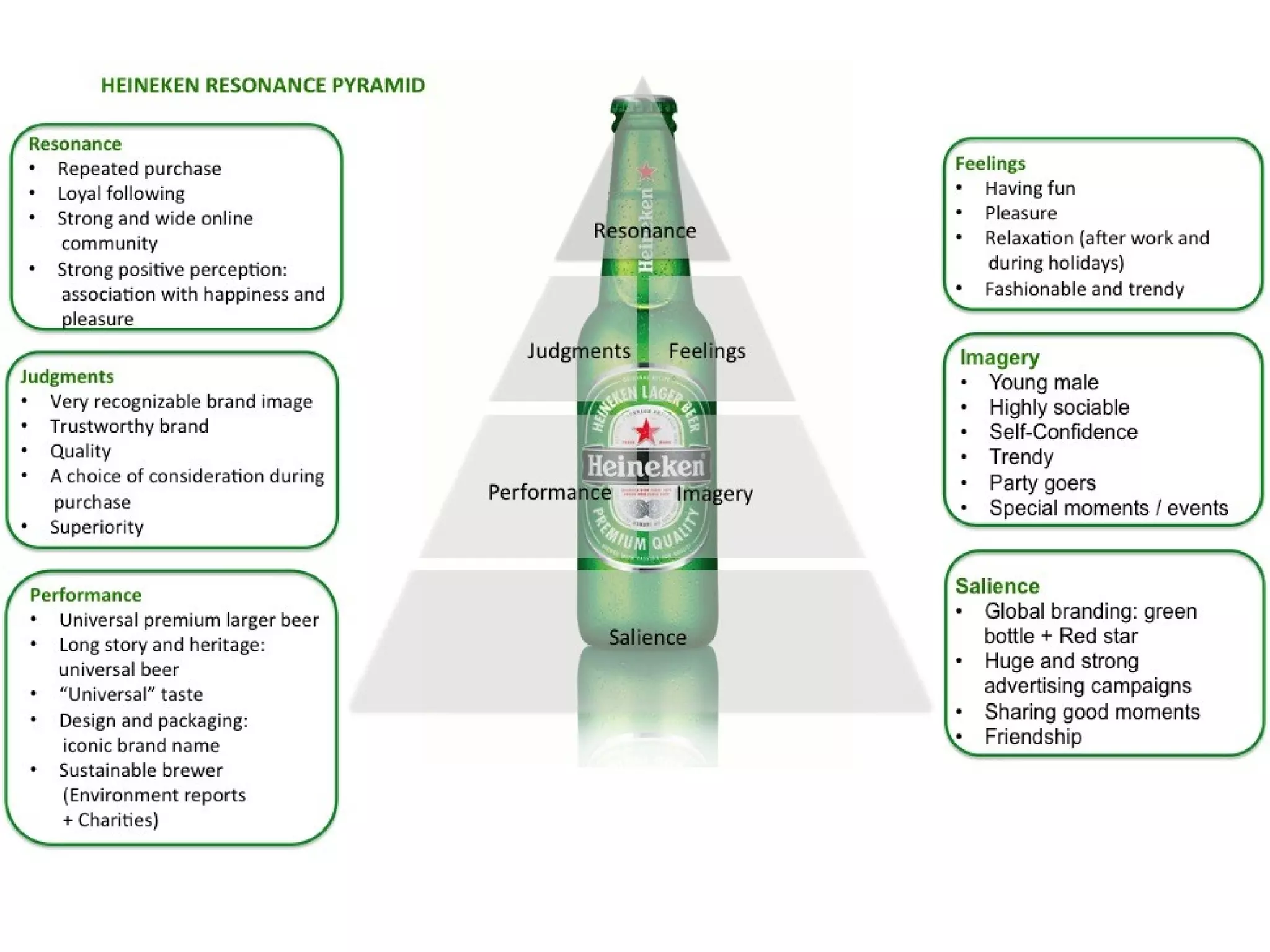
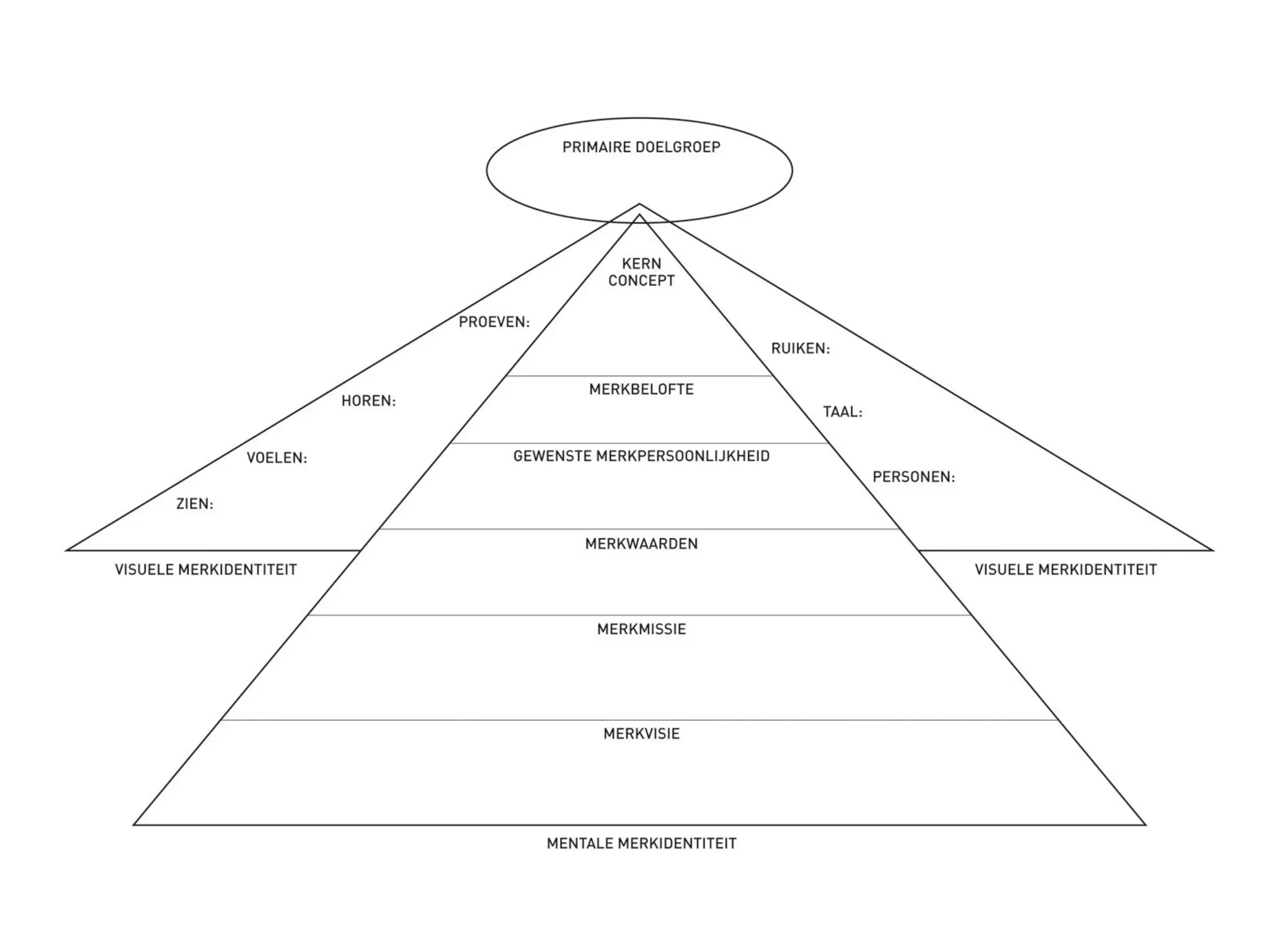
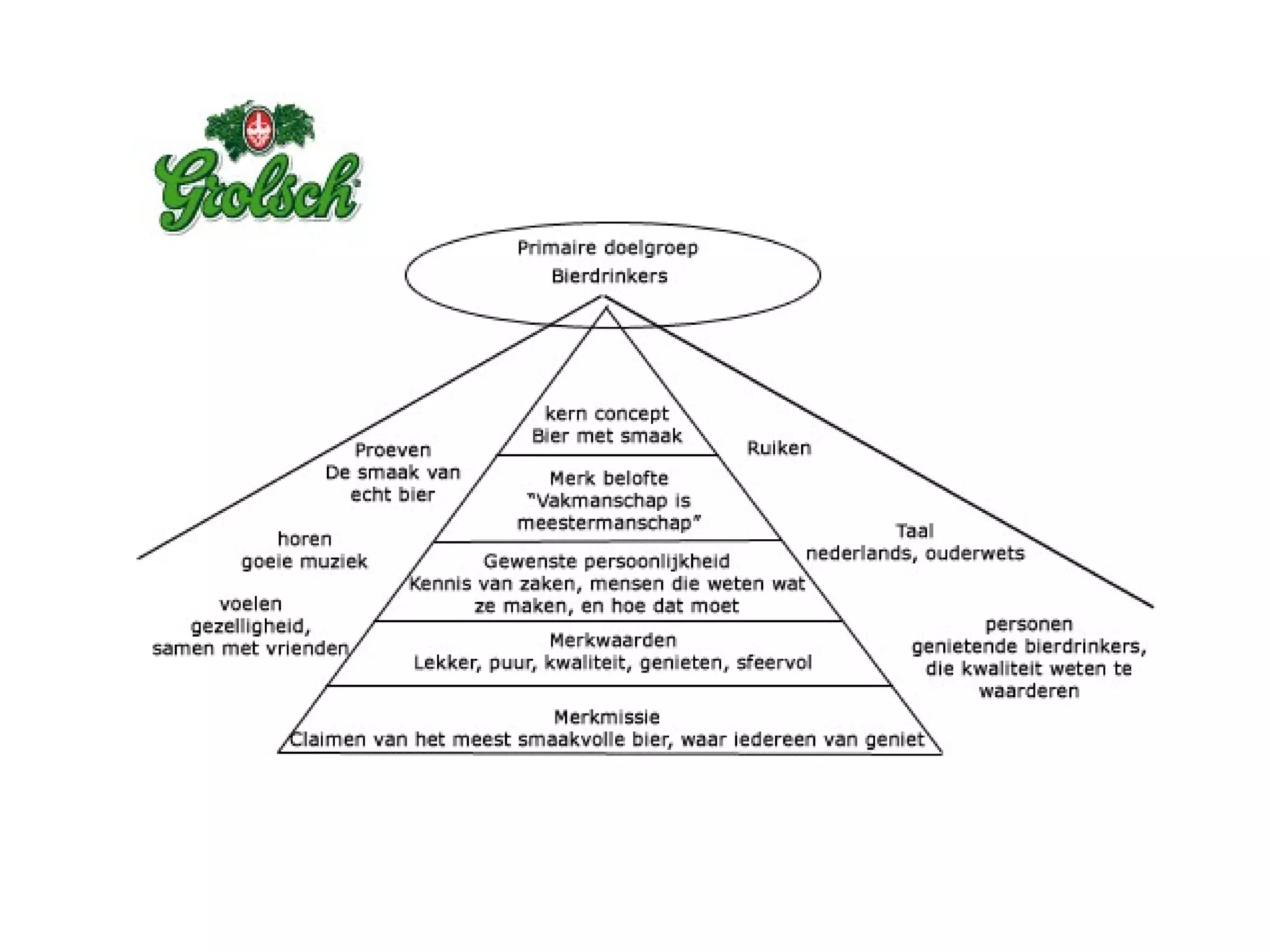
- Sessions explore strategic brand management processes and frameworks, including customer-based brand equity and Keller's brand resonance pyramid.
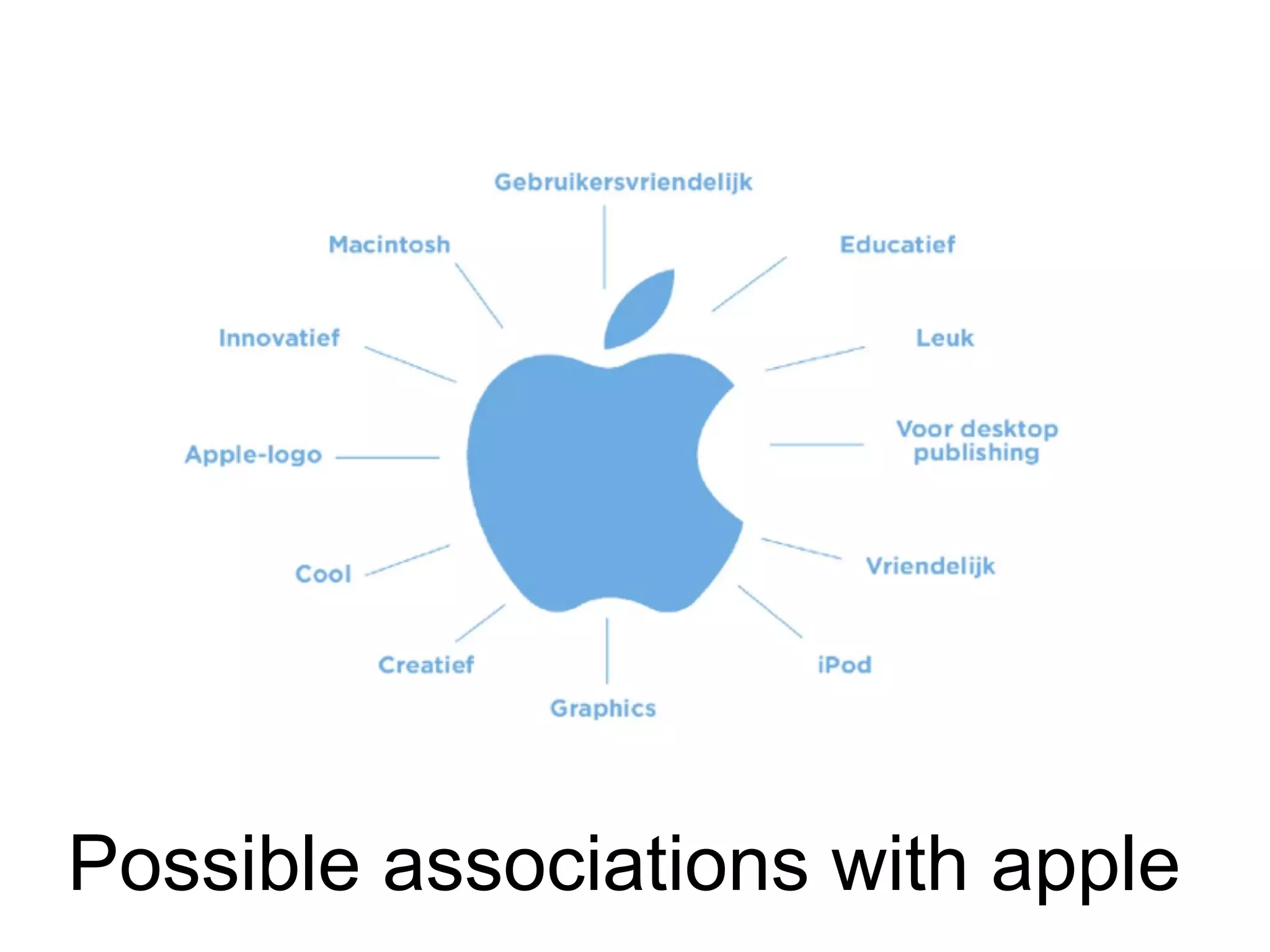
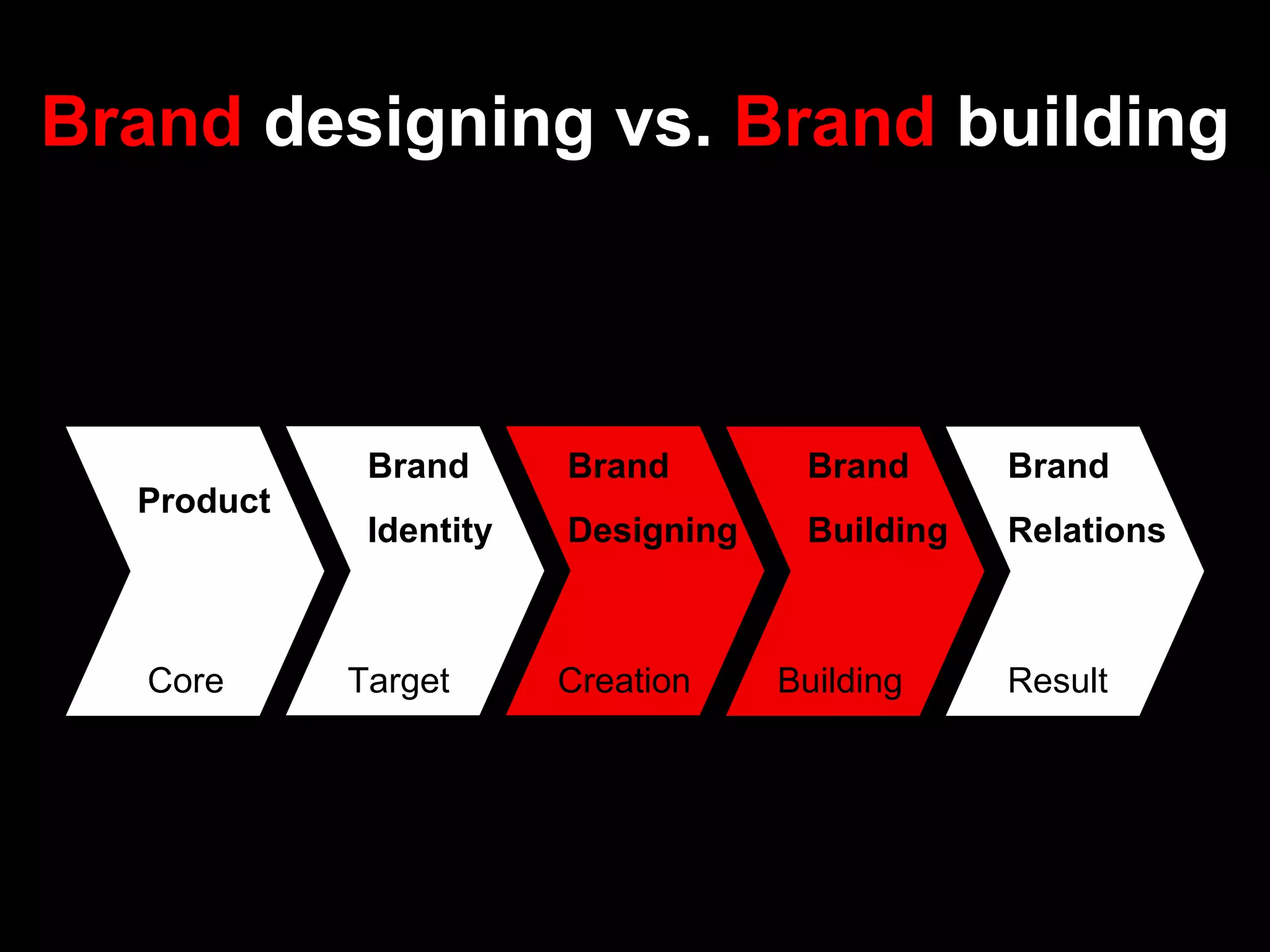
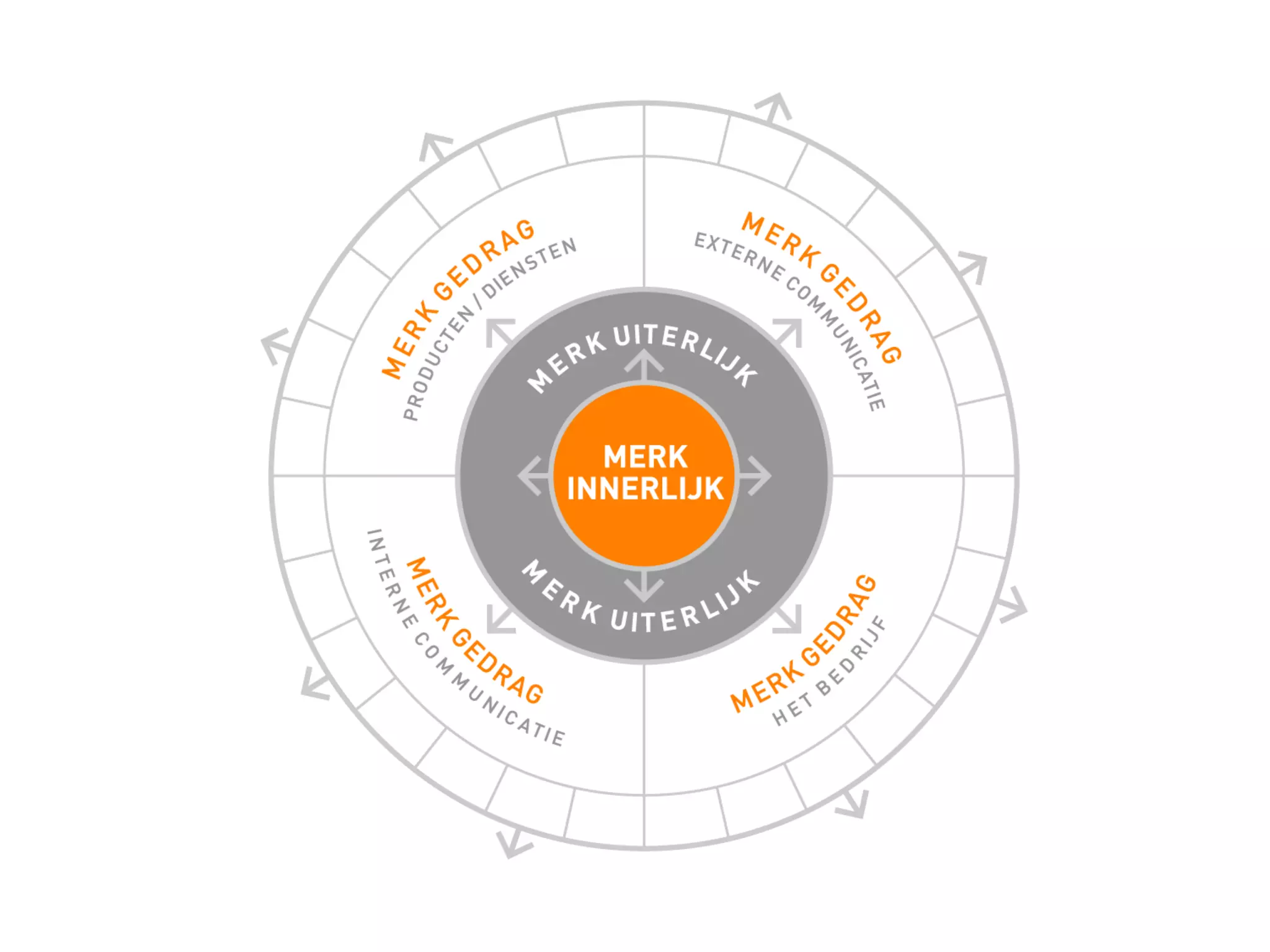
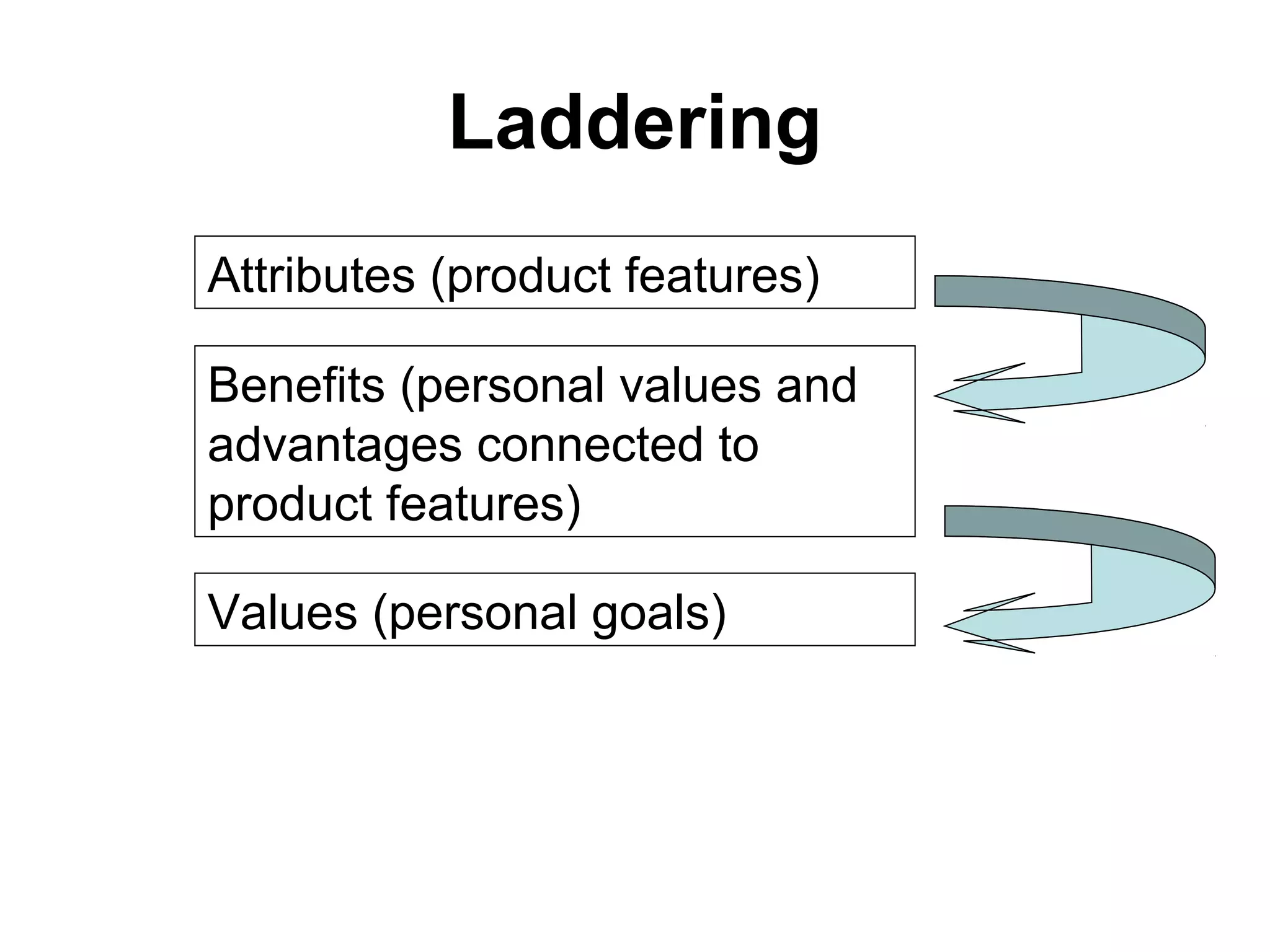
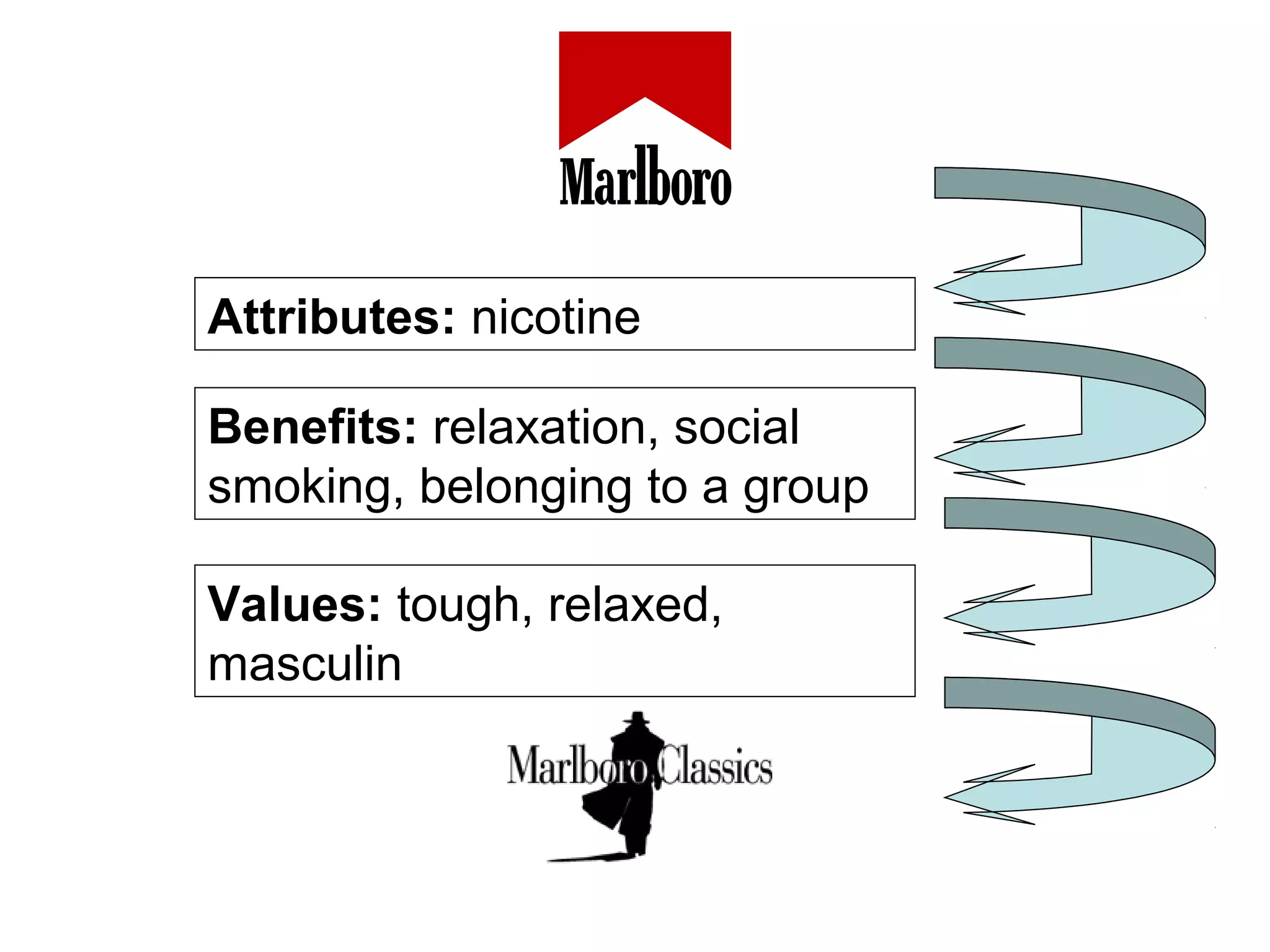
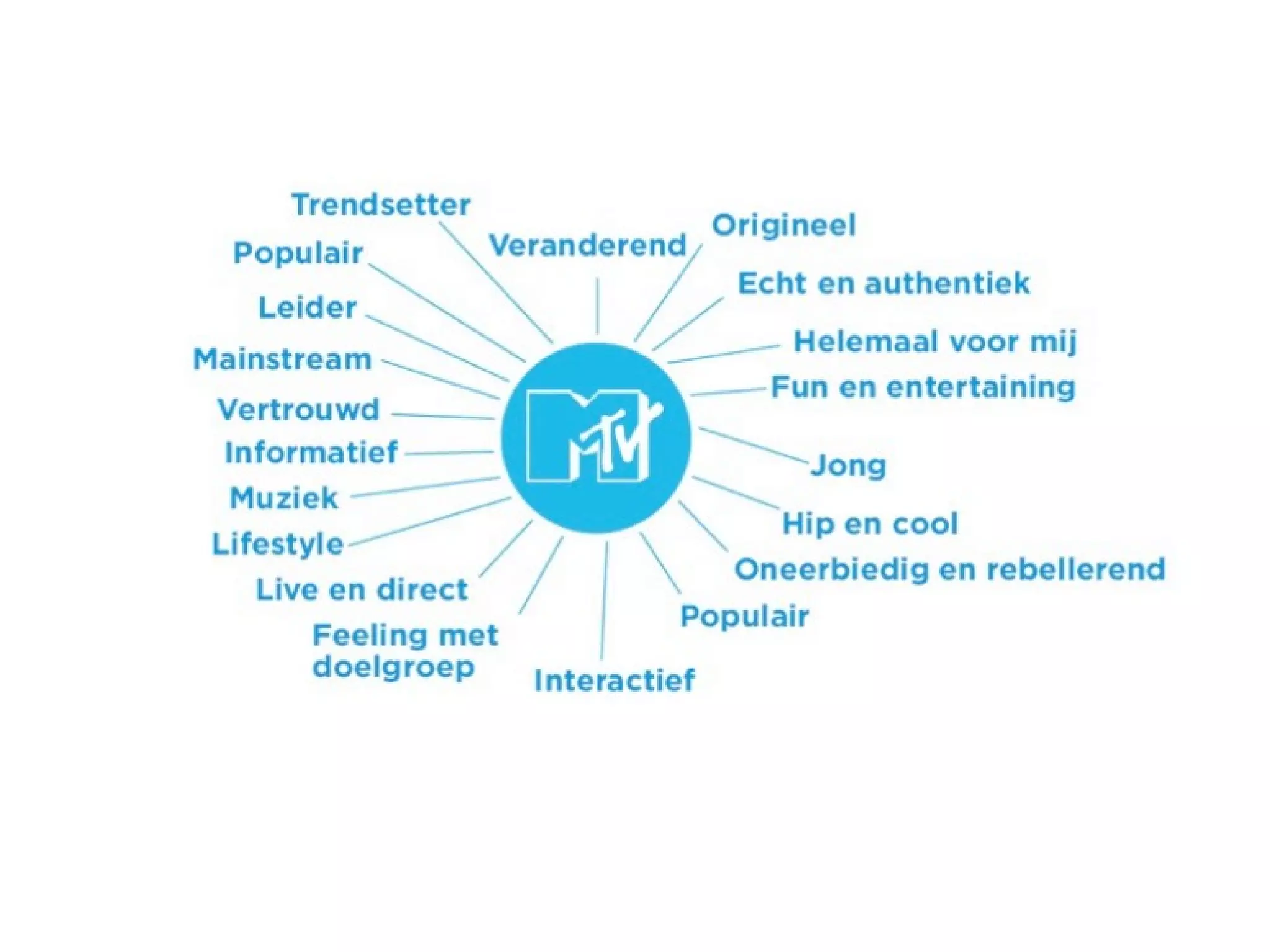
- Brand designing is distinguished from brand building, and the document outlines factors that go into creating a brand's identity and visualizing it, like logo, colors, and language.
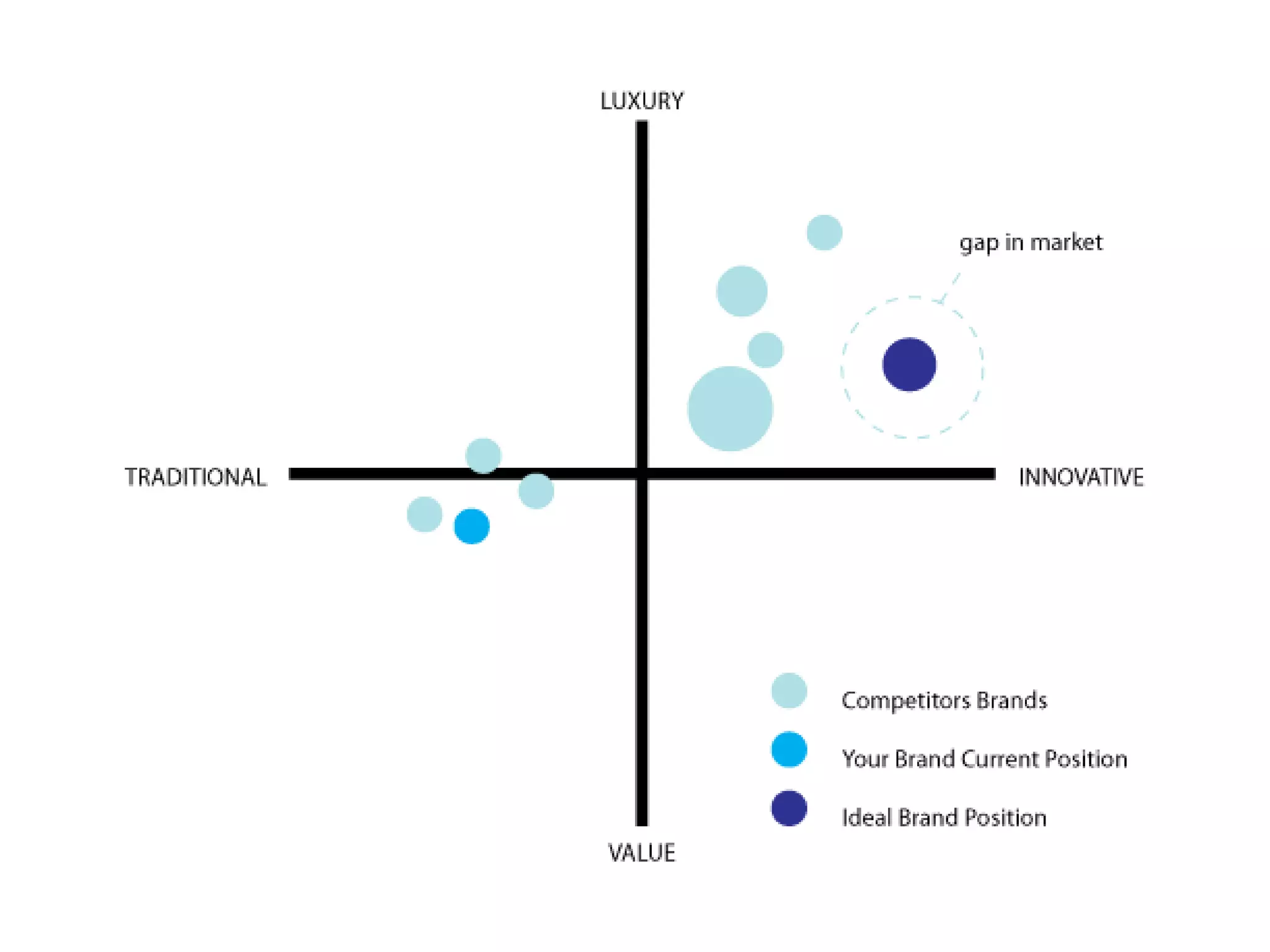
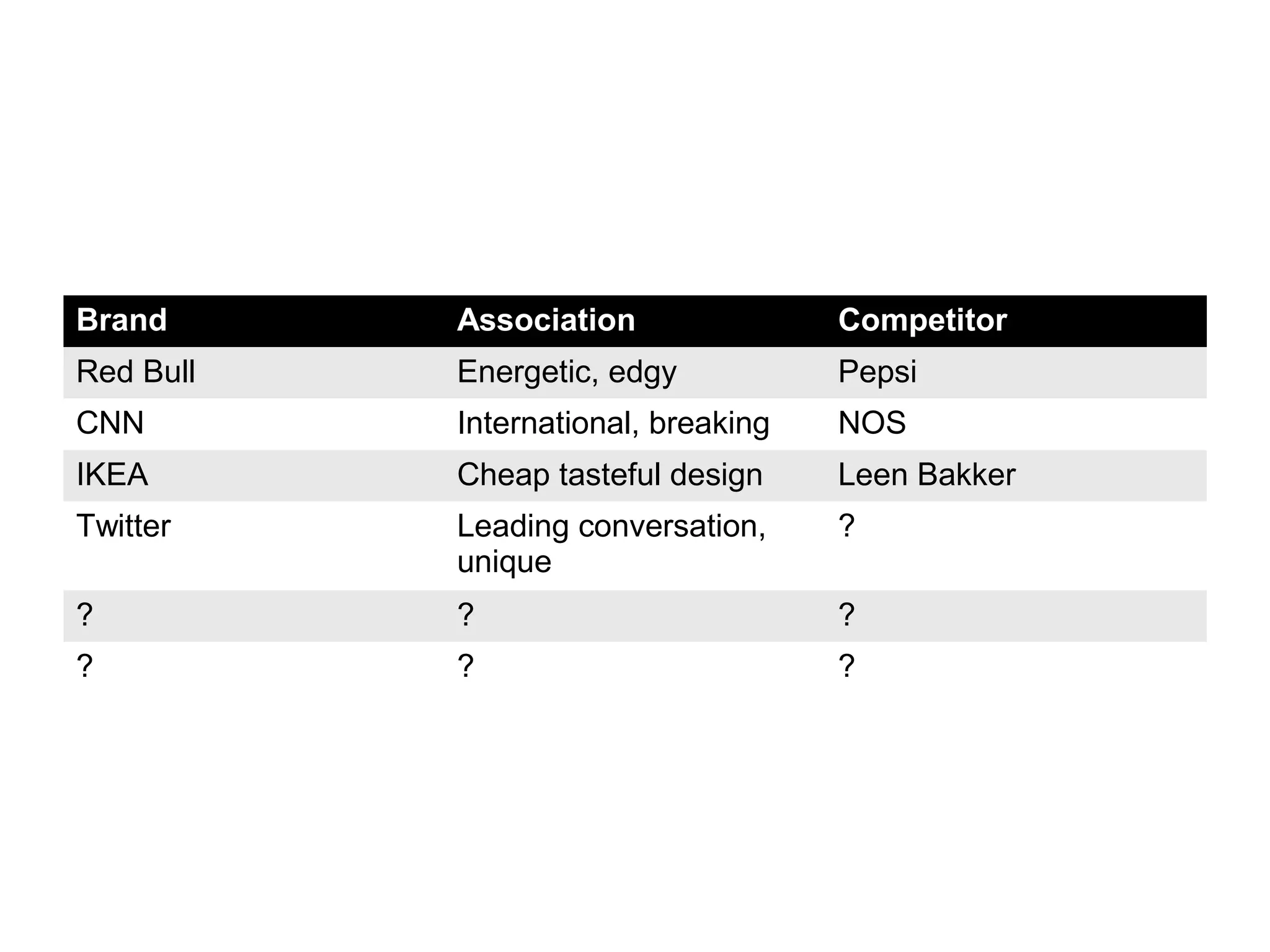
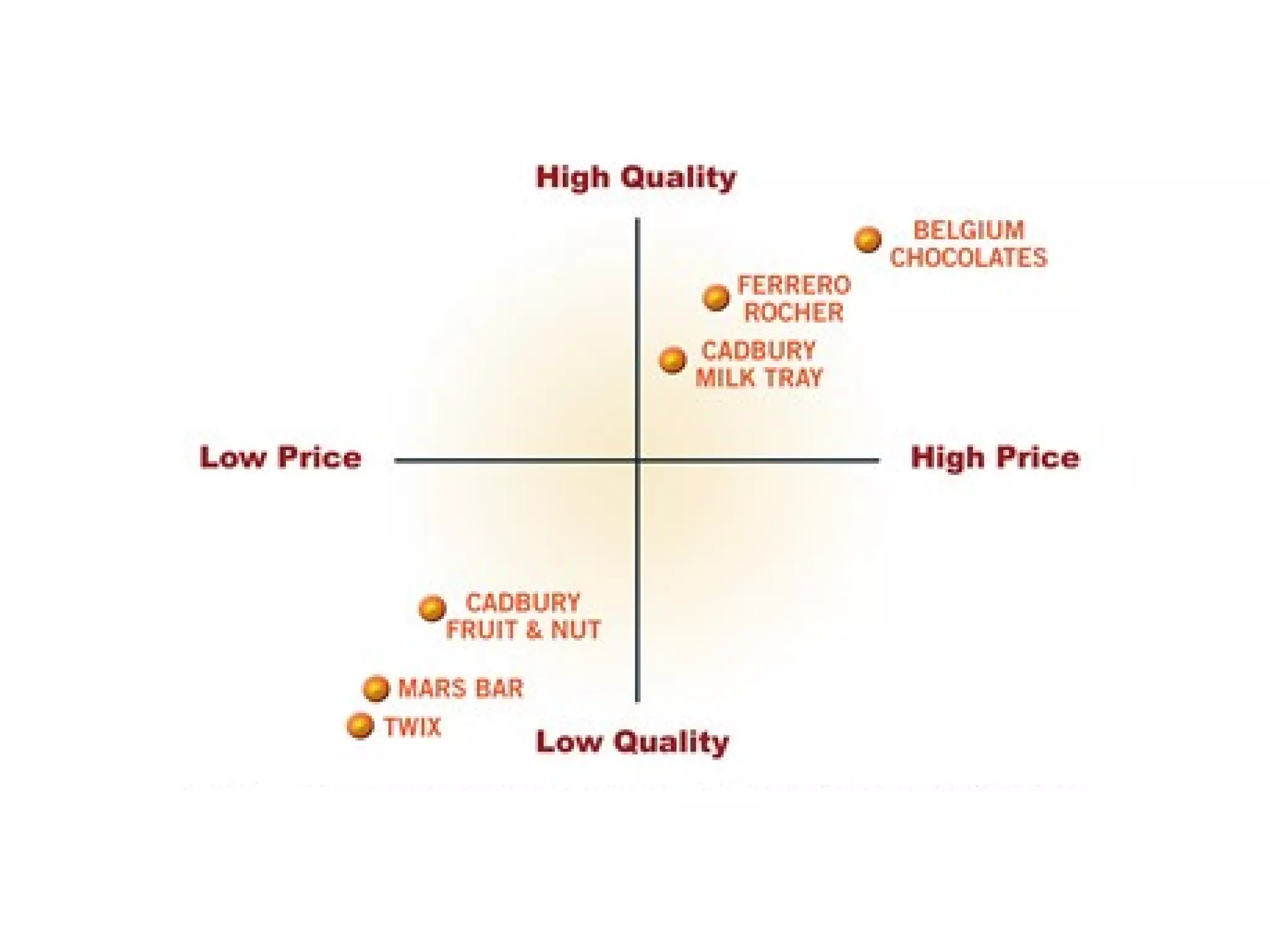
- Brand positioning and repositioning are discussed in the context of points of parity, points of difference, and ensuring differences are relevant, distinctive, credible and communicable