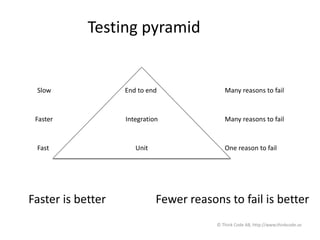
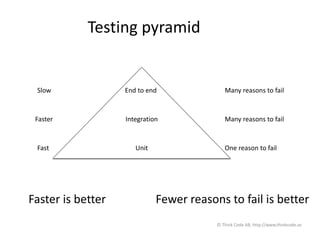
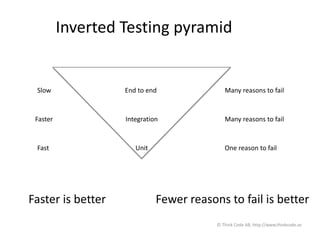
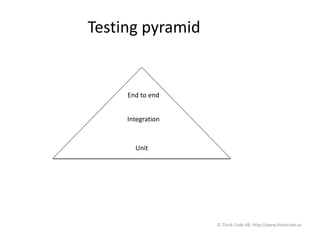
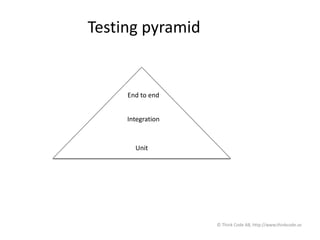
The document discusses Selenium WebDriver, a tool for automating tests of web applications. It provides an introduction to testing web applications, including manual vs automated testing. Selenium WebDriver is introduced as a browser automation tool that supports many programming languages like Java. Page object design pattern is recommended for organizing Selenium tests, with each page getting its own class. The document emphasizes testing at different levels, from unit to integration to end-to-end tests, using the testing pyramid as a guide.