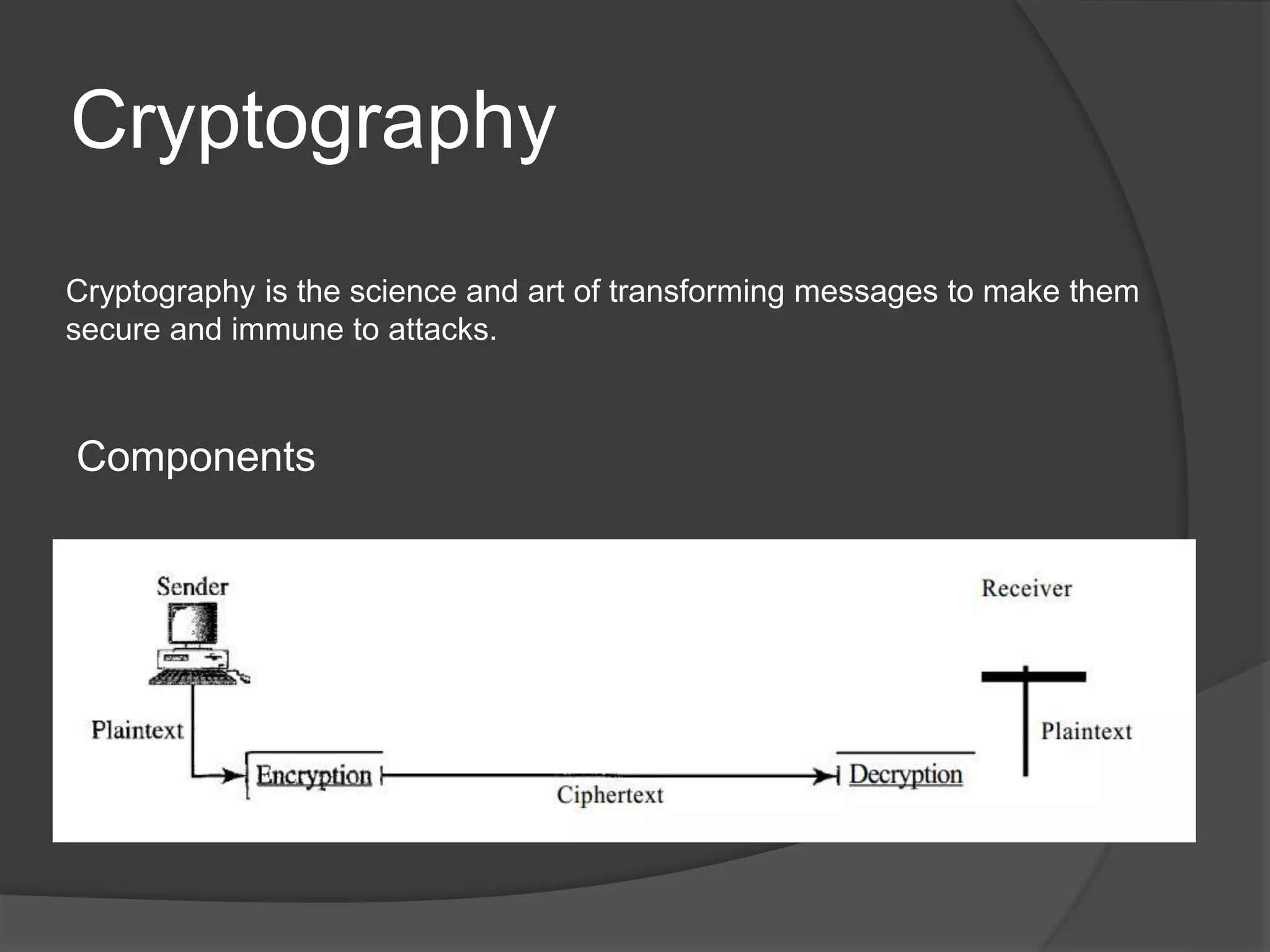
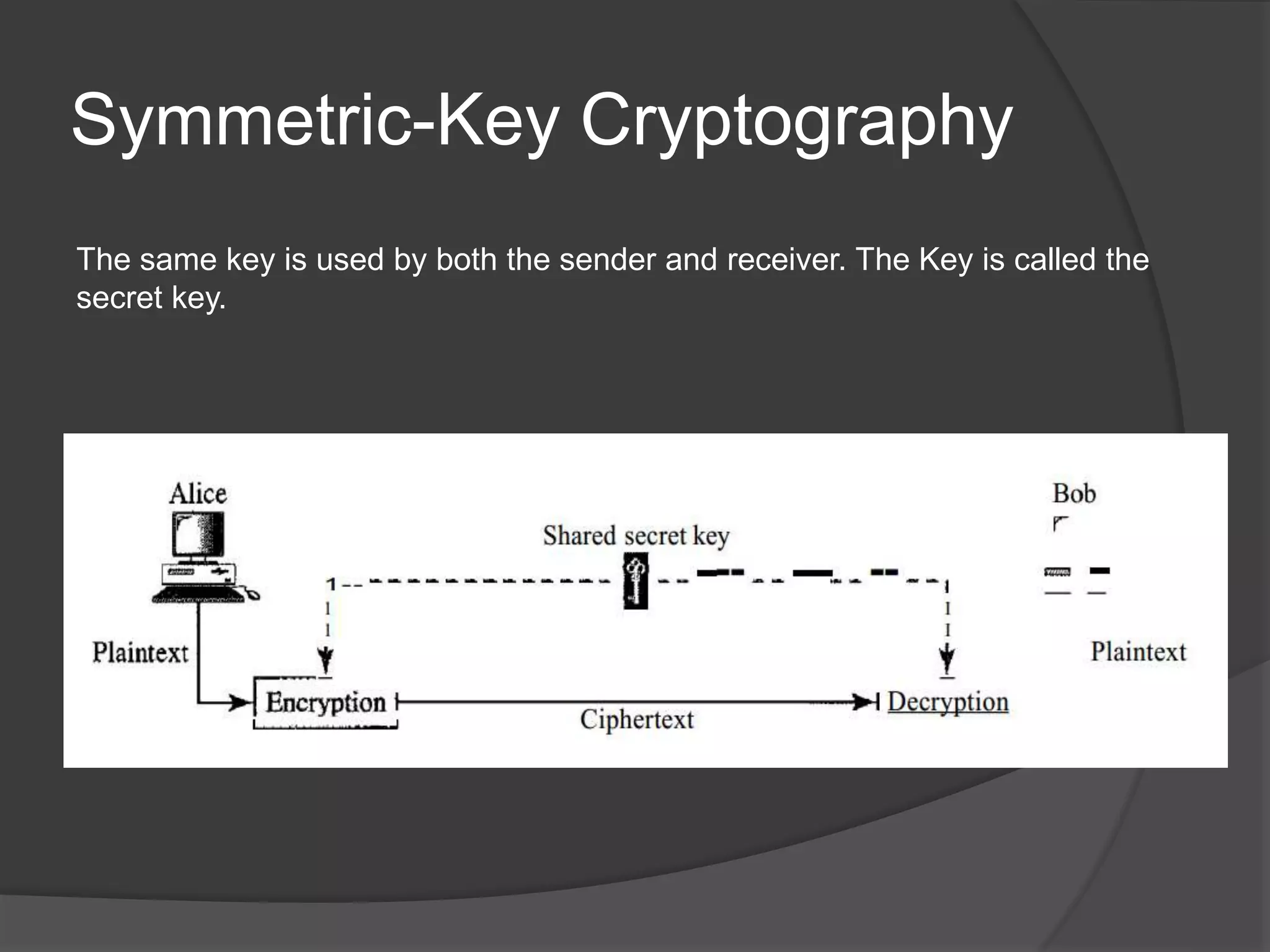
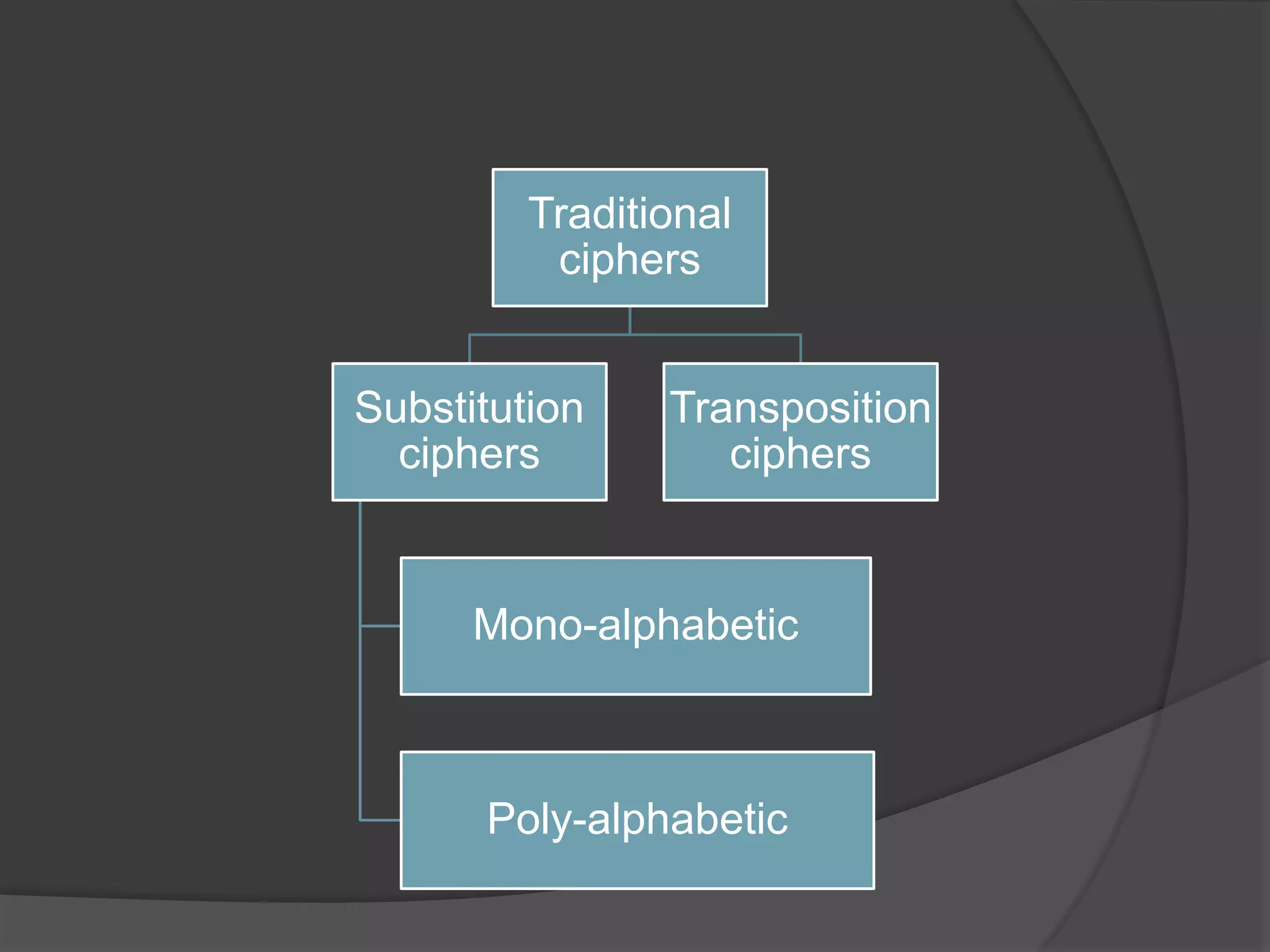
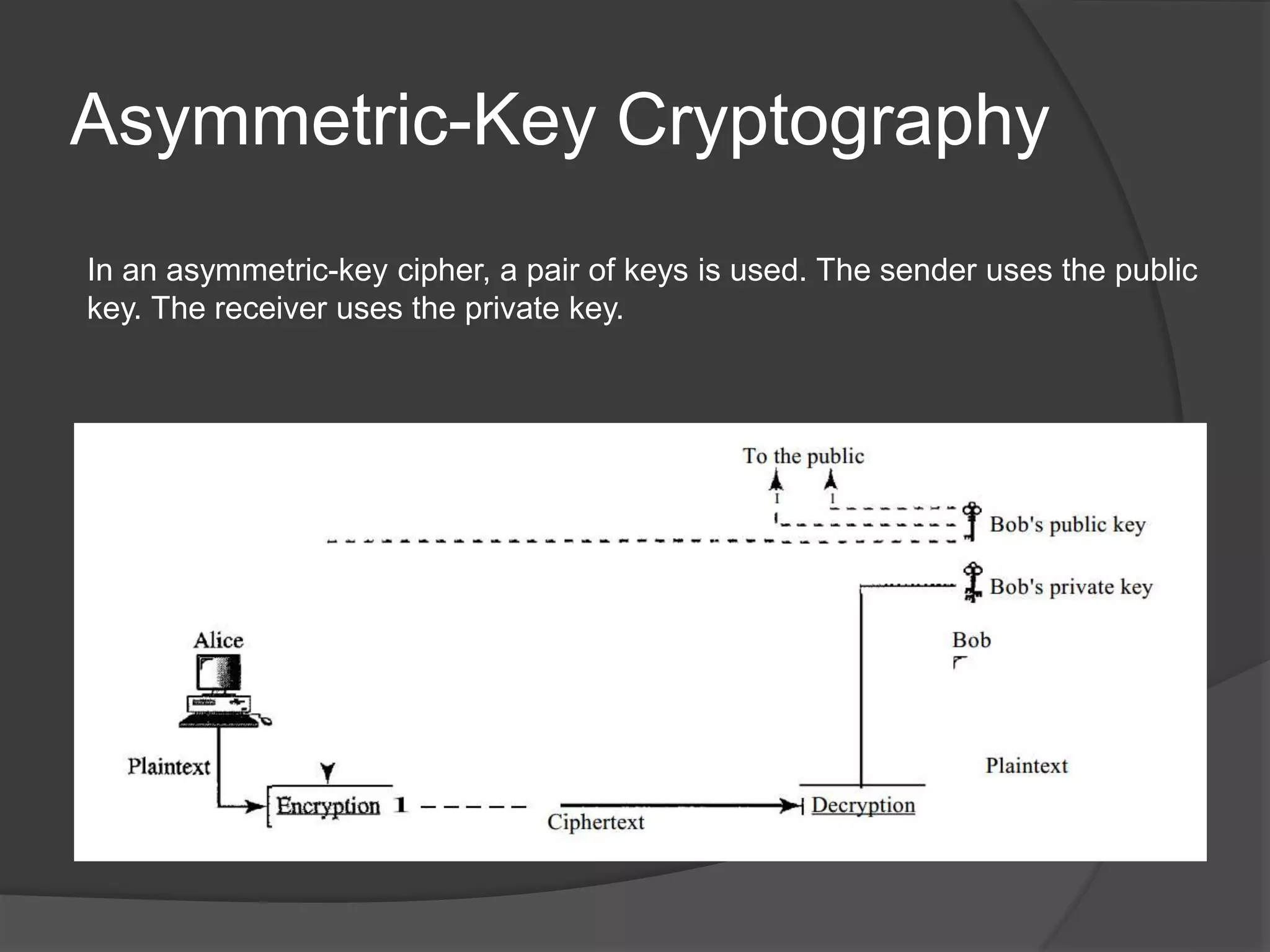
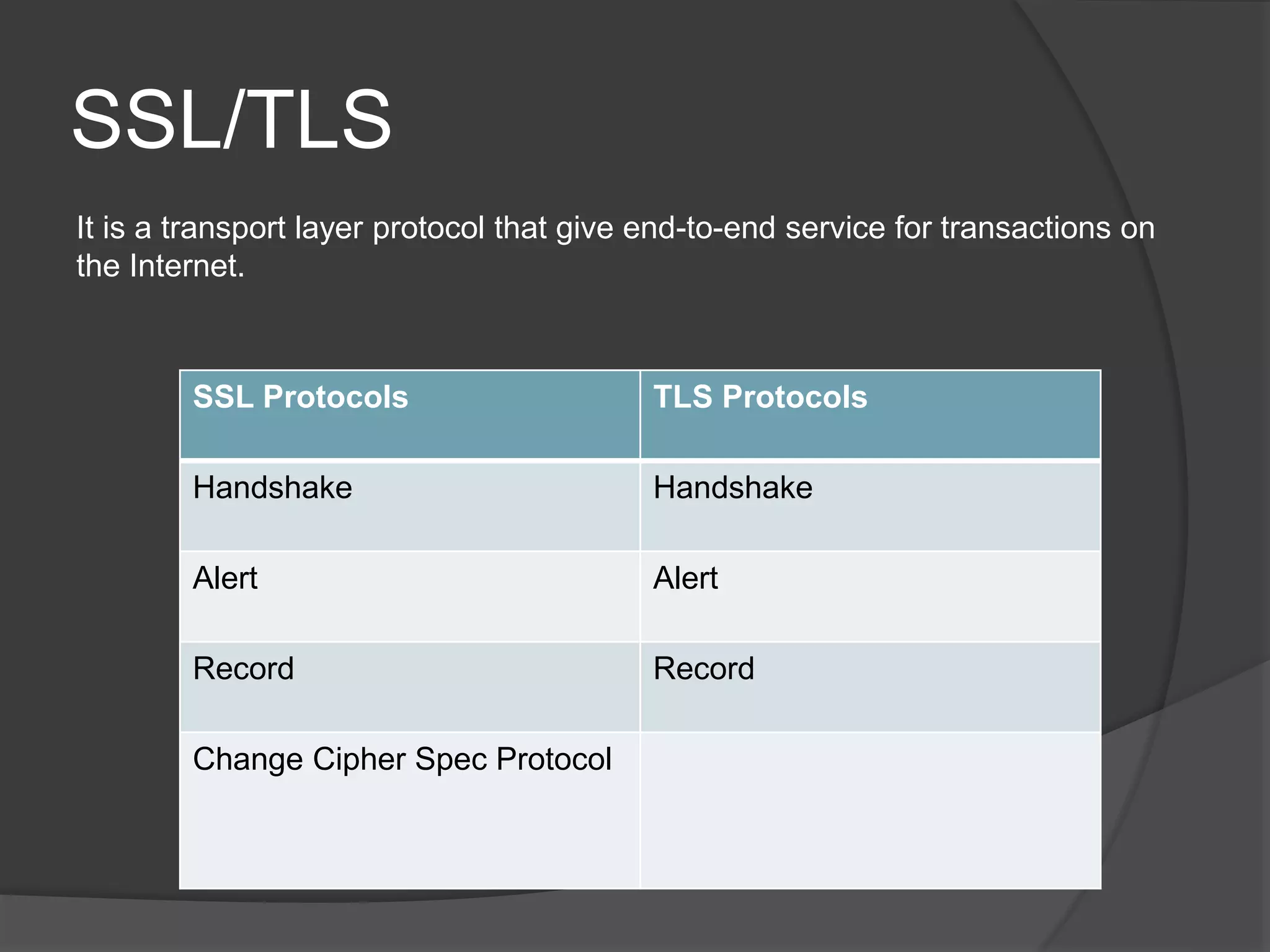
This document discusses cryptography, security services, and security in the internet. It describes symmetric-key cryptography which uses a shared secret key, and asymmetric-key cryptography which uses a public-private key pair. The document outlines five security services: message confidentiality, integrity, authentication, nonrepudiation, and entity authentication. It also discusses protocols for security at the network layer (IPSec), transport layer (SSL/TLS), and application layer (PGP), as well as the use of firewalls to filter network traffic.