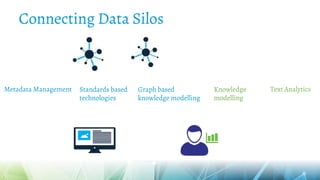
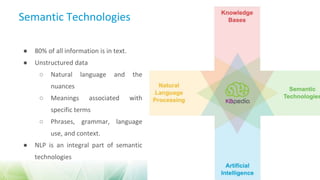
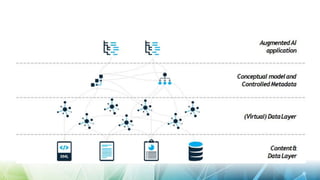
The document discusses semantic web technologies for business and industry. It covers topics like knowledge graphs, linked data, semantic text mining, semantic data integration, and the semantic web architecture. The overall goal is to explain how semantic technologies can help businesses and industries address challenges in areas such as e-commerce, media publishing, and knowledge discovery by better managing digital assets and connecting data silos.