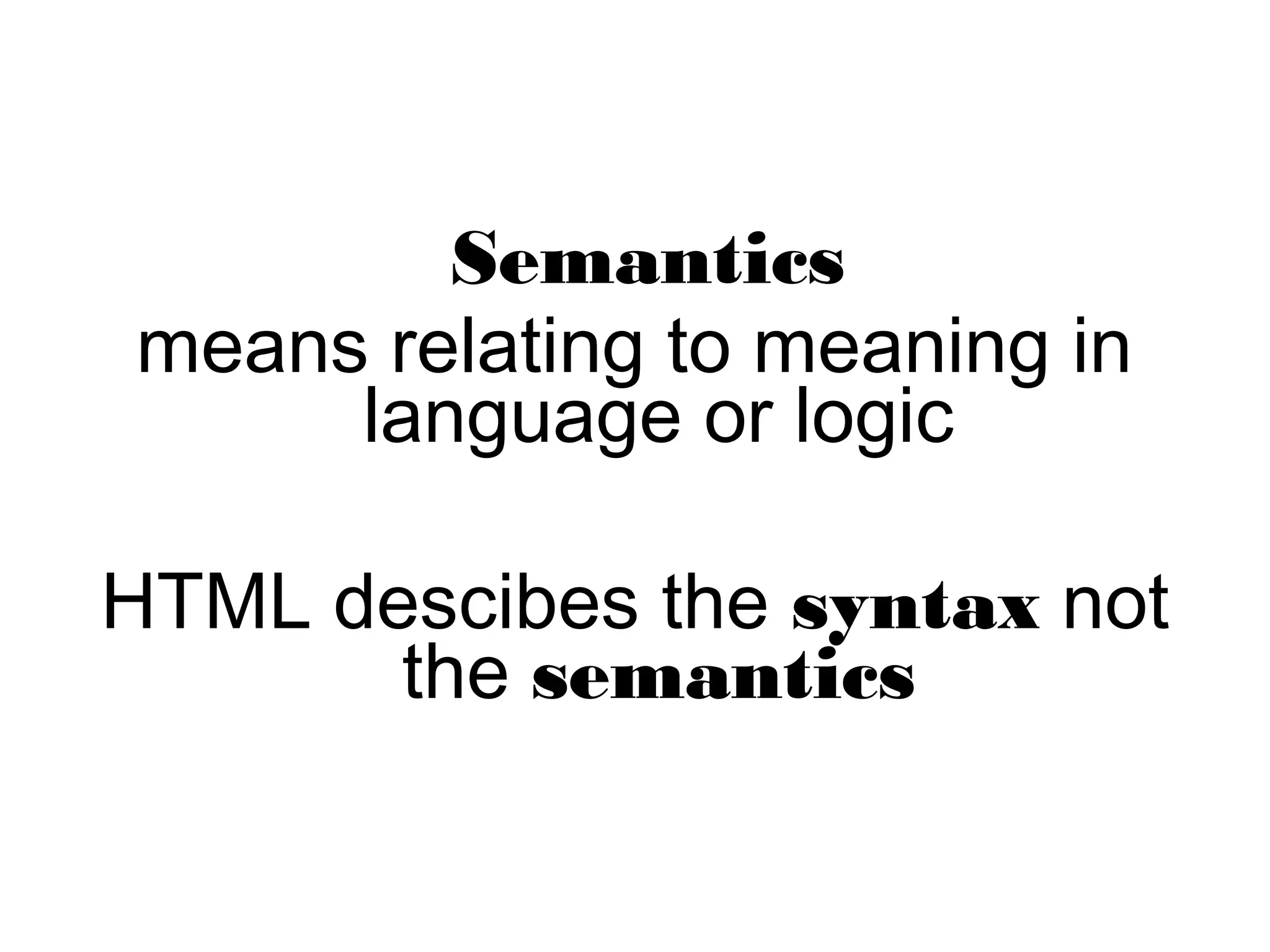
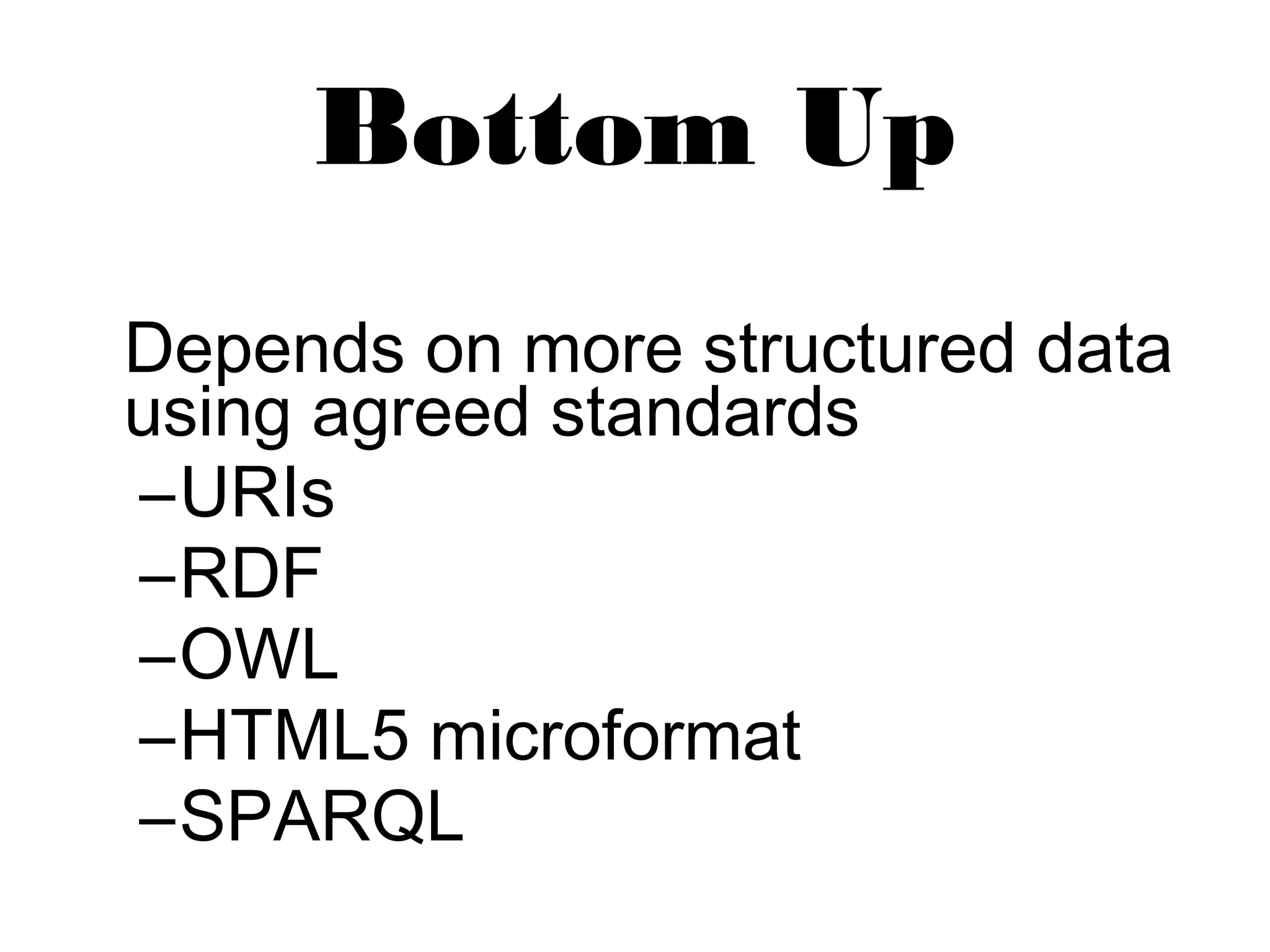
The document discusses the evolution of the web from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0, focusing on the semantic web as an extension that allows for better data sharing and understanding between machines and humans. It highlights key developments, such as the foundation of schema.org and the need for structured data formats. The advantages include improved data quality and collaboration, but challenges like vastness and inconsistency remain.