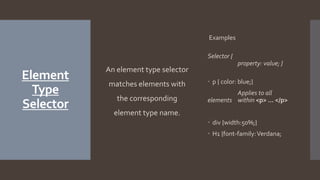
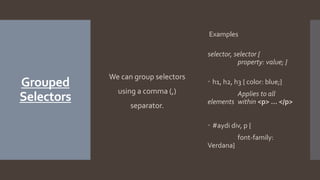
The document covers various types of CSS selectors including element type, grouped, descendant, id, class, universal, and pseudo-class selectors. It provides examples and syntax for each type, illustrating how they apply styles to HTML elements. Additionally, it explains the usage of pseudo-elements like ::first-letter, ::first-line, ::before, and ::after for modified content presentation.