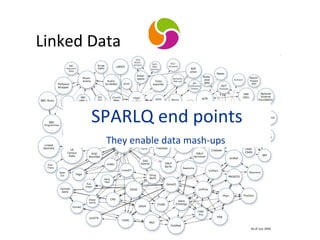
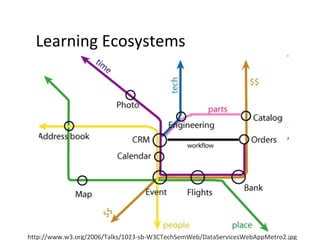
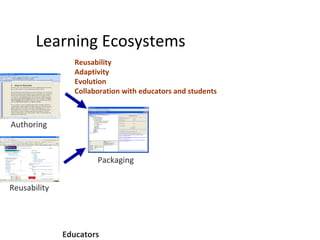
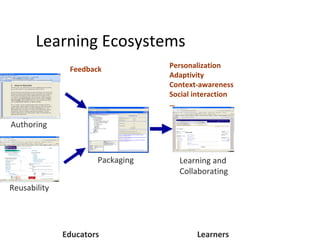
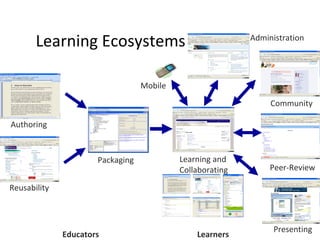
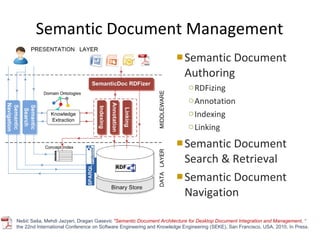
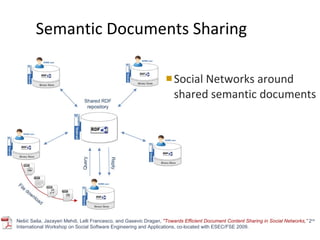
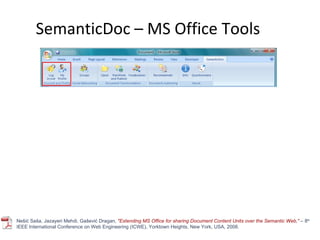
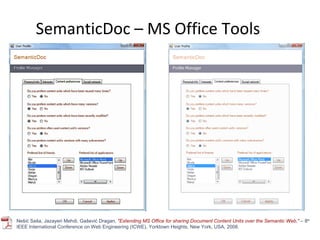
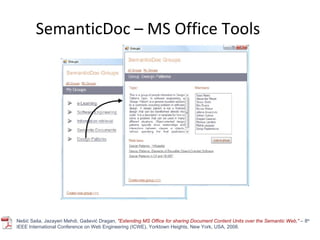
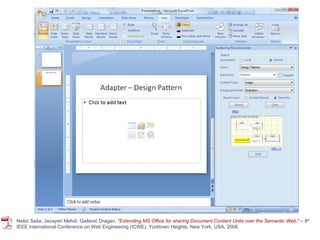
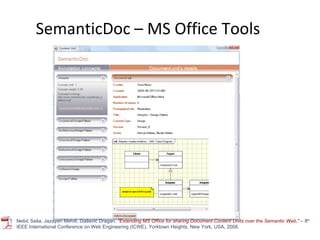
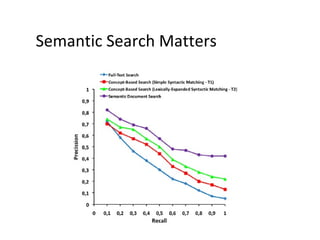
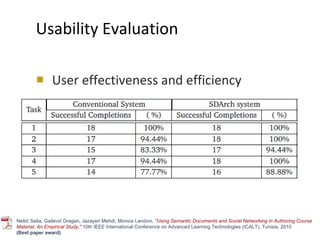
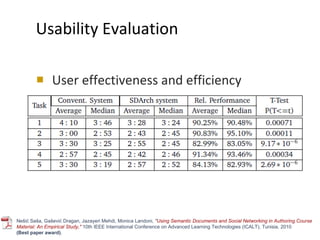
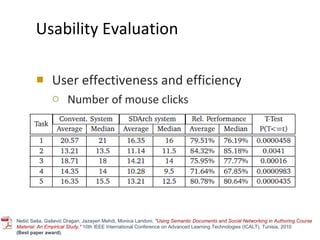
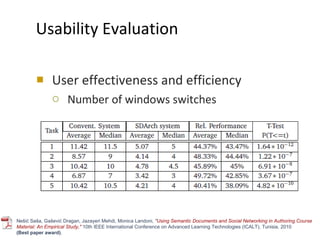
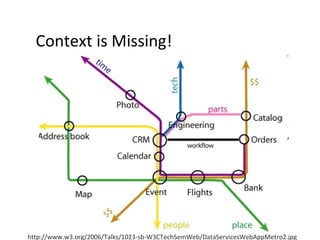
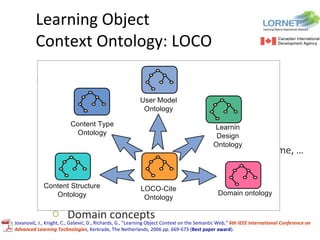
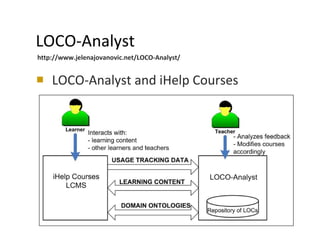
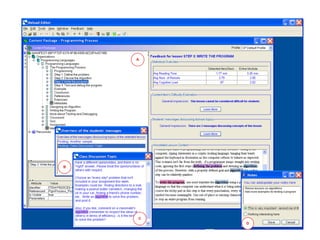
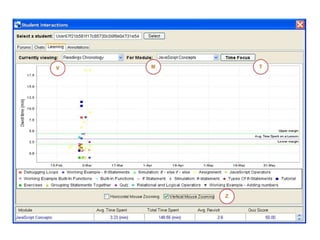
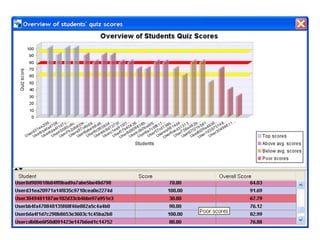
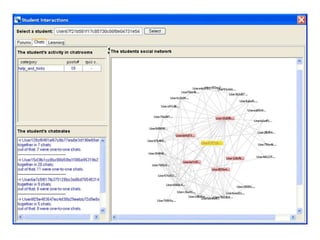
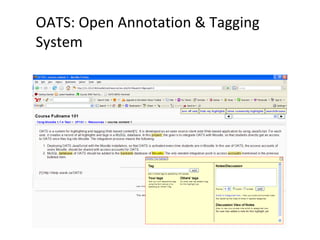
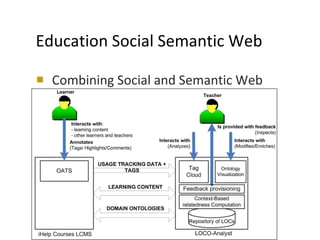
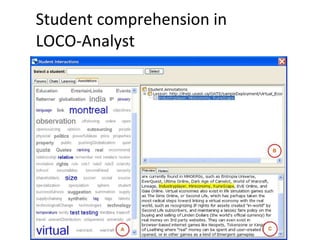
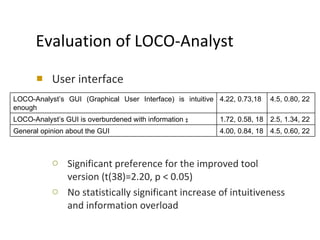
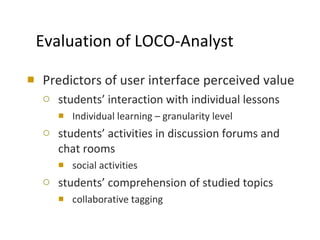
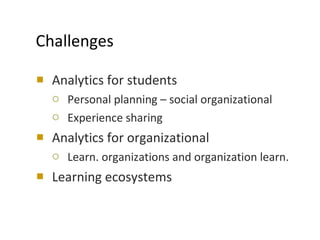
The document discusses the integration of semantic technologies in learning environments, highlighting the potential of the semantic web to enhance data sharing and collaboration in educational contexts. It covers topics such as authoring and reusability of learning content, the importance of learning ecosystems, and the challenges in developing effective ontologies. Additionally, it presents various projects and studies related to semantic document management and user interactions within these systems.