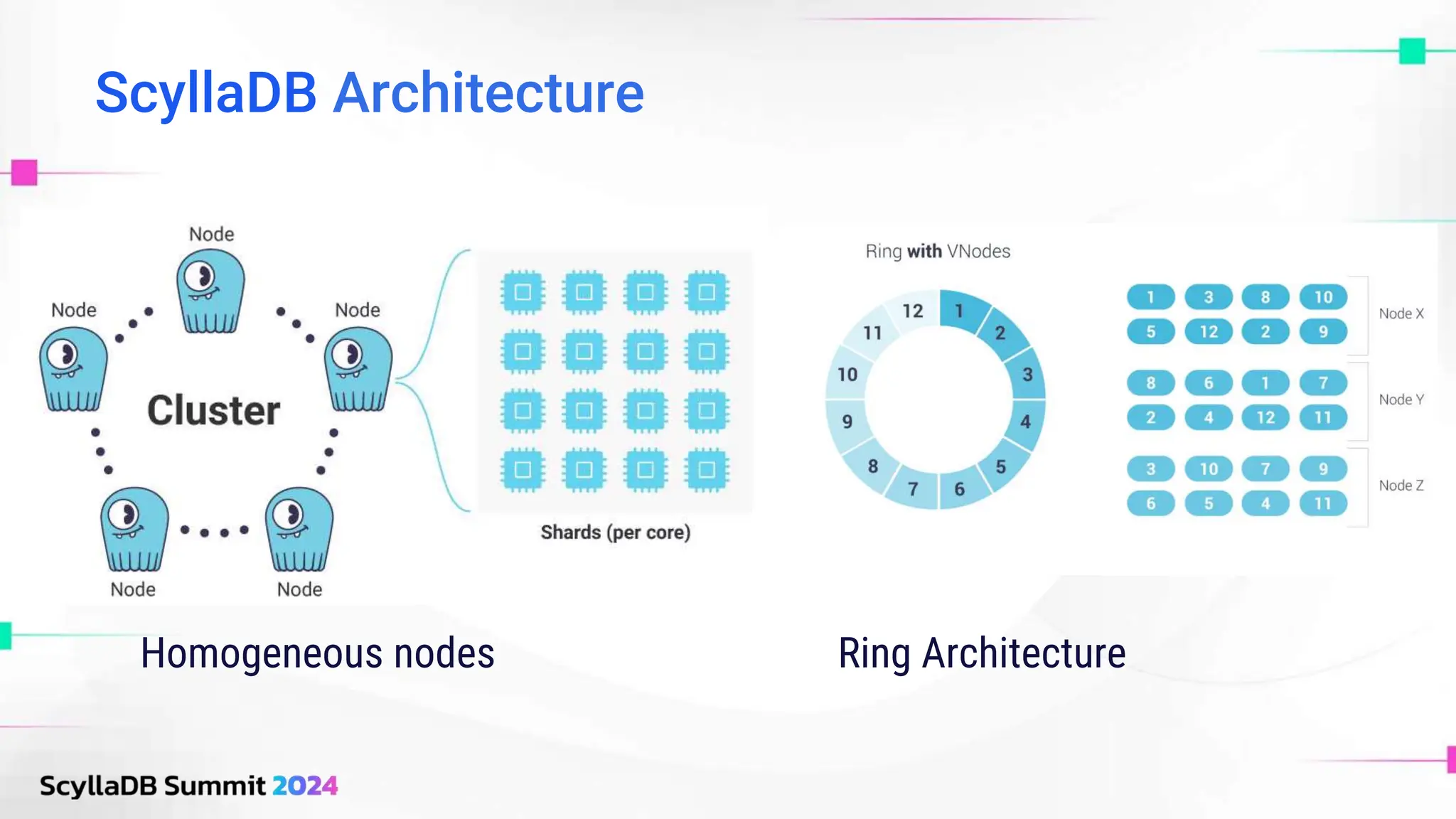
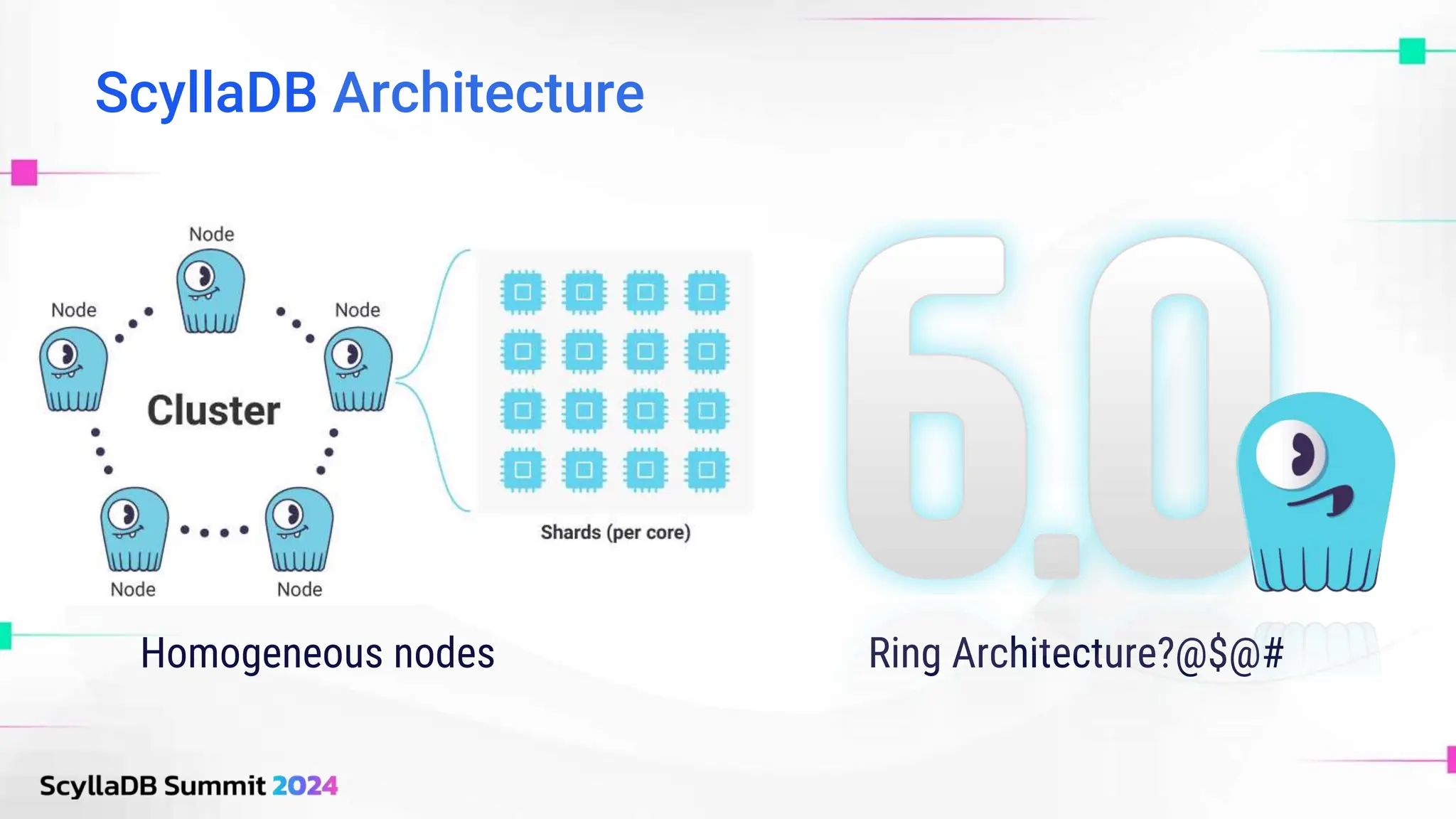
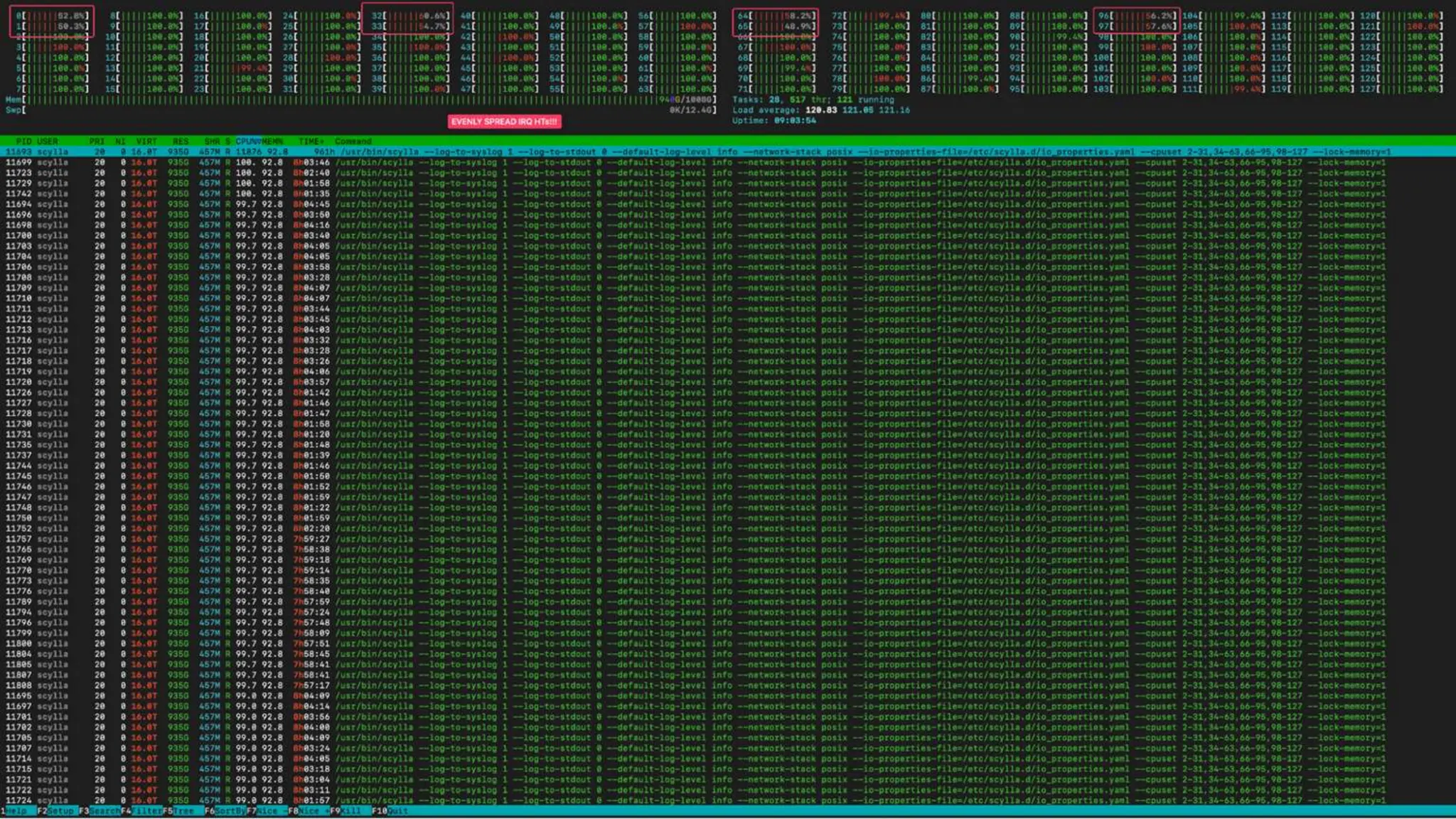
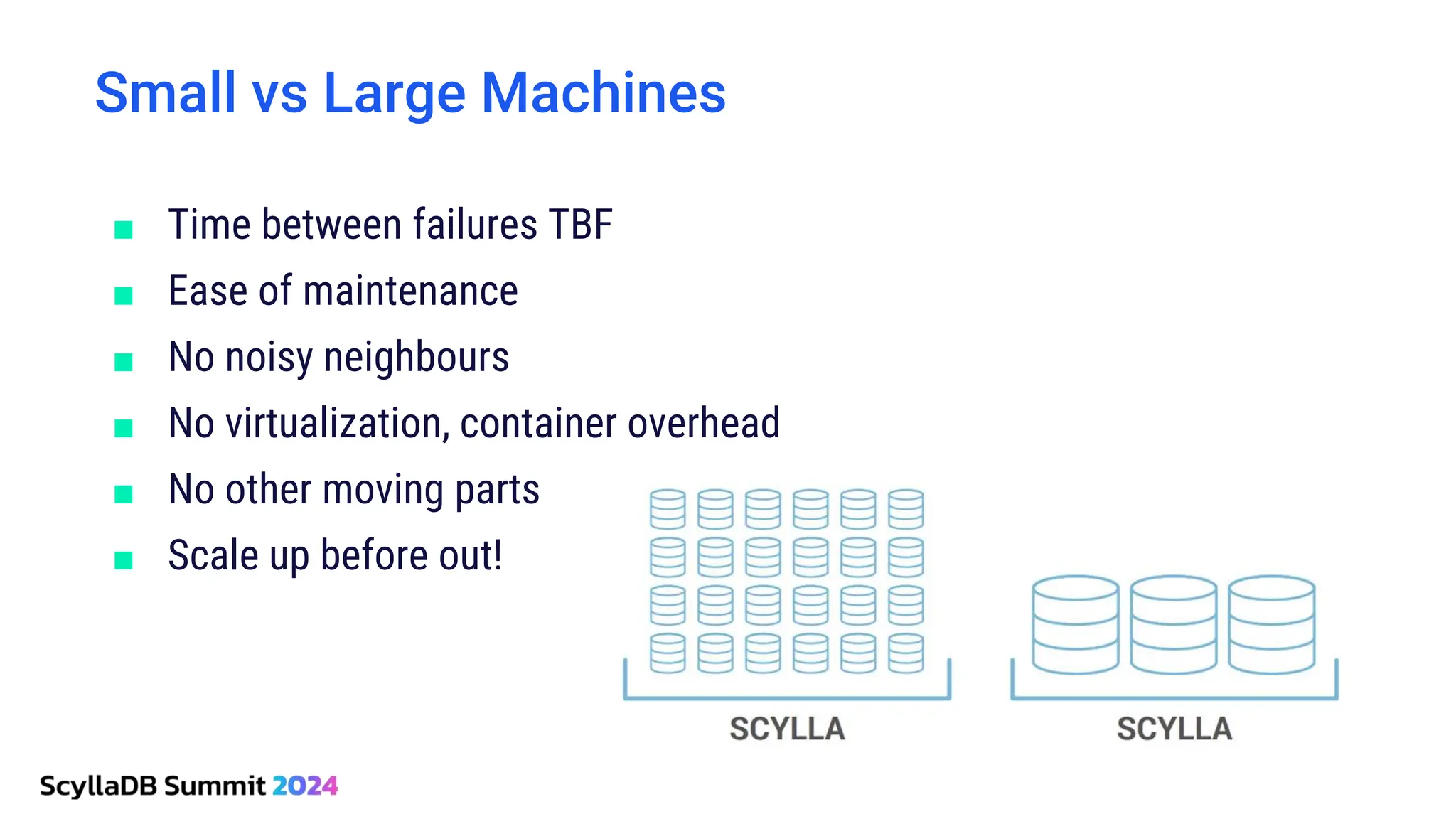
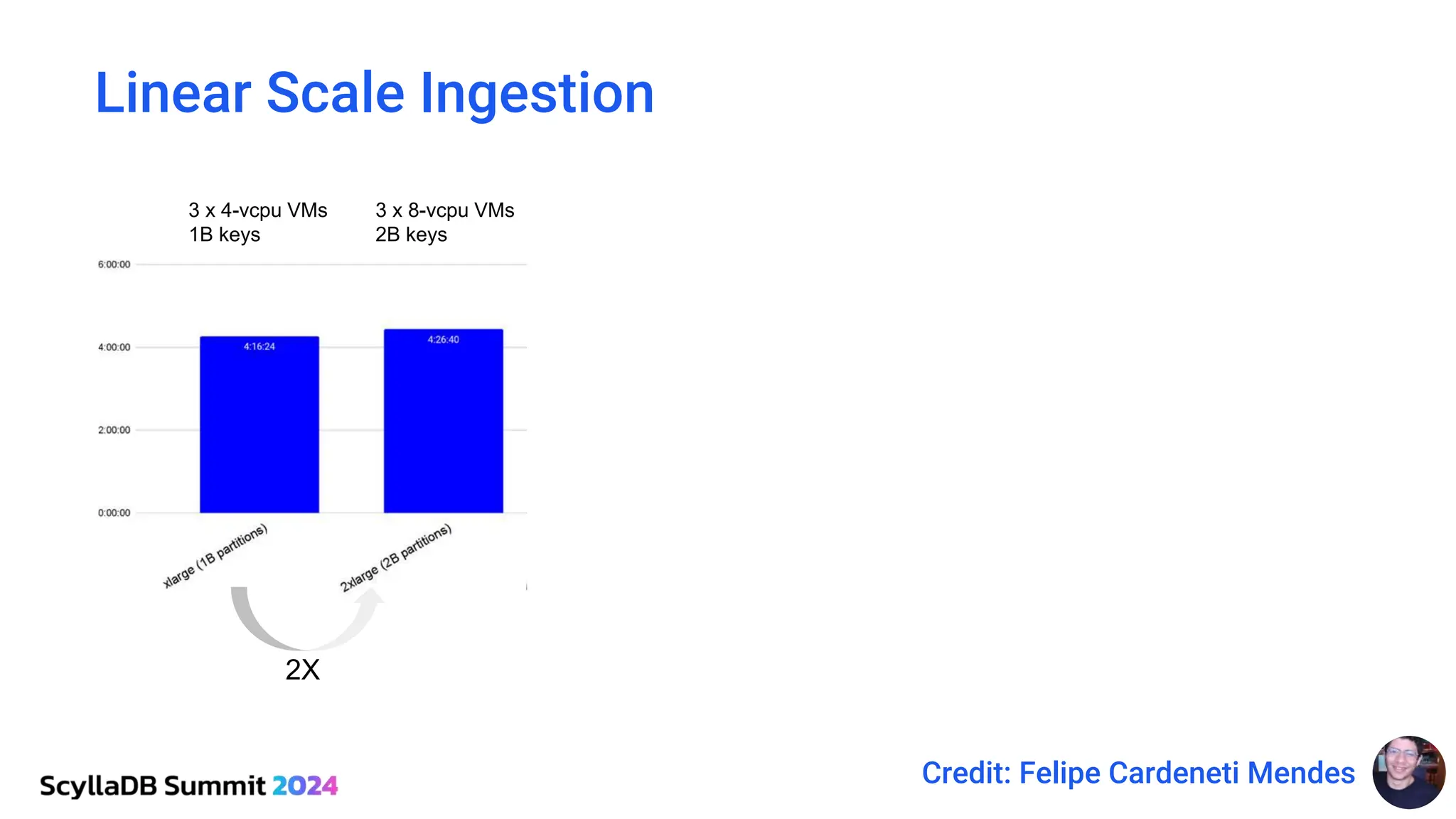
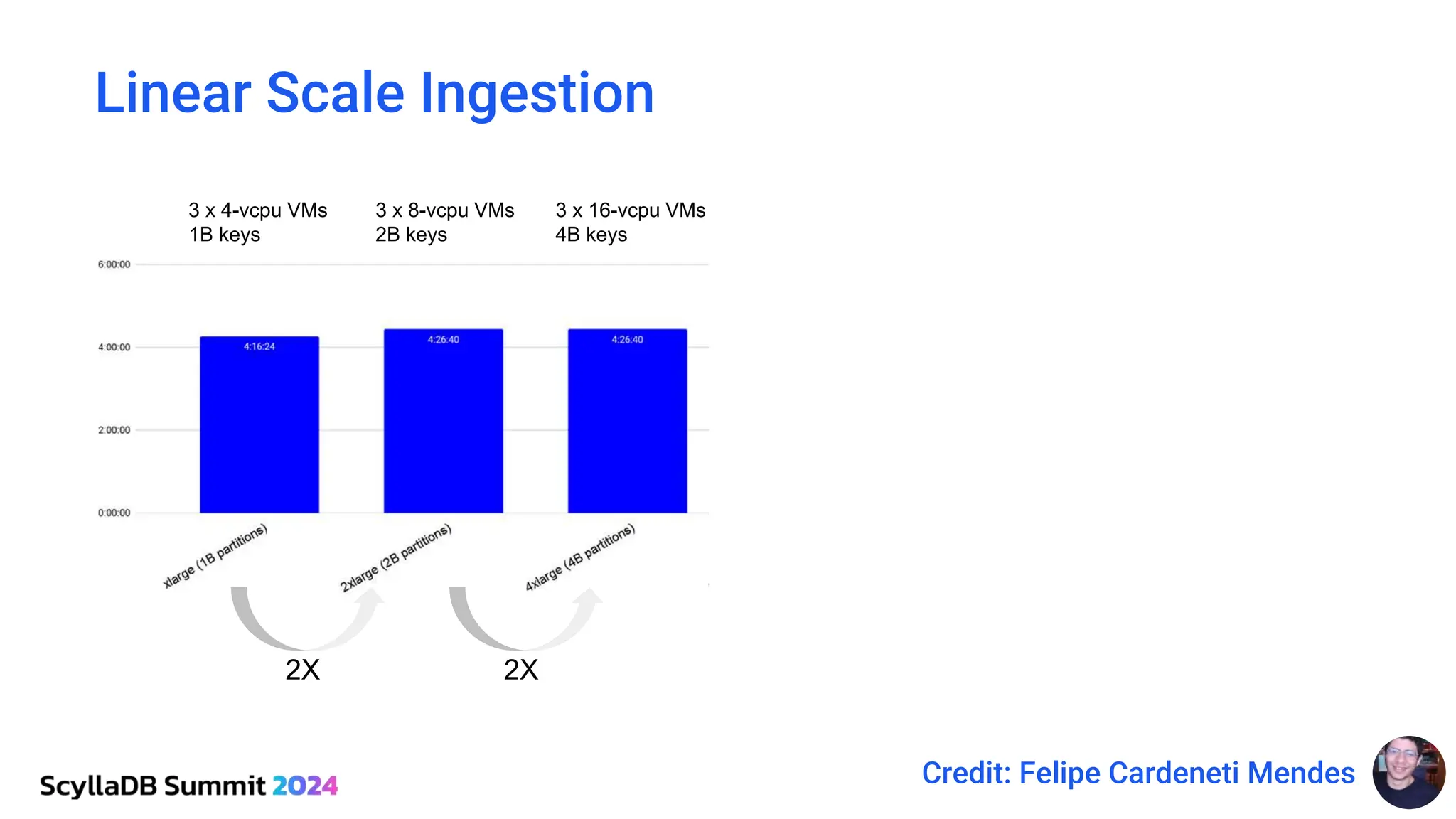
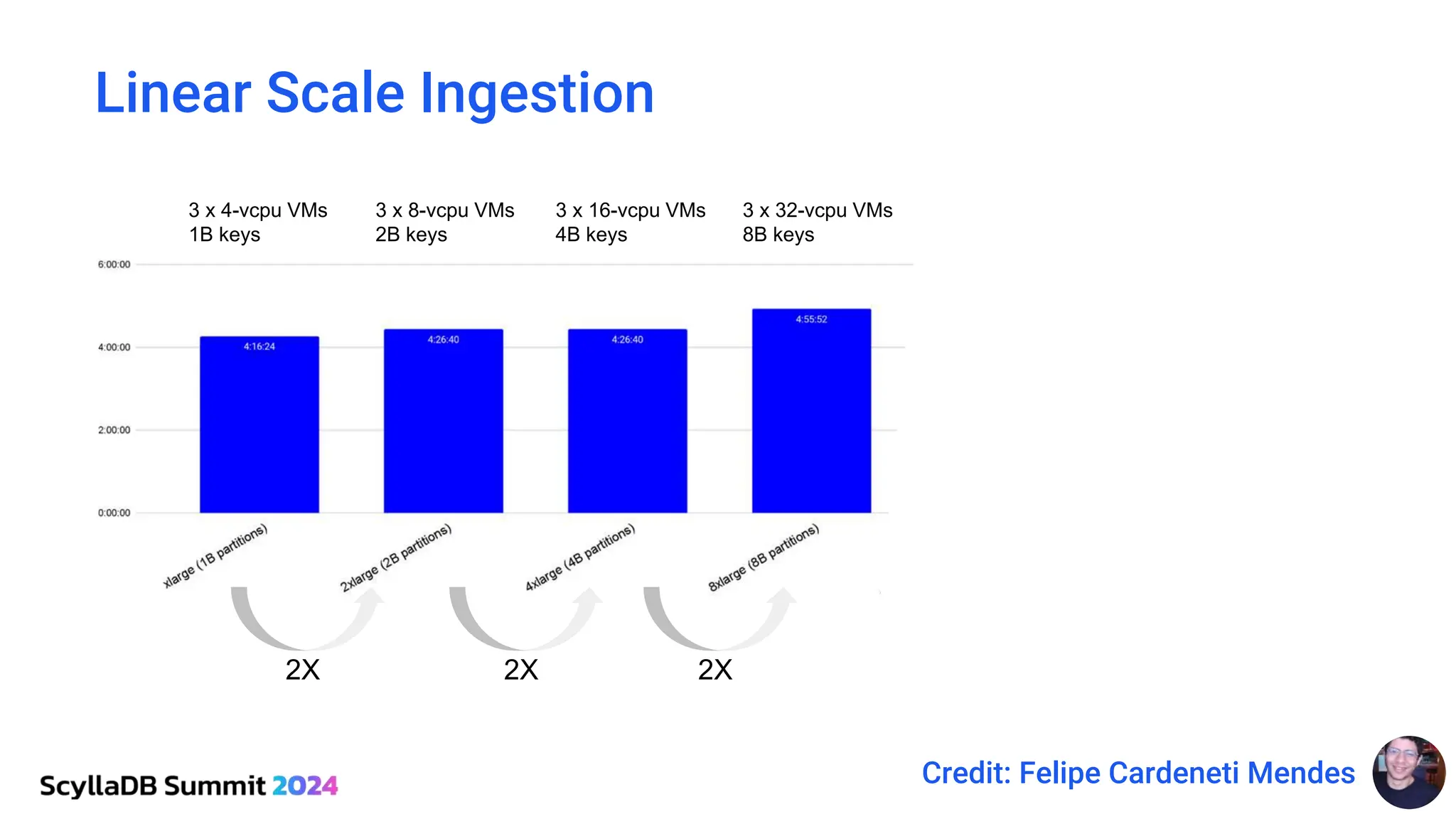
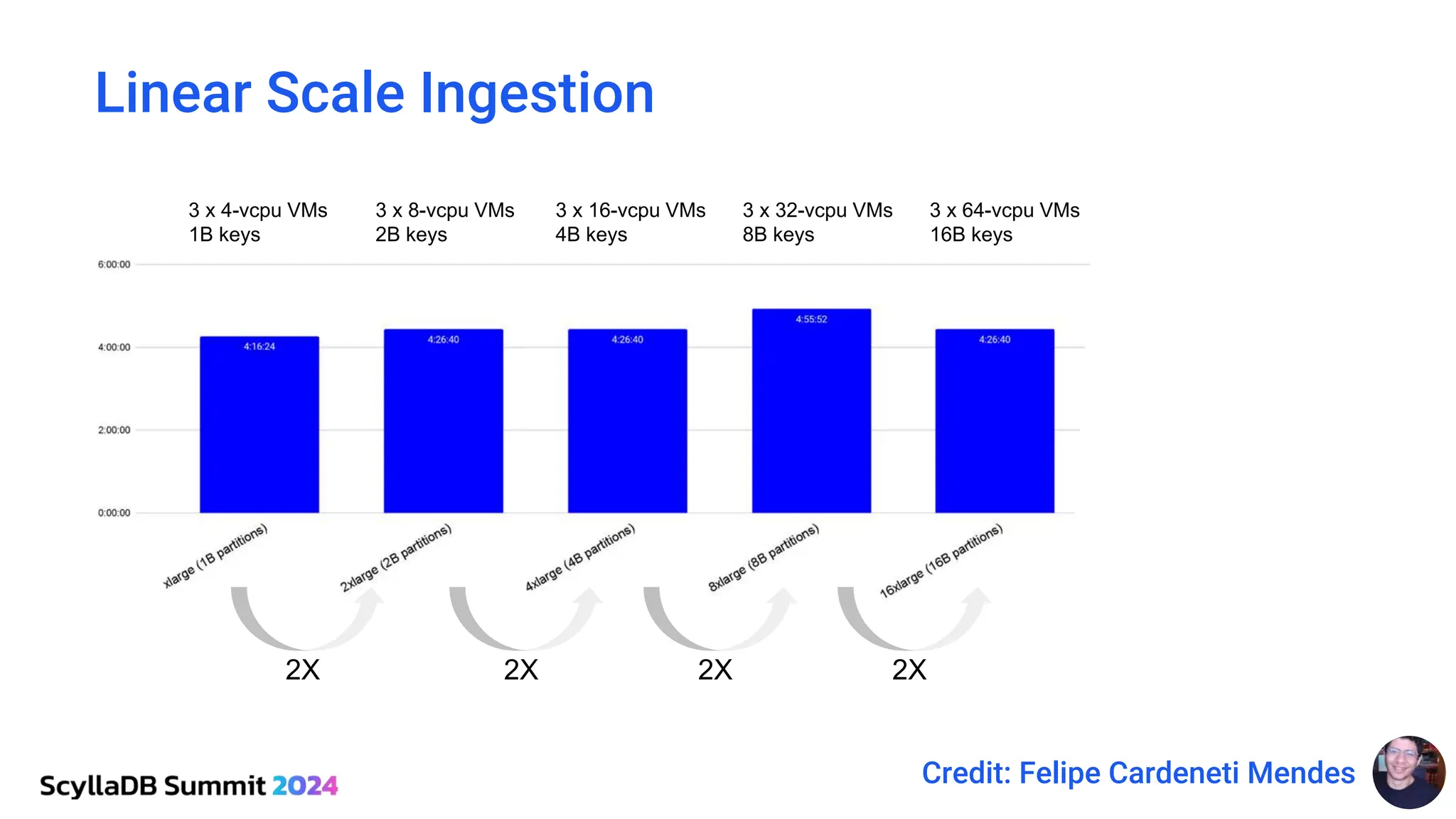
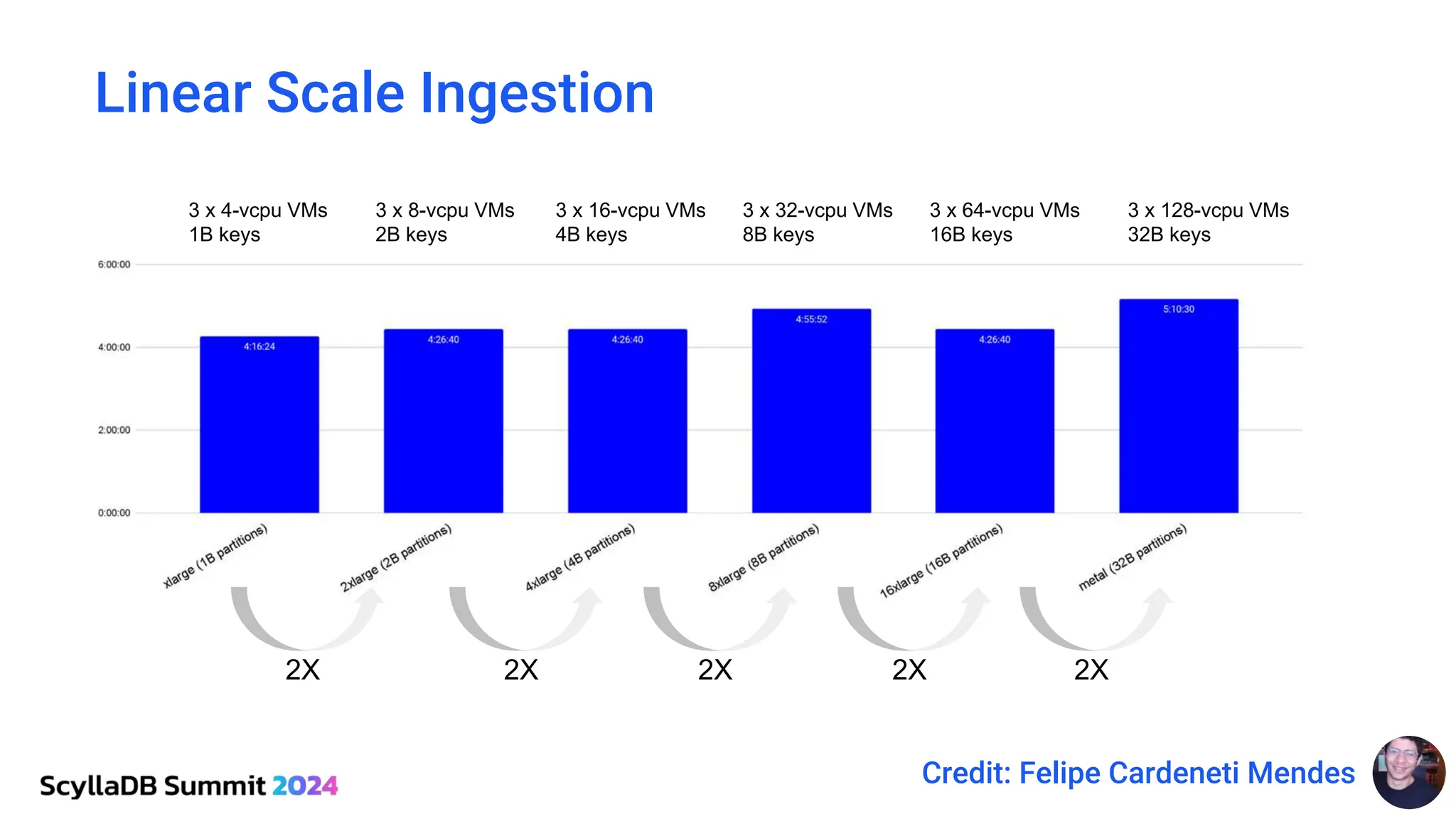
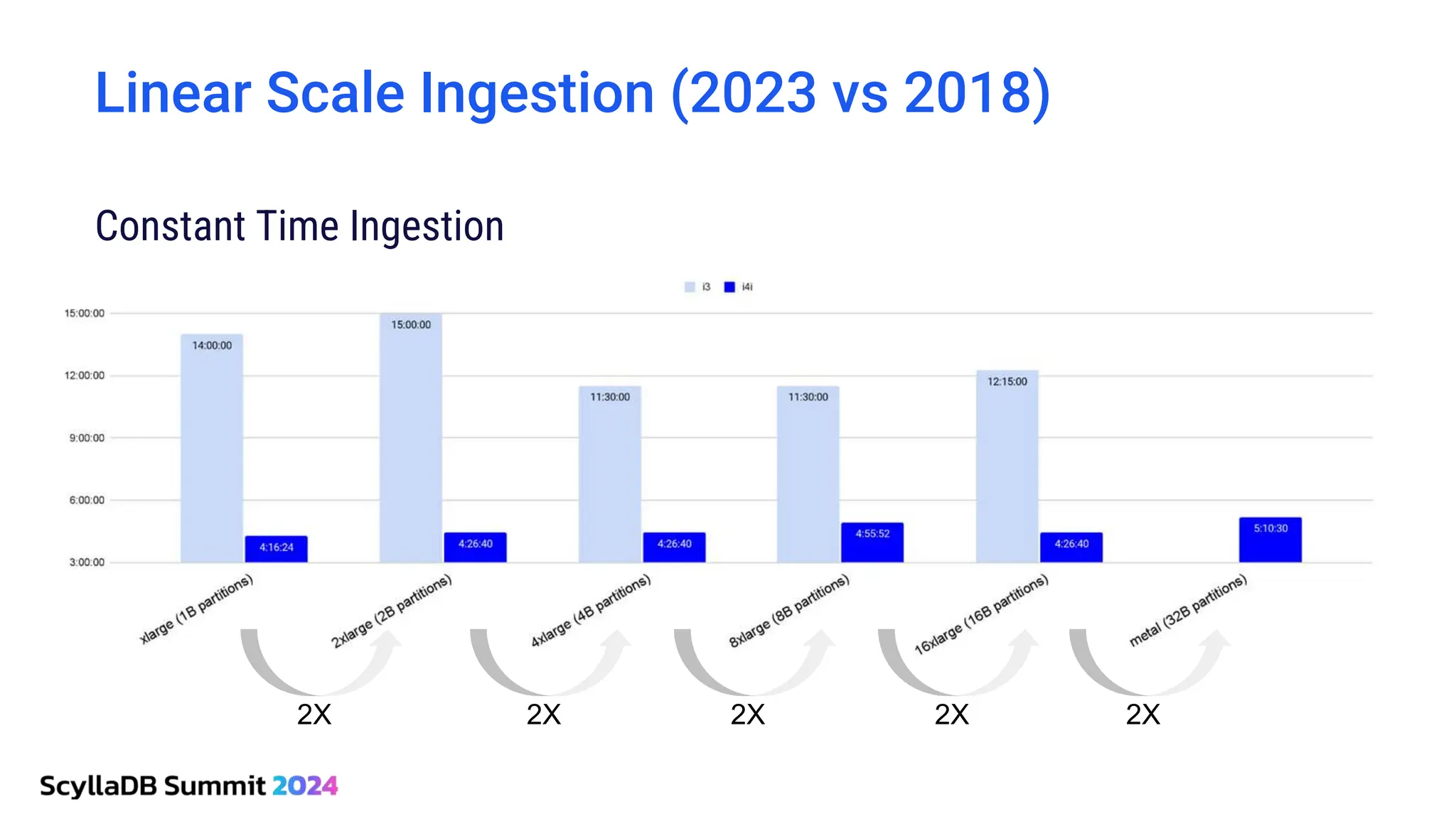
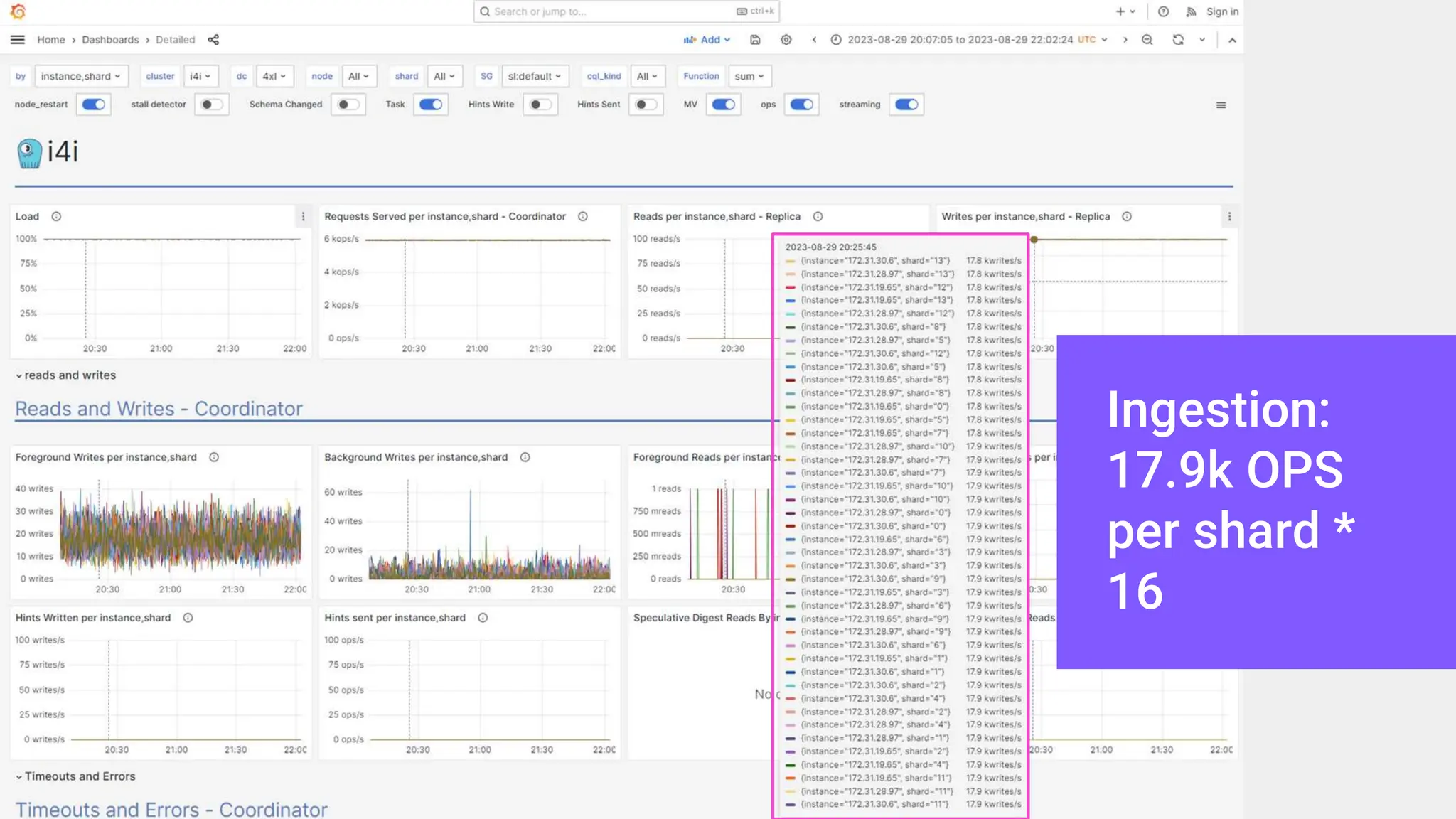
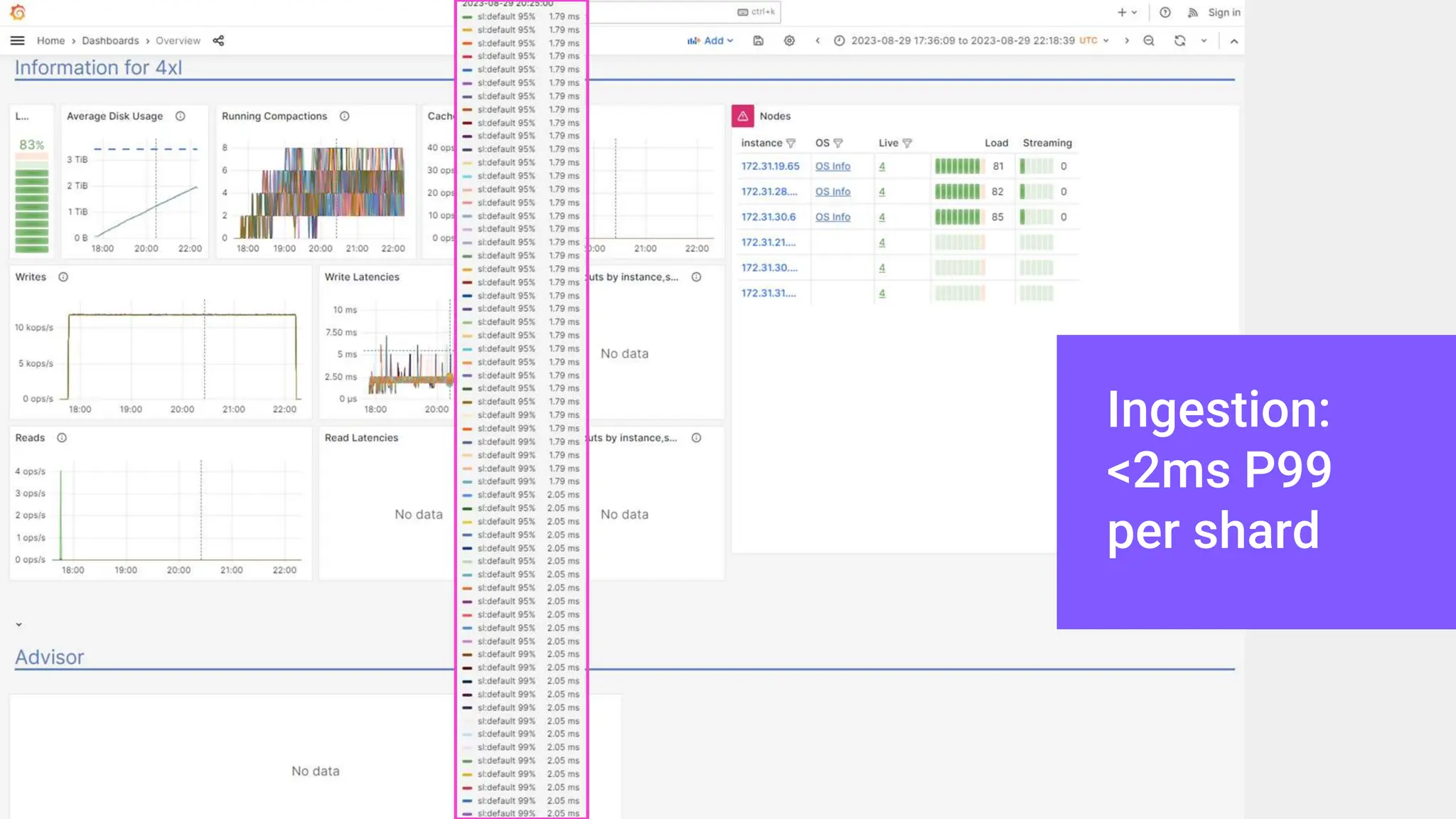
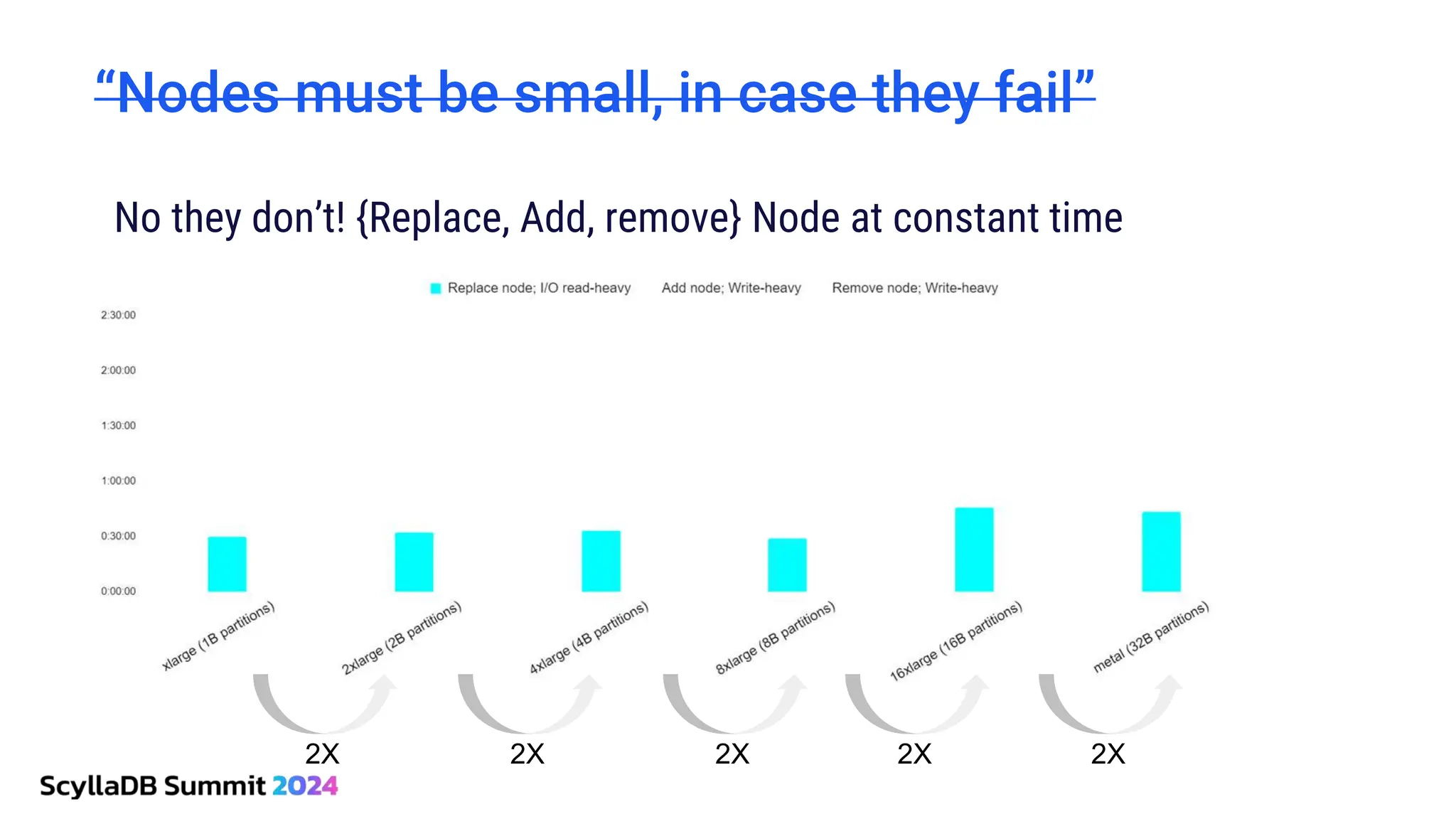
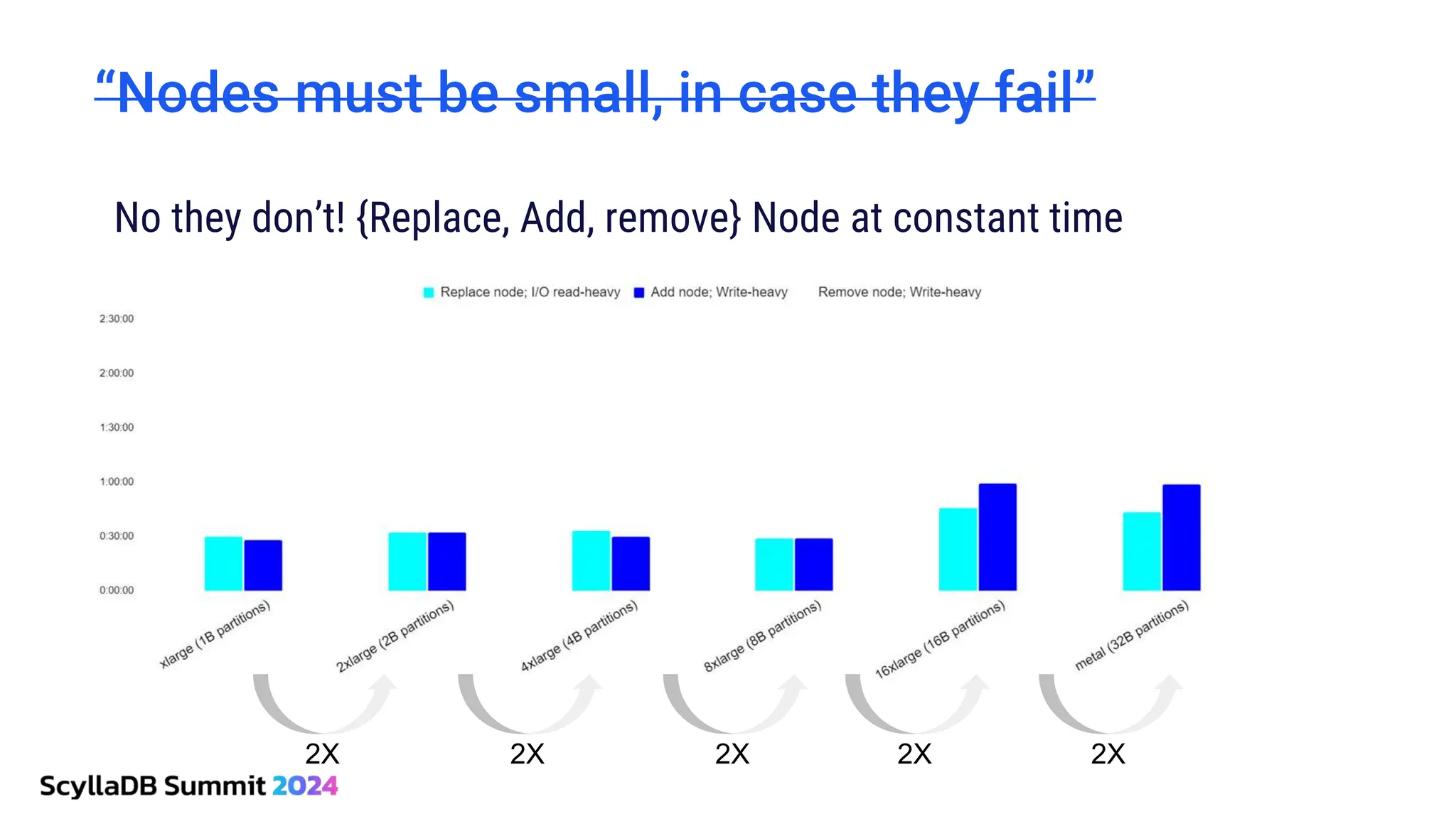
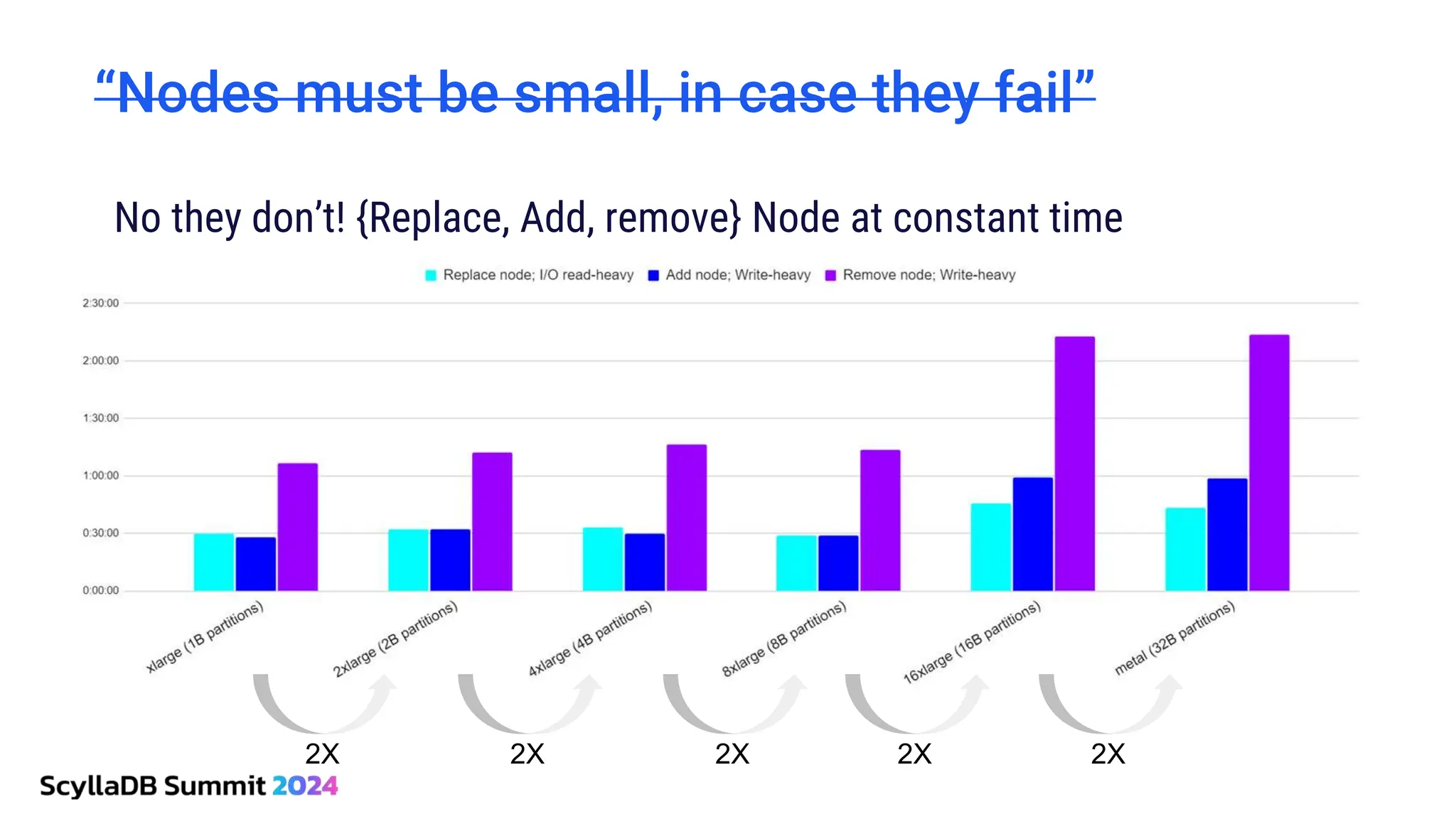
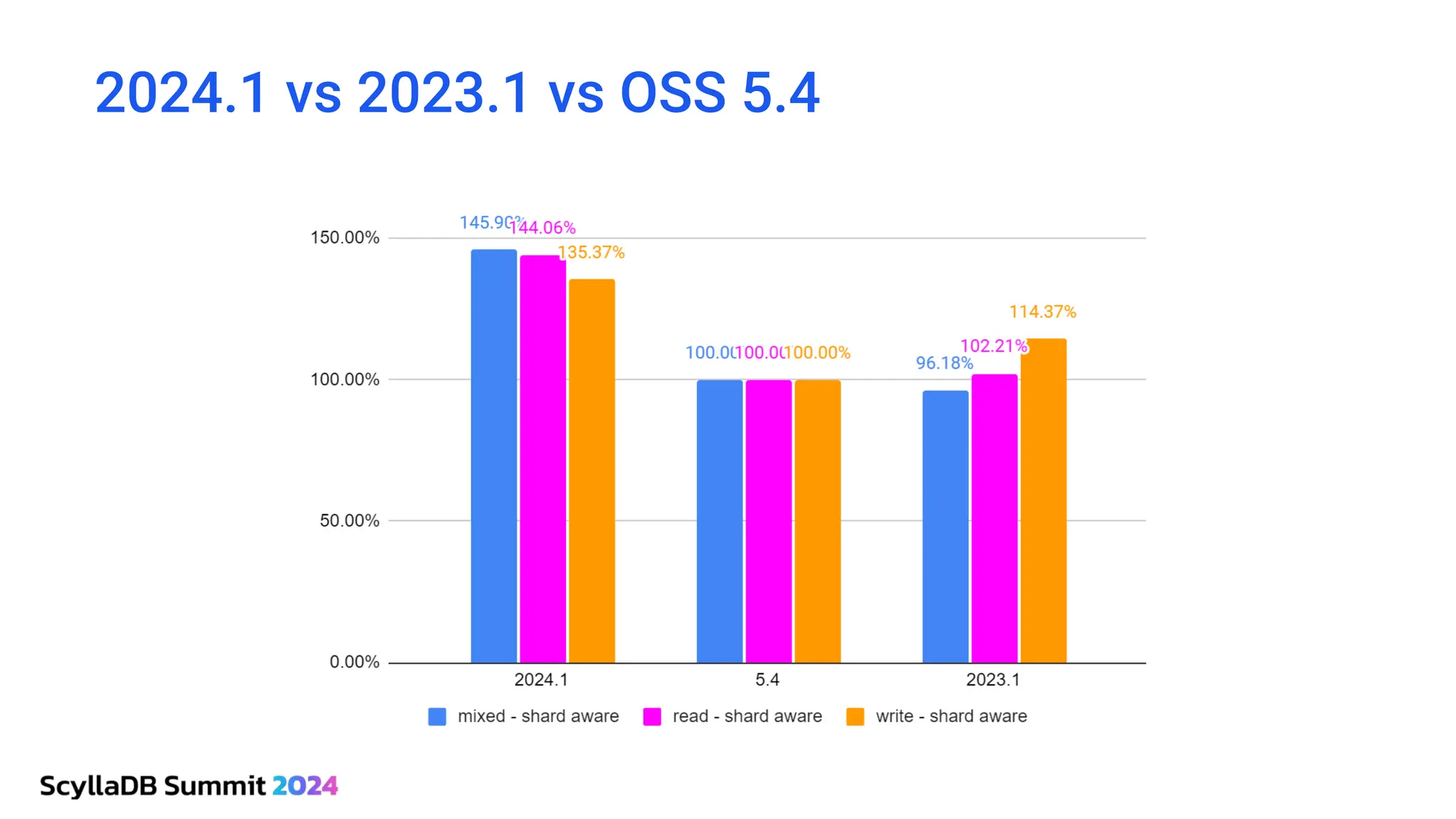
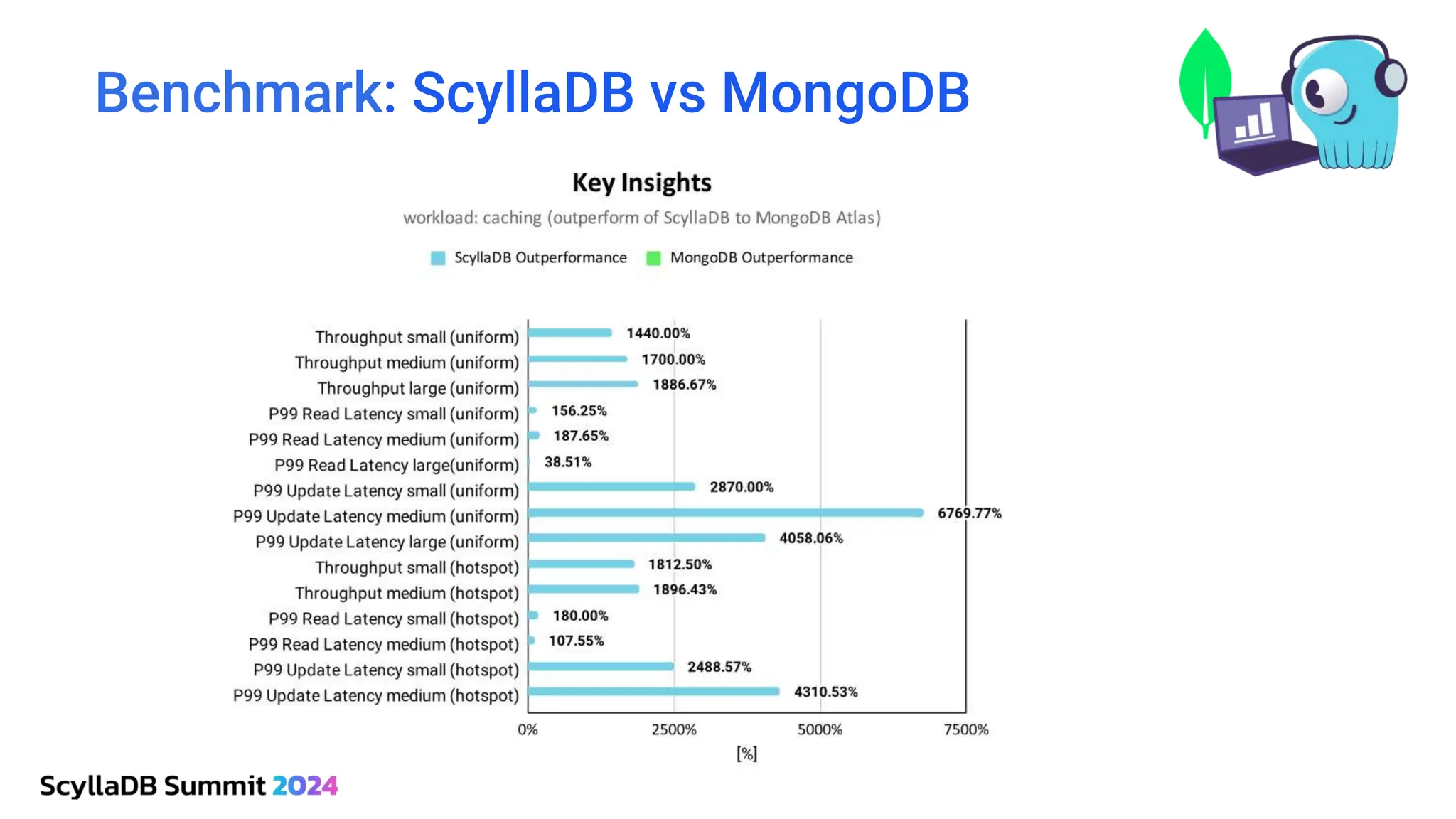
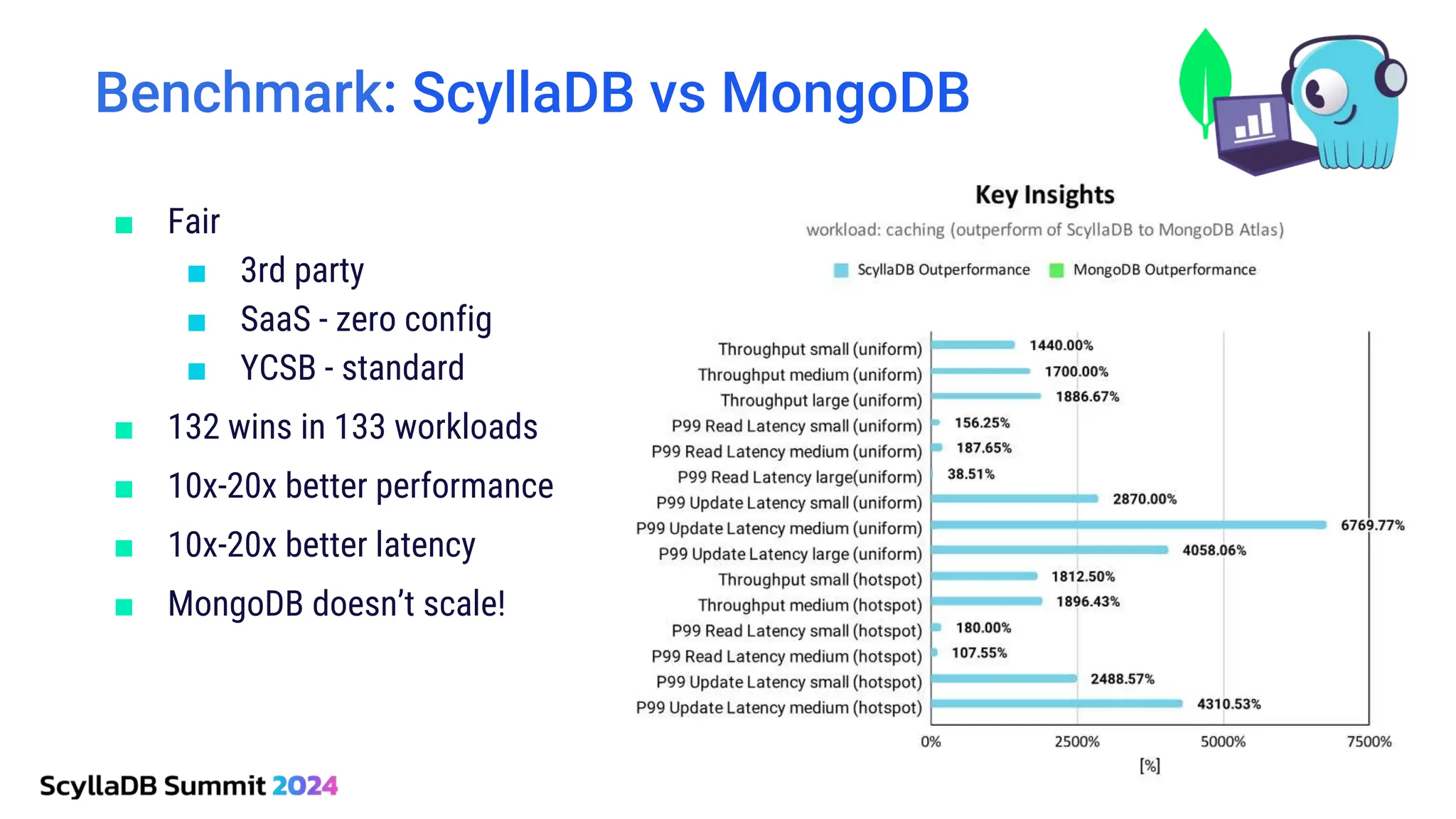
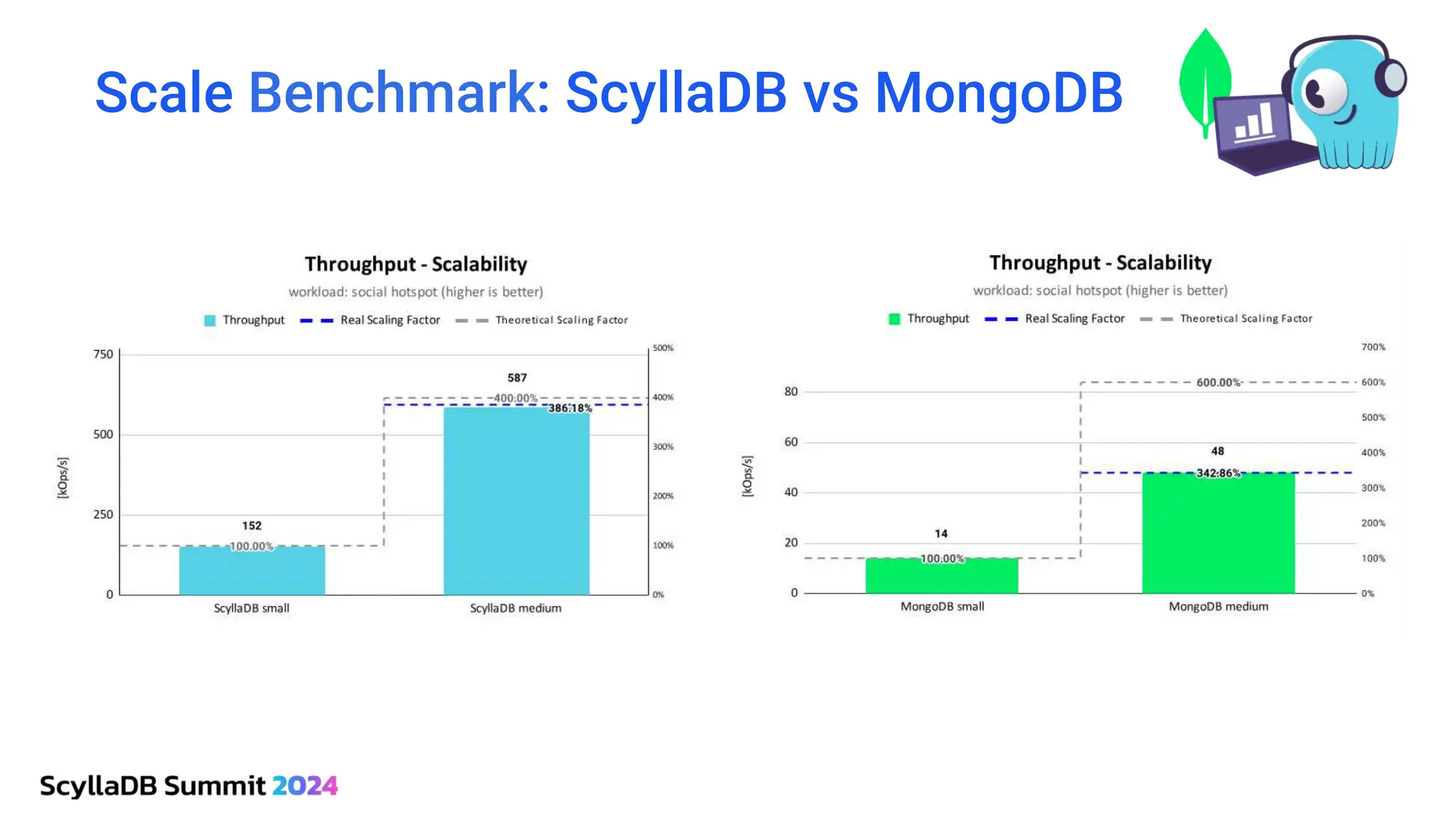
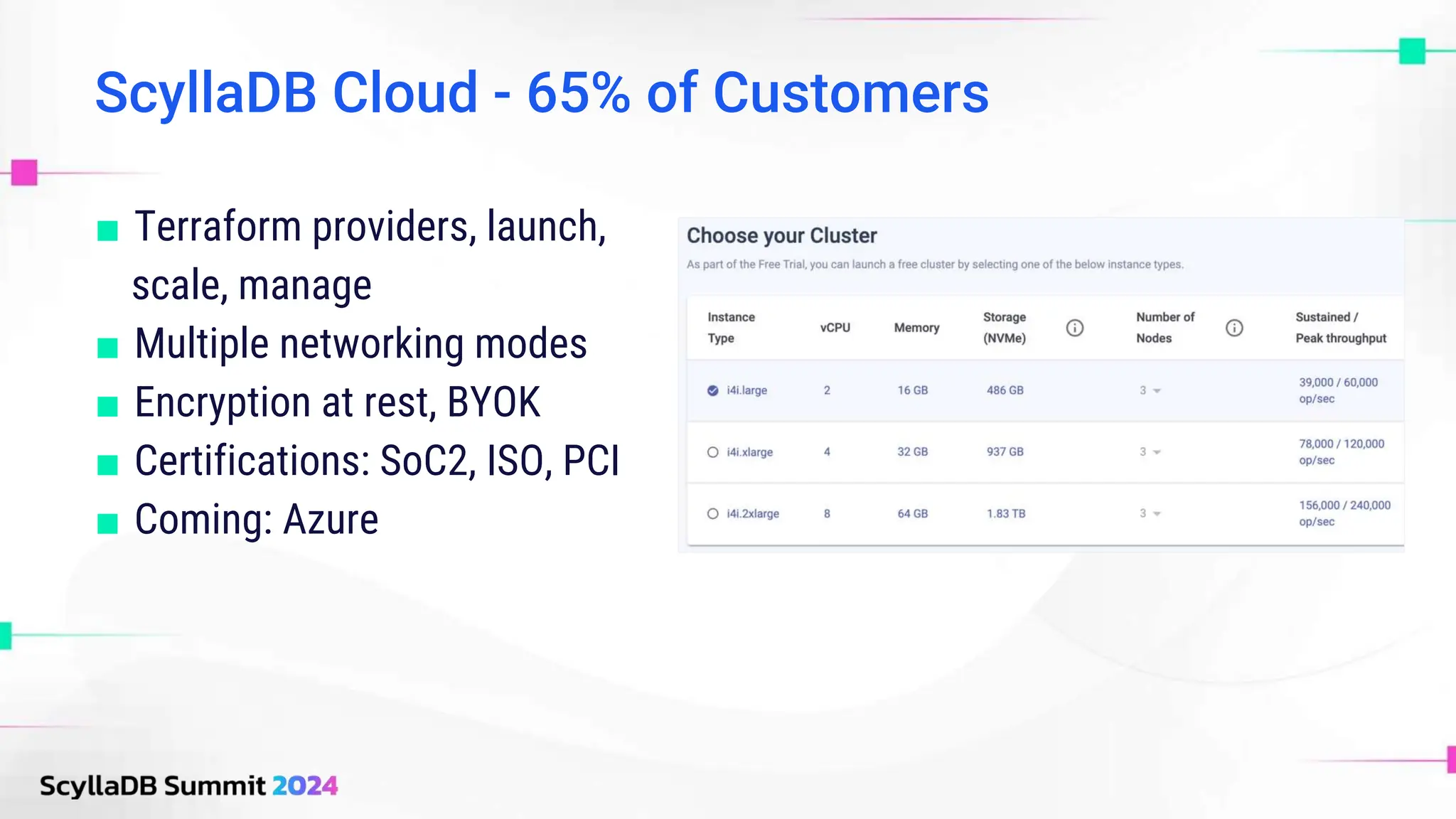
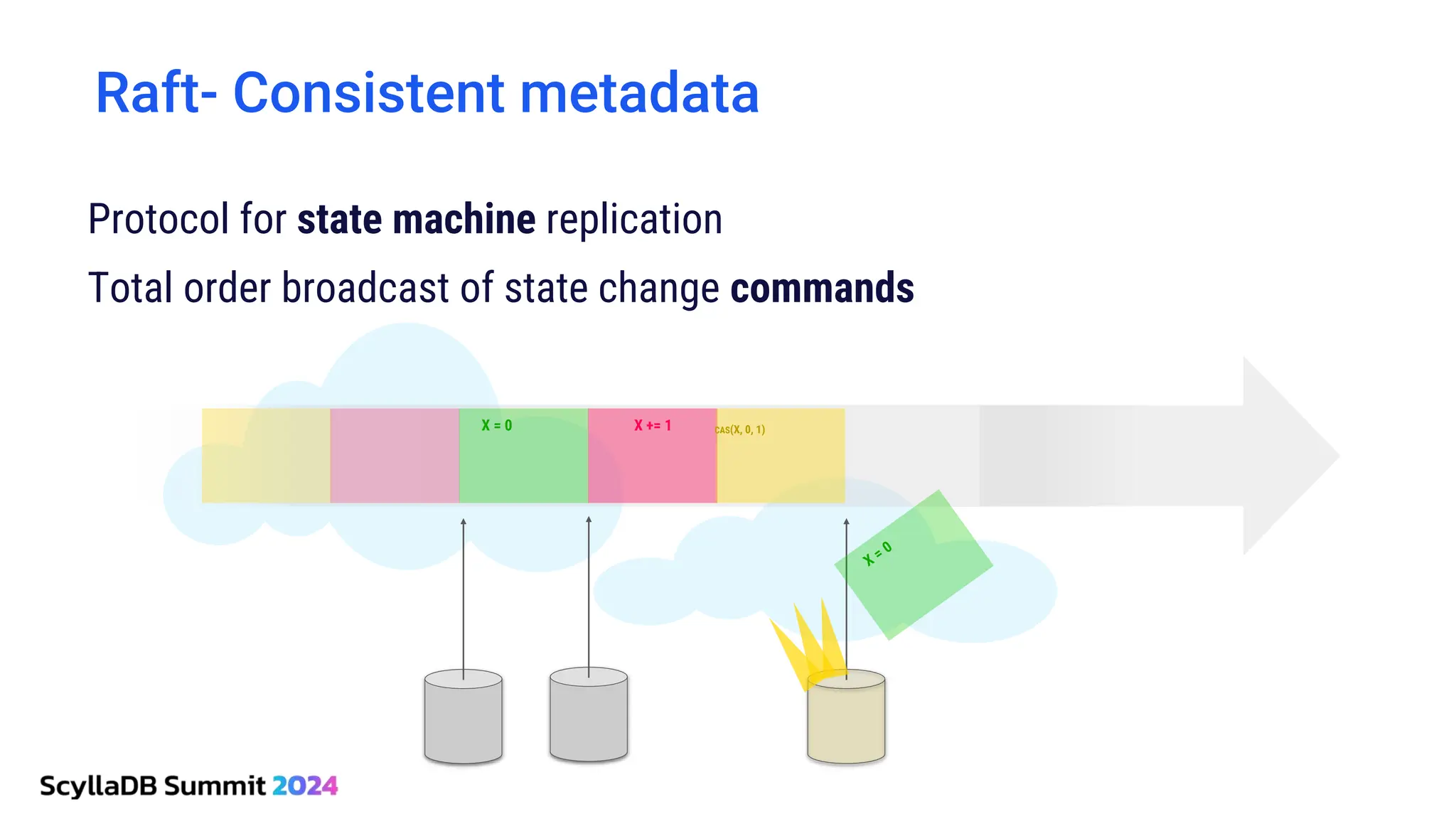
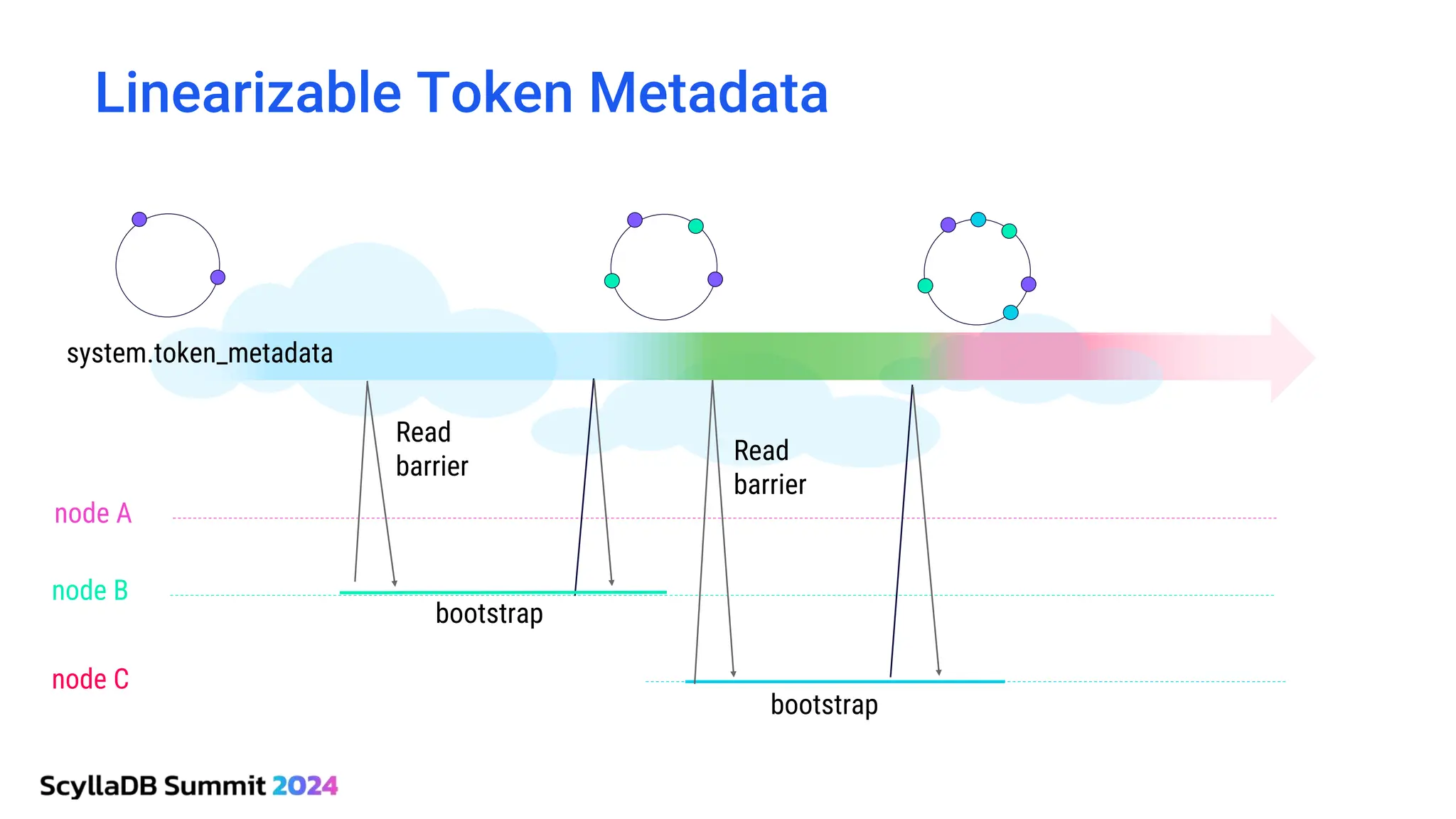
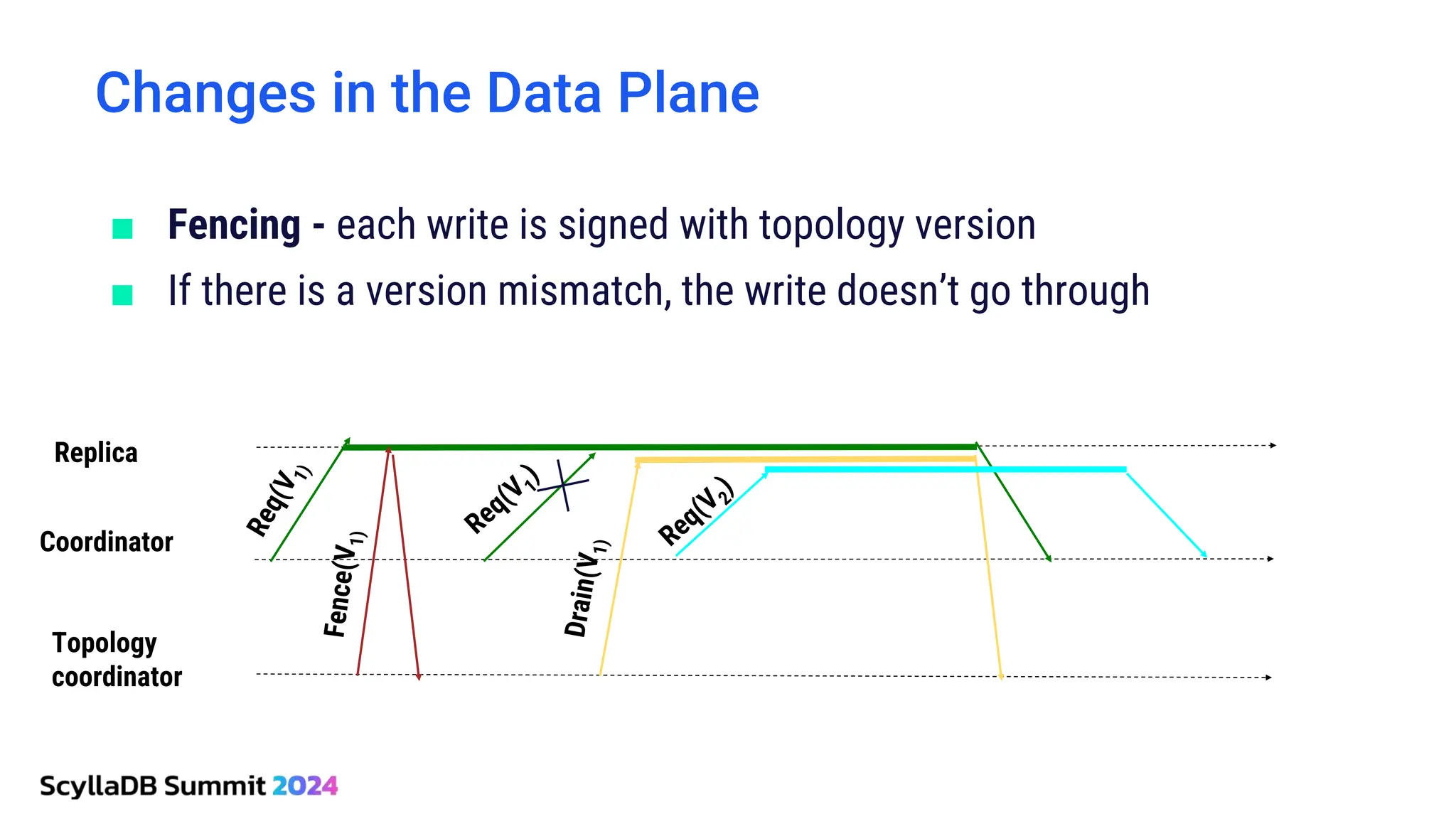
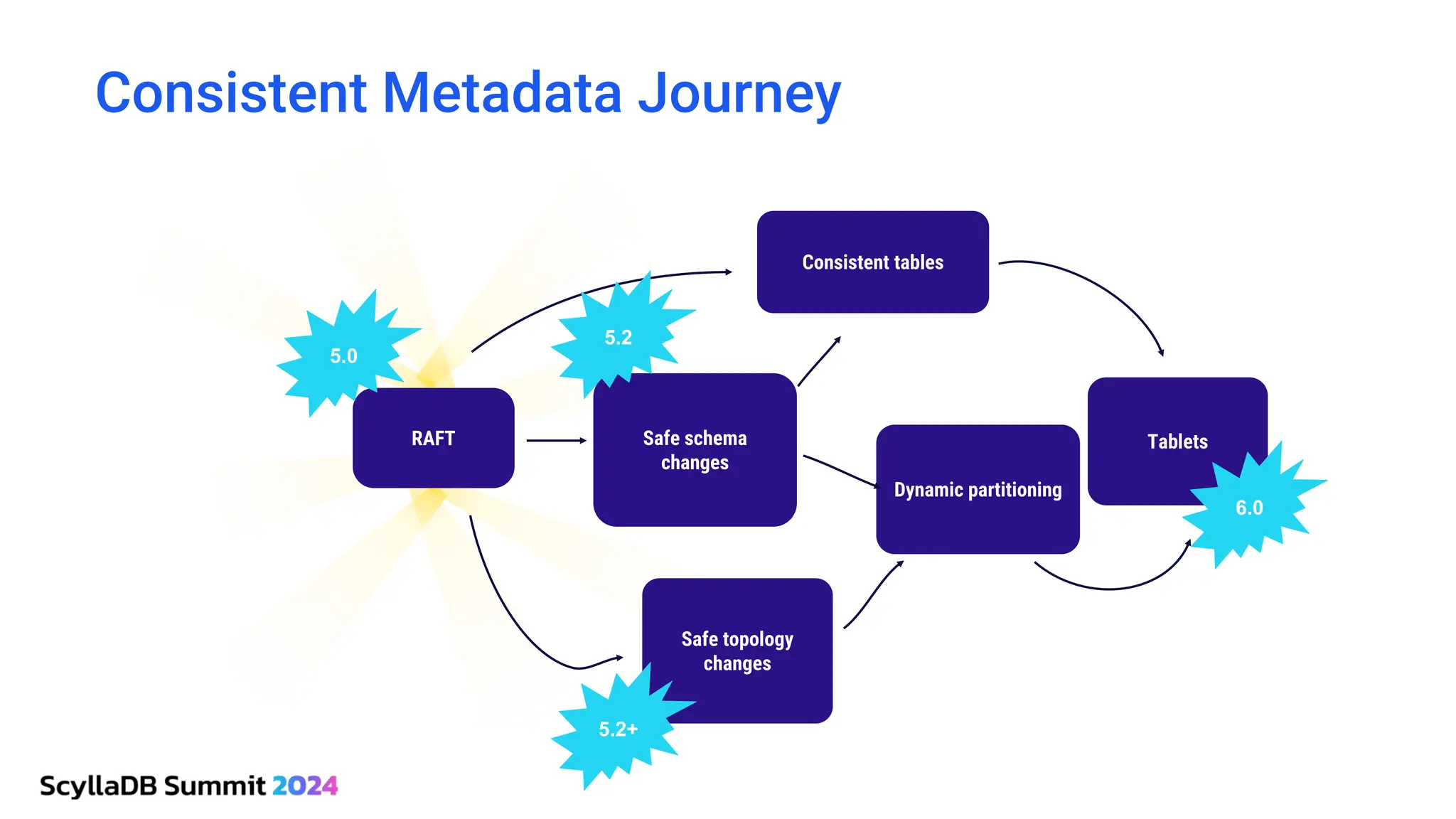
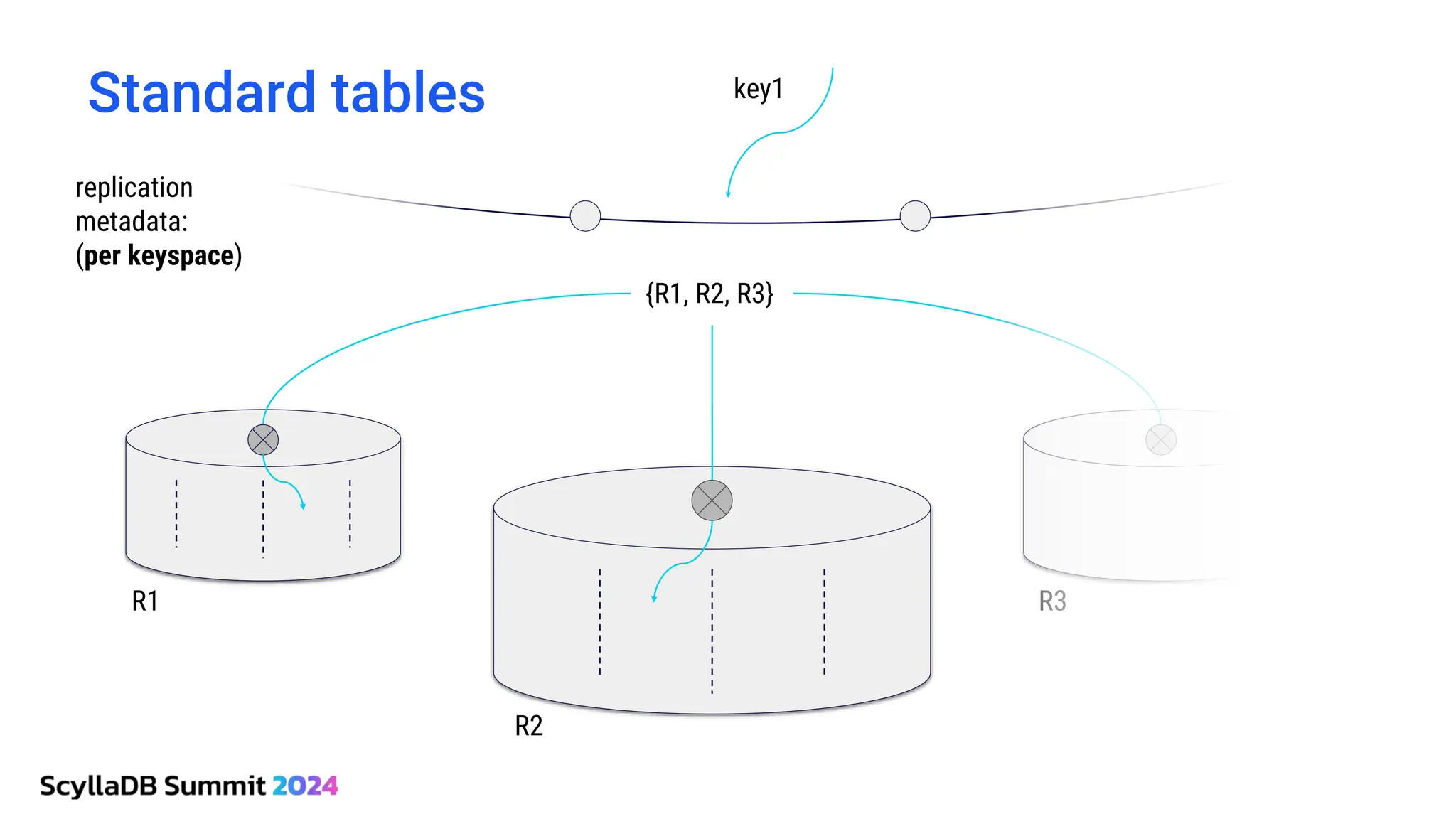
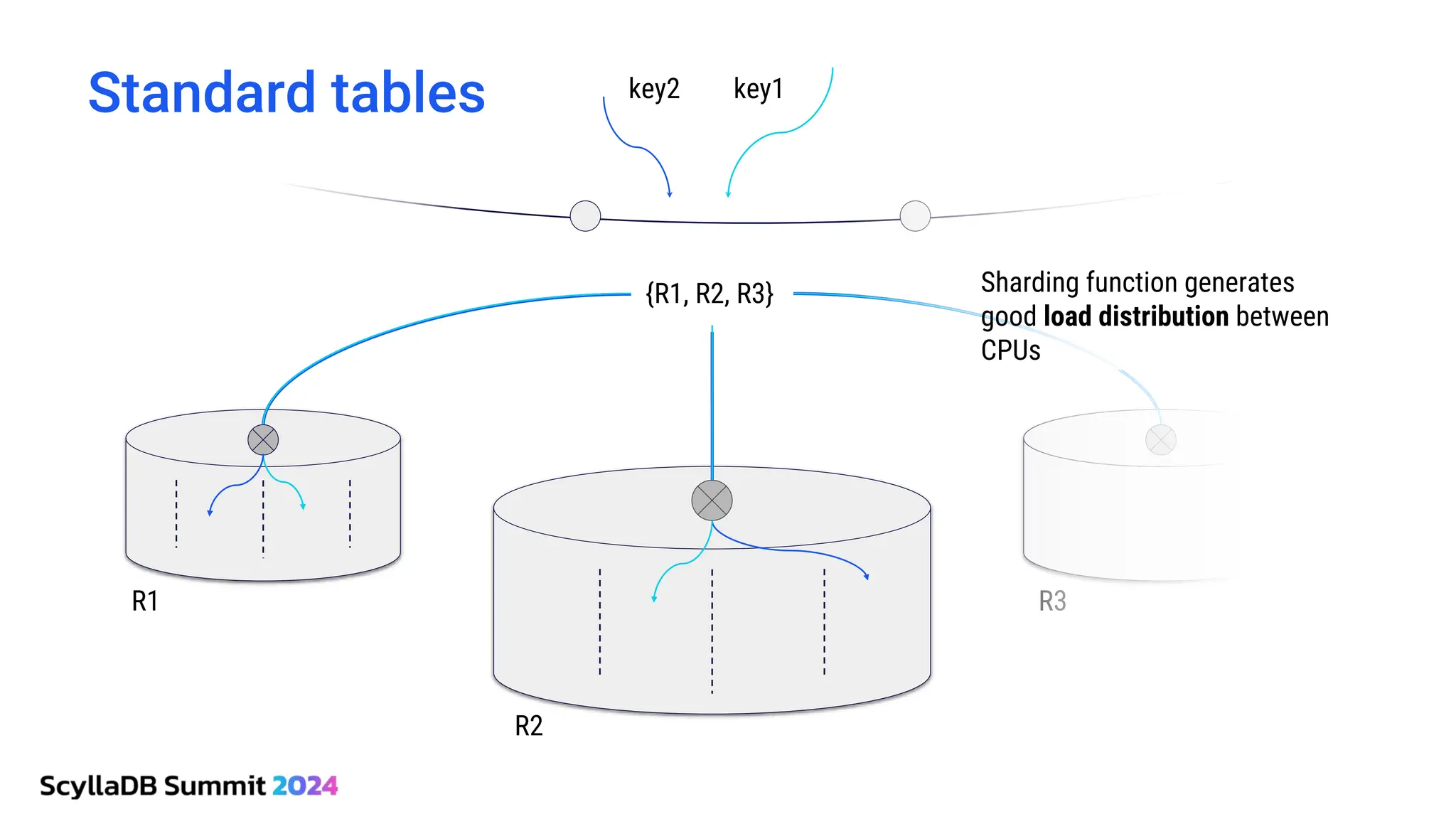
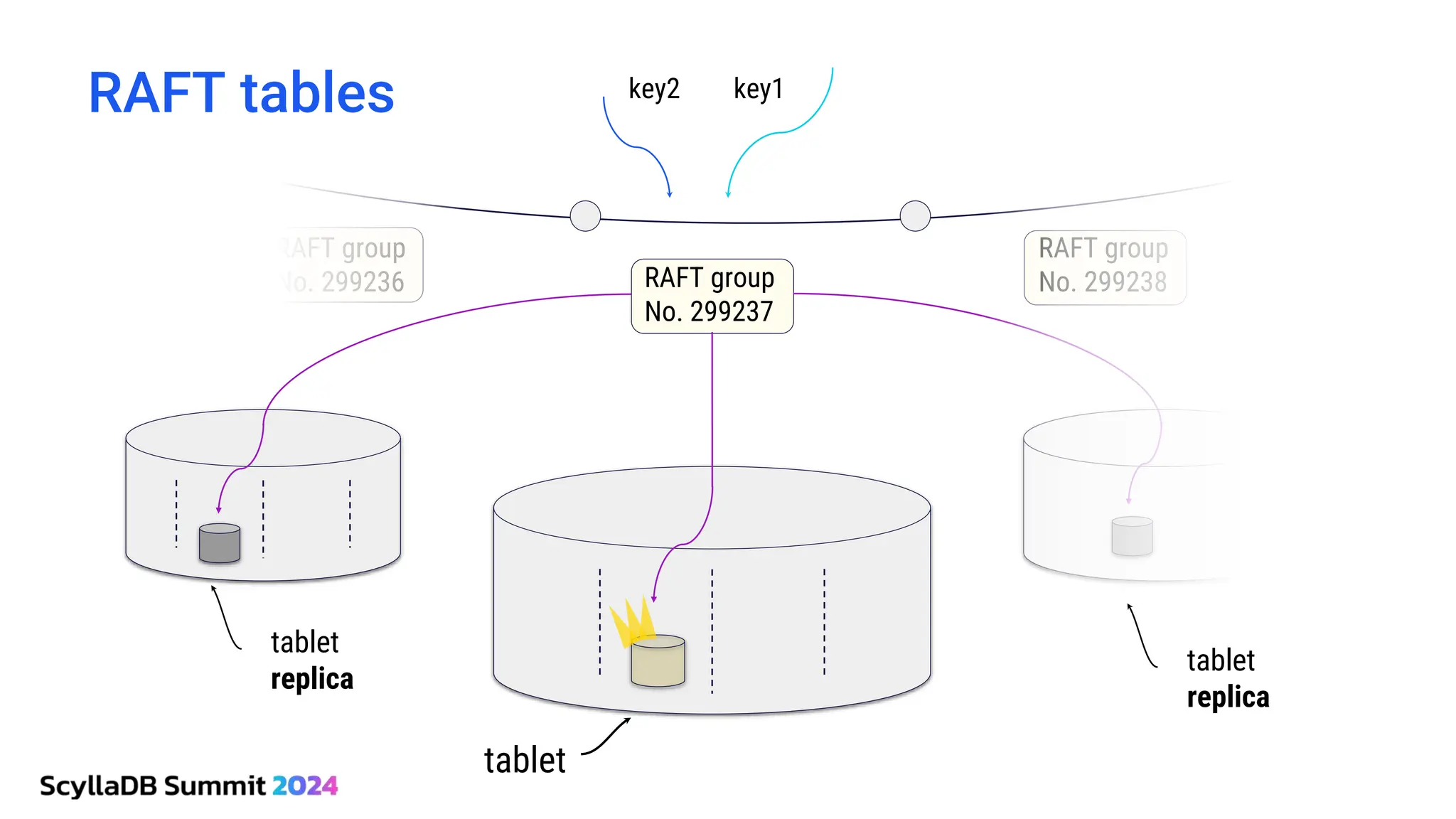
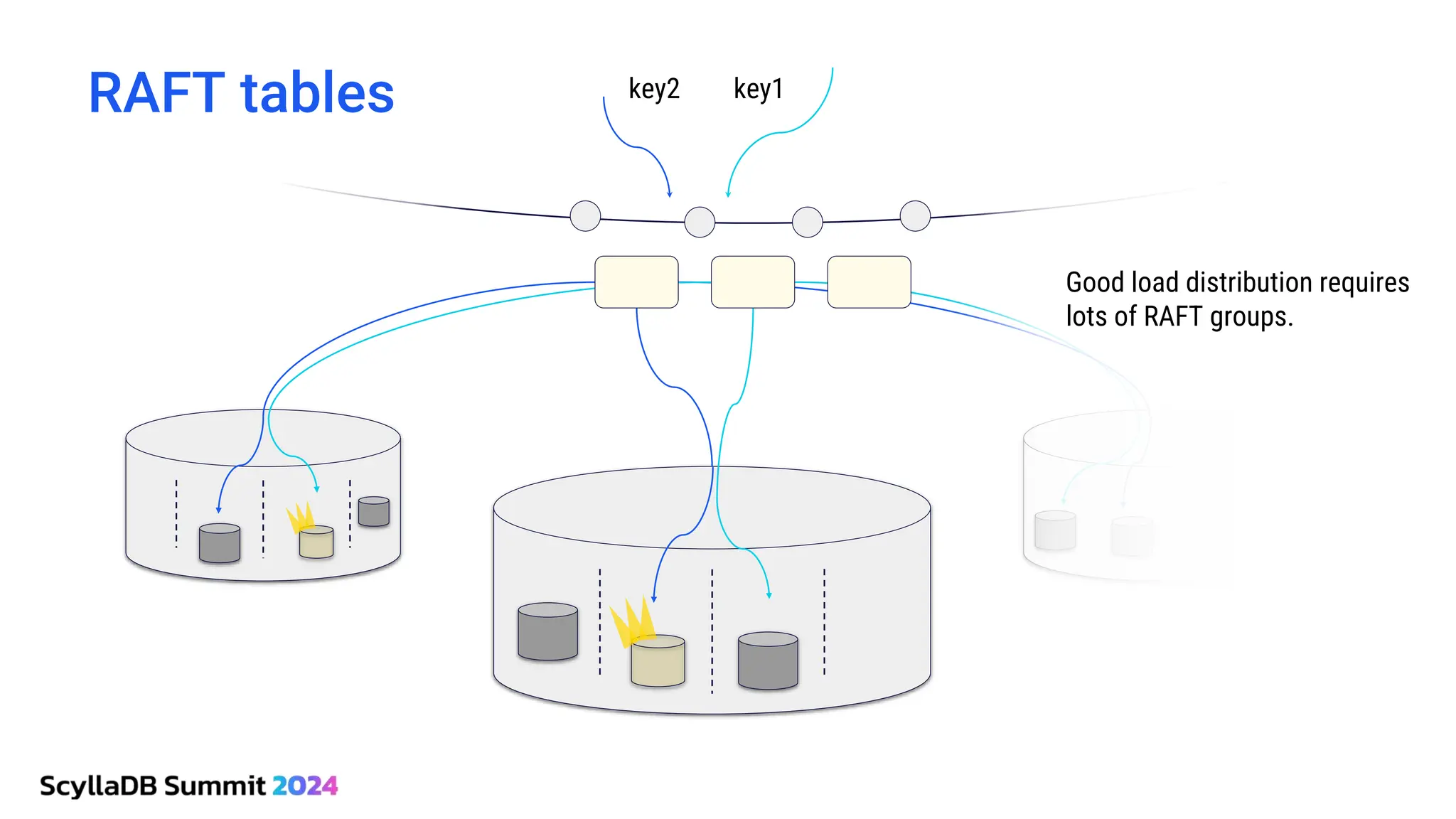
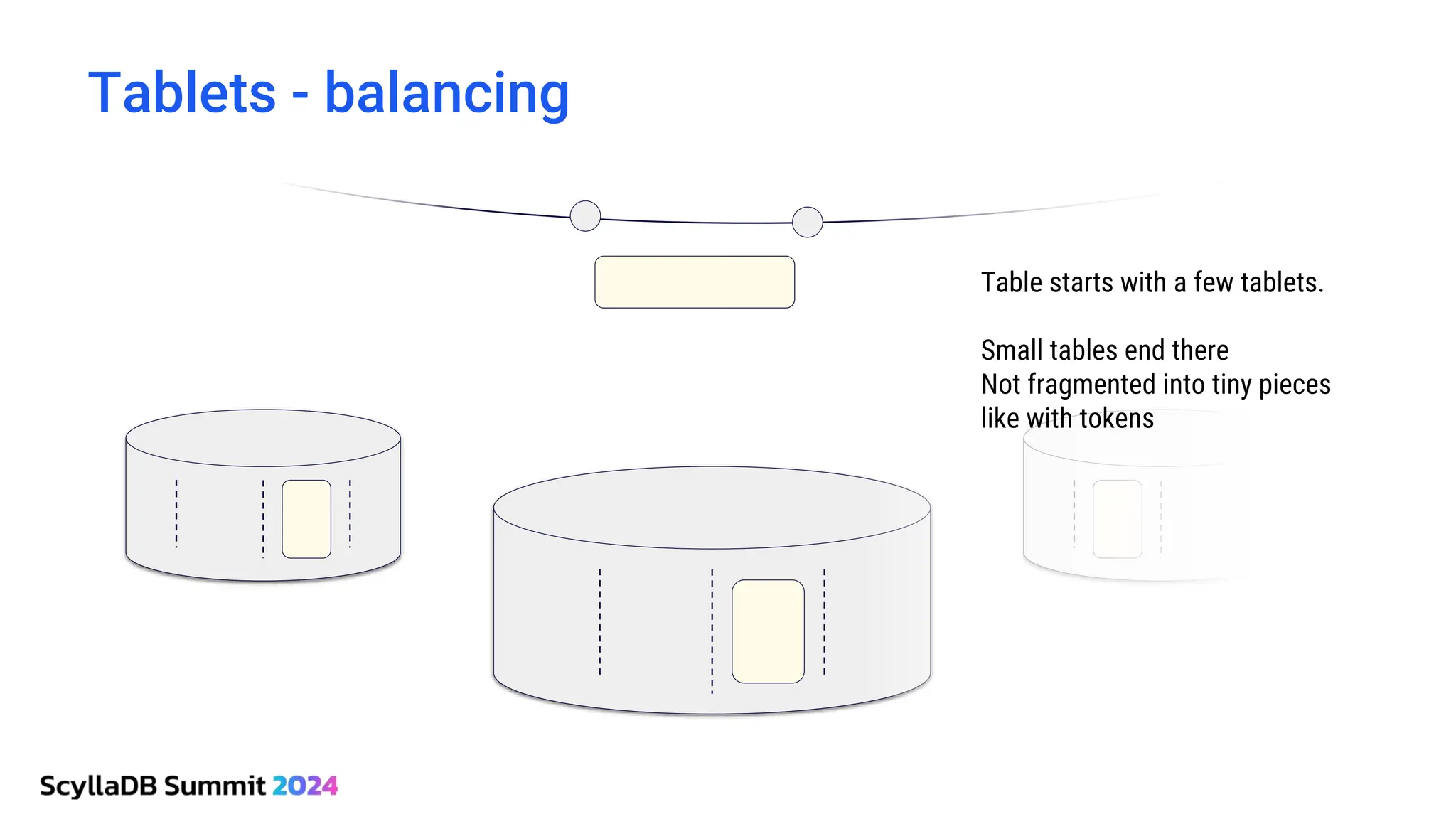
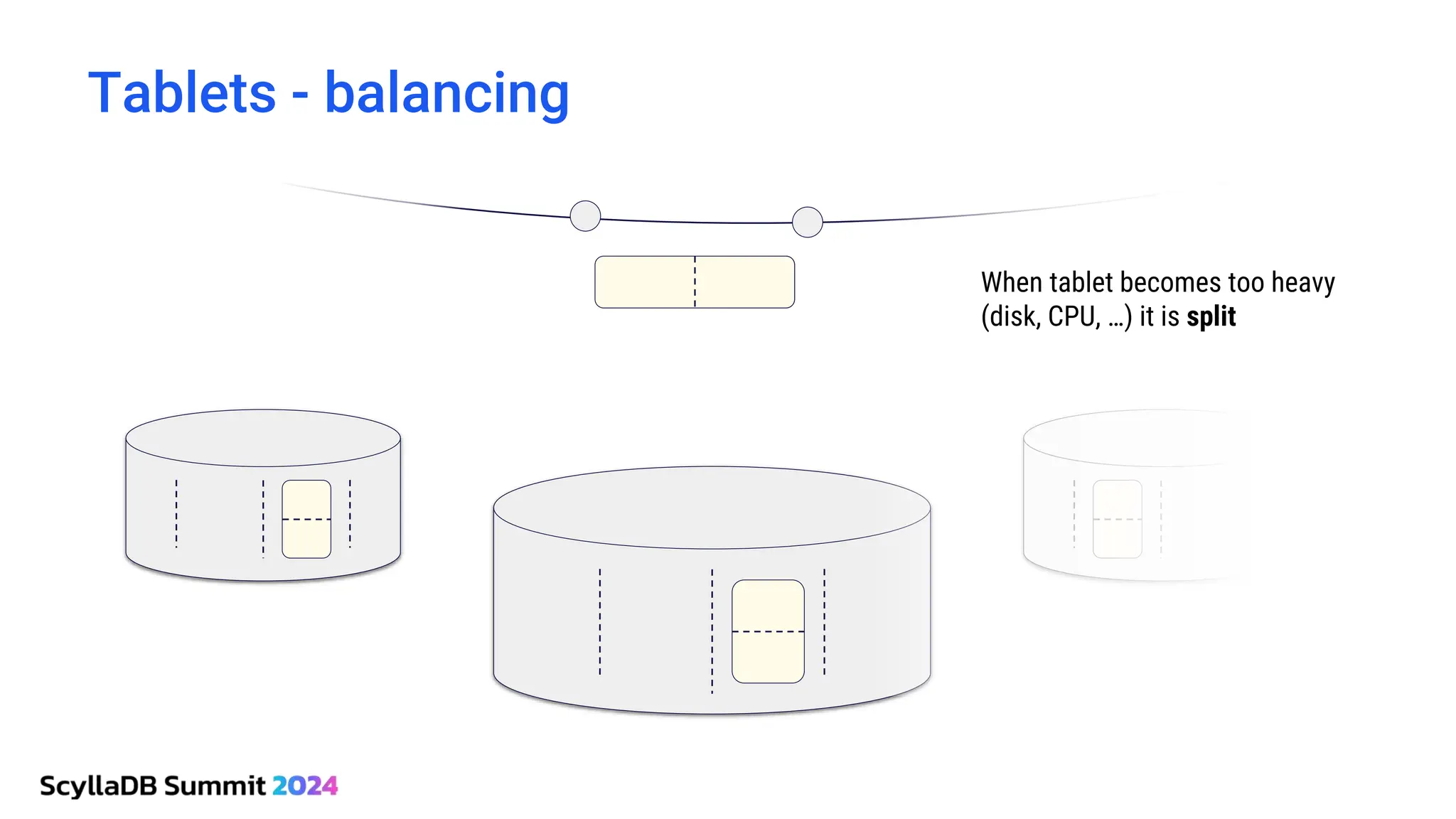
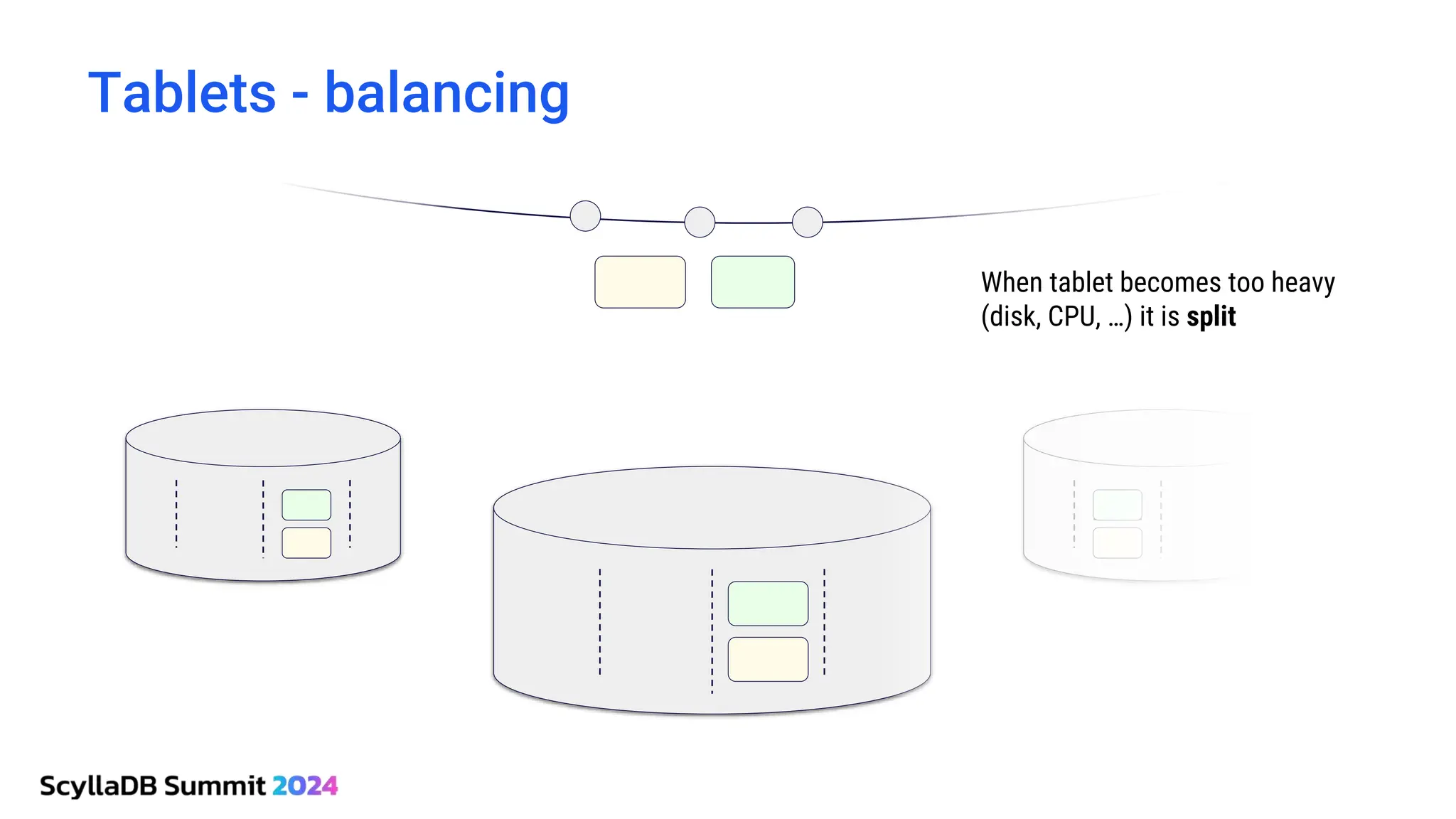
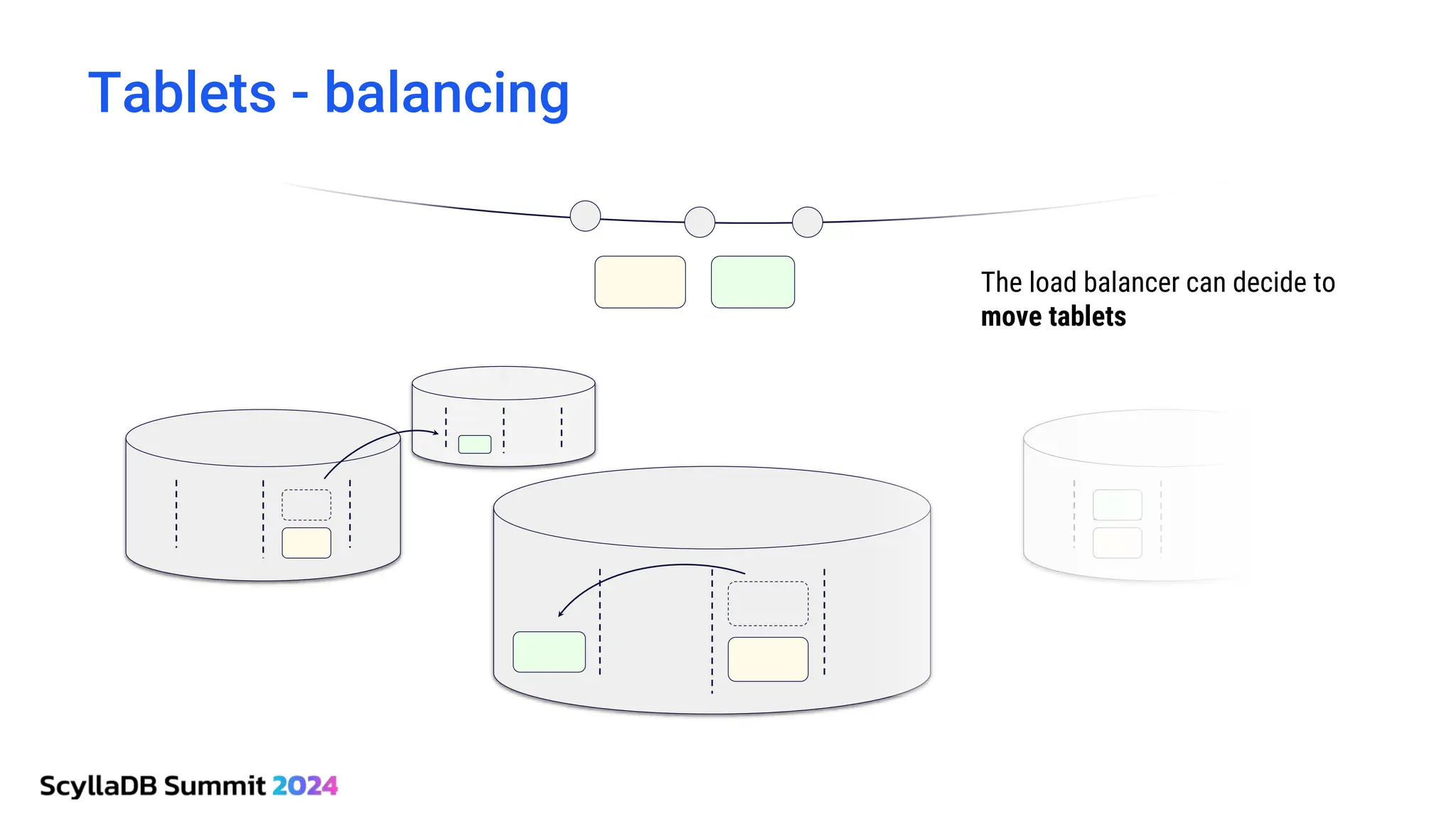
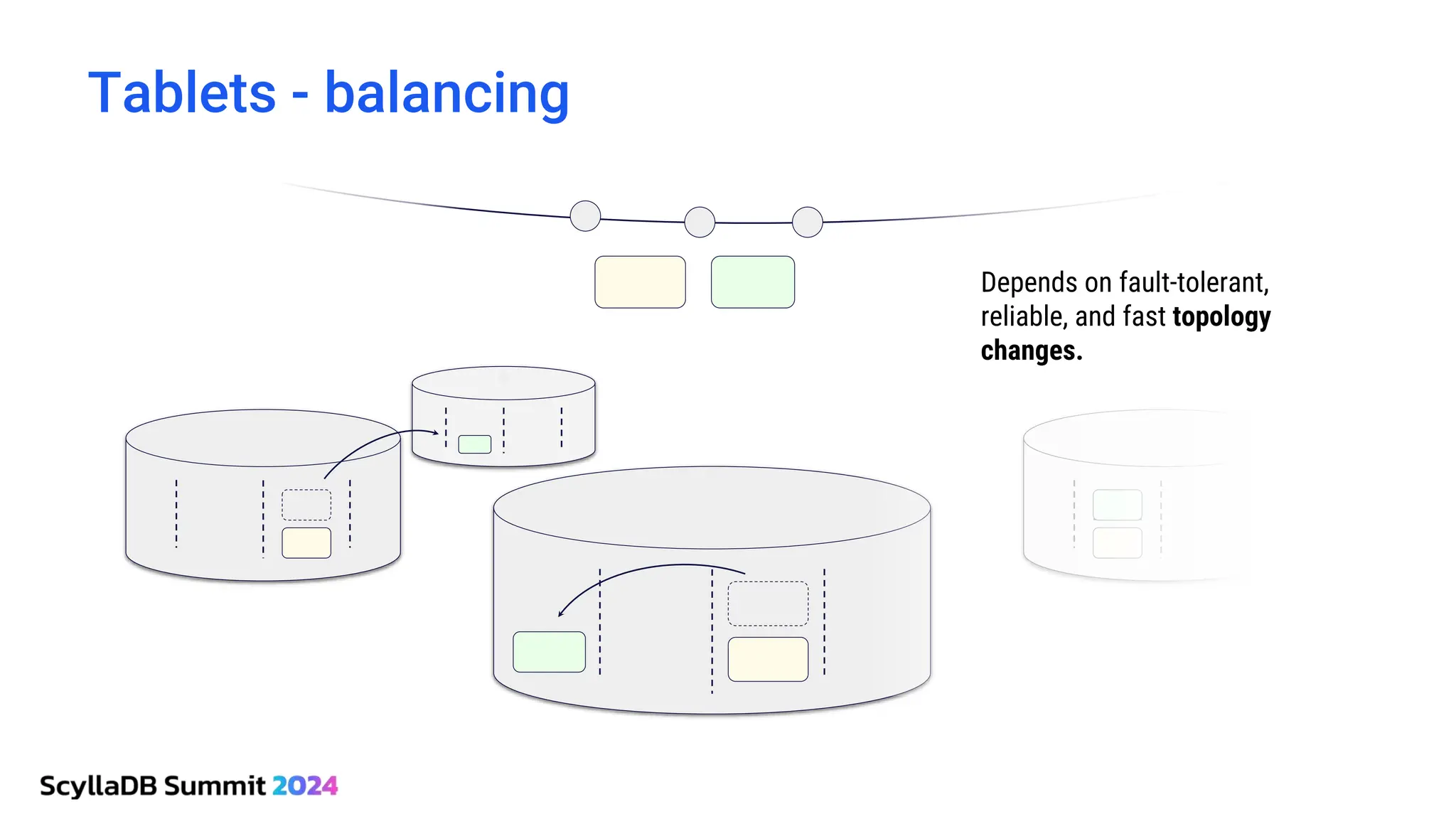
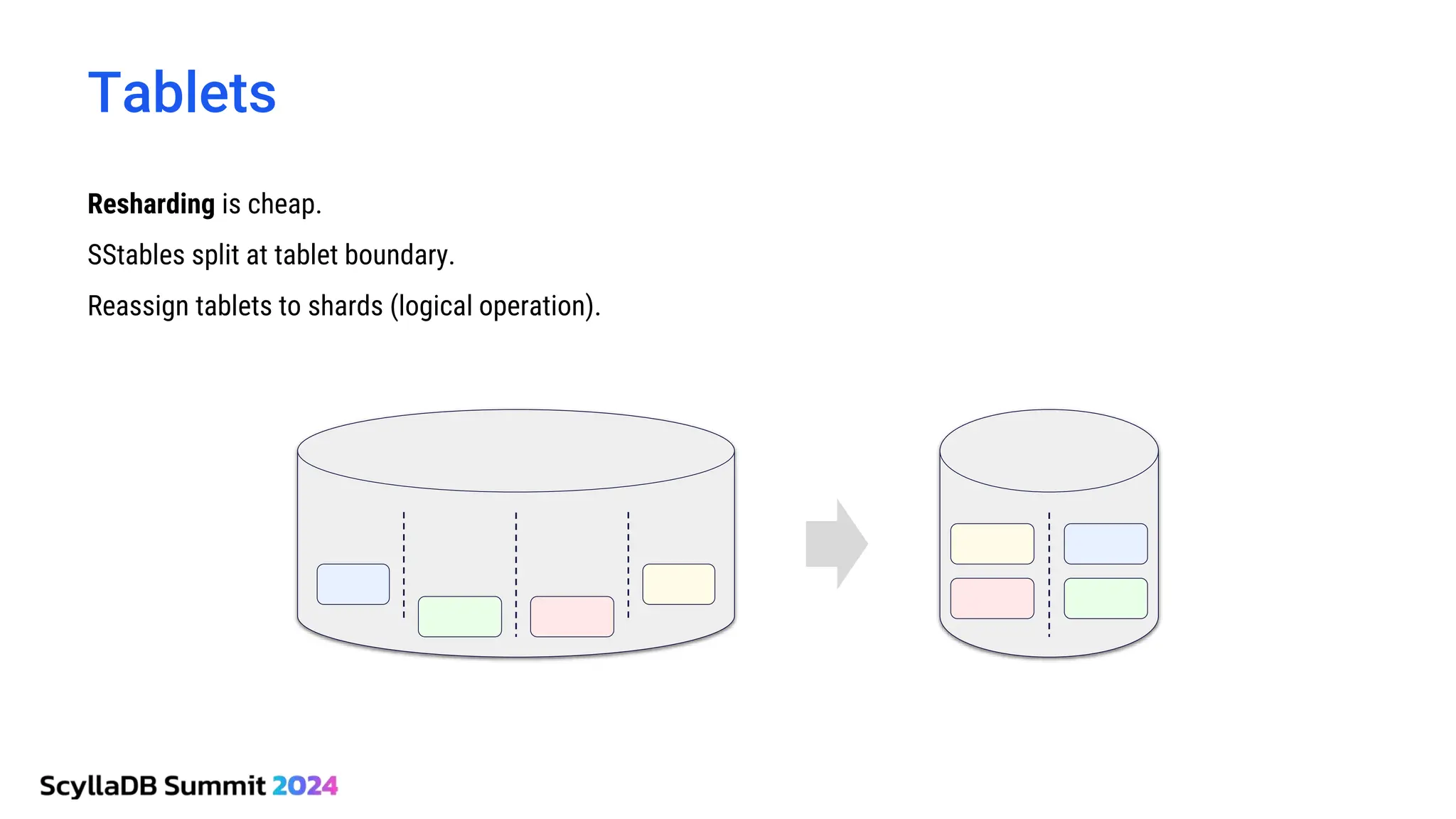
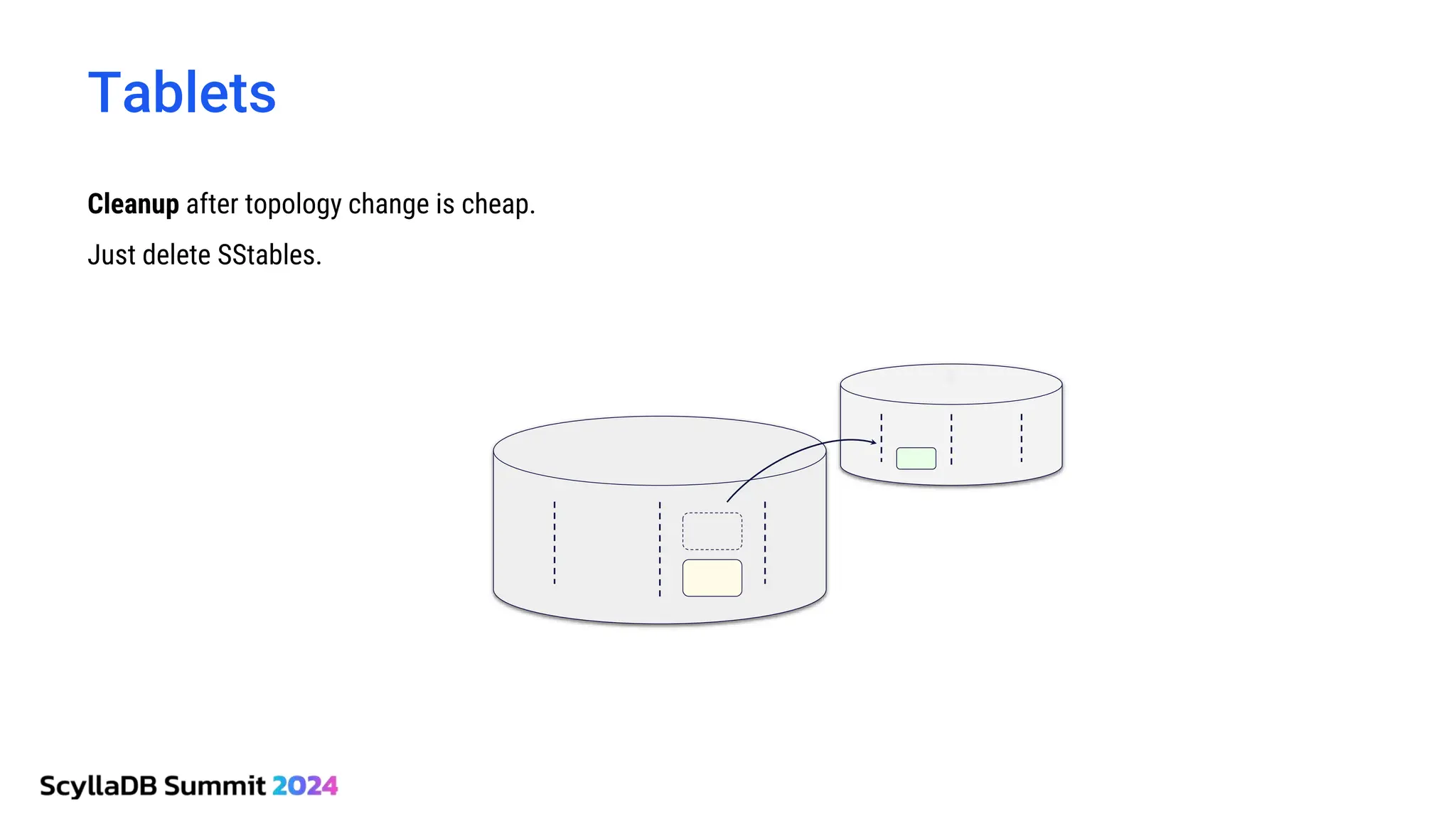
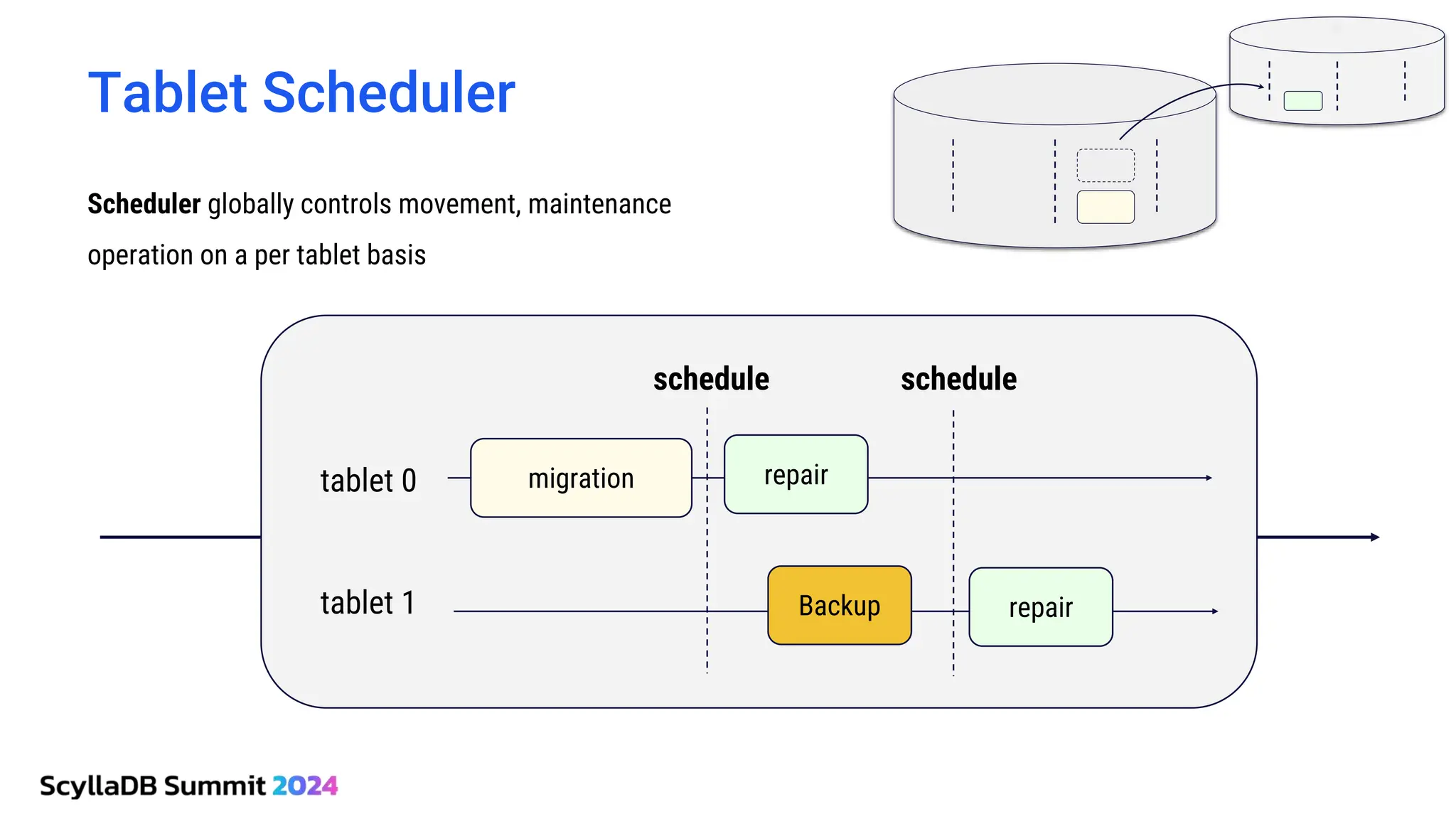
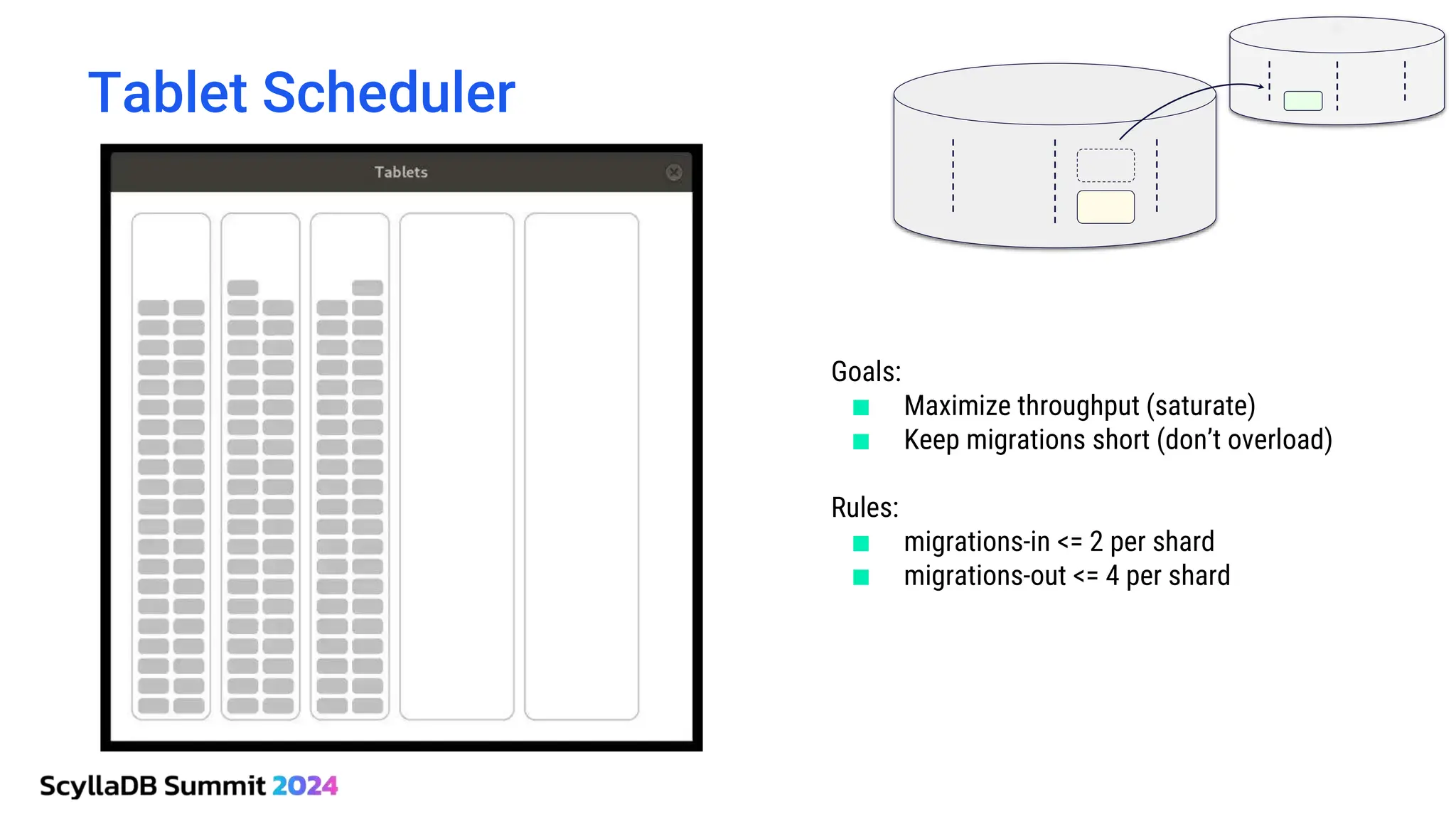
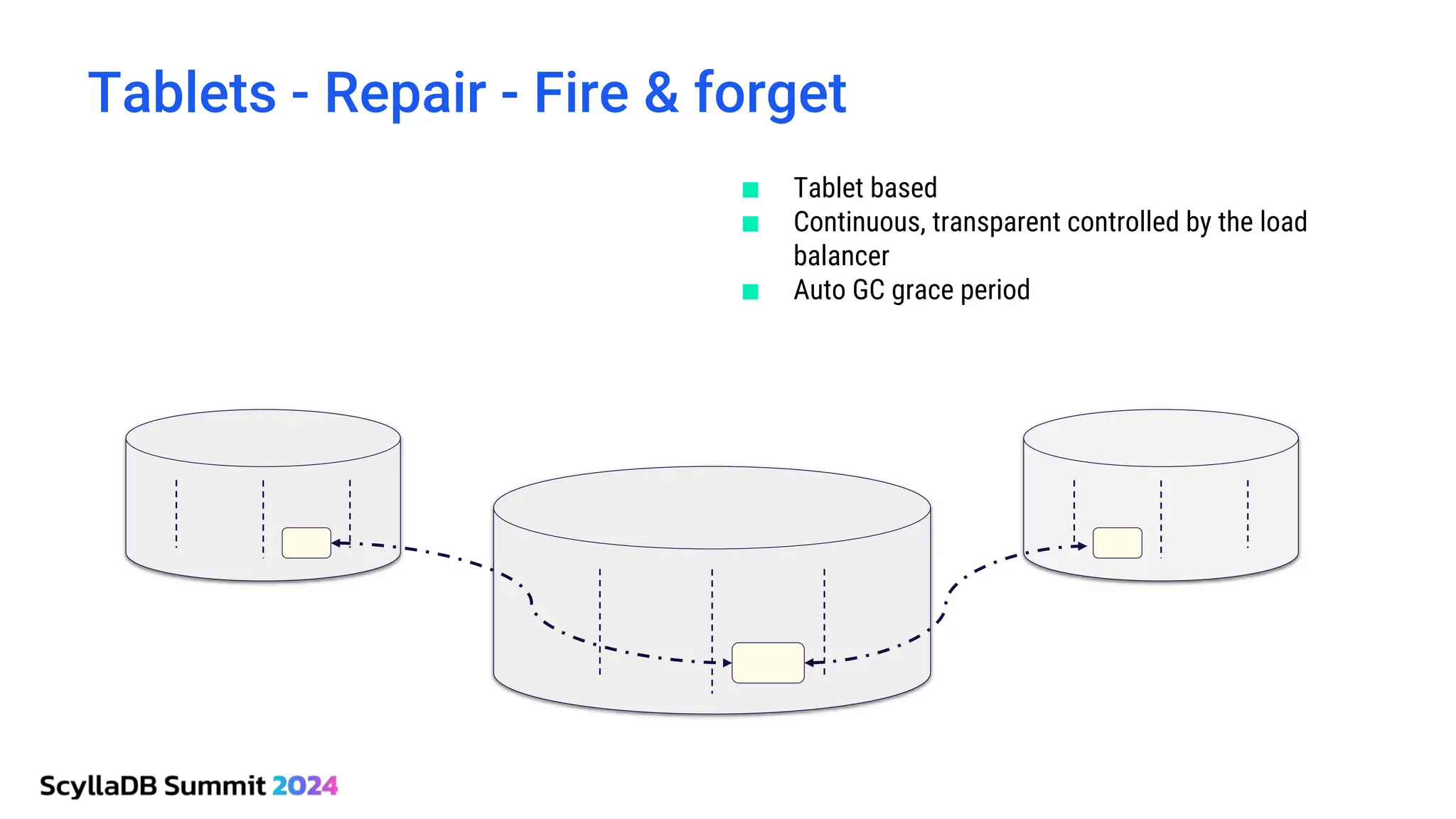
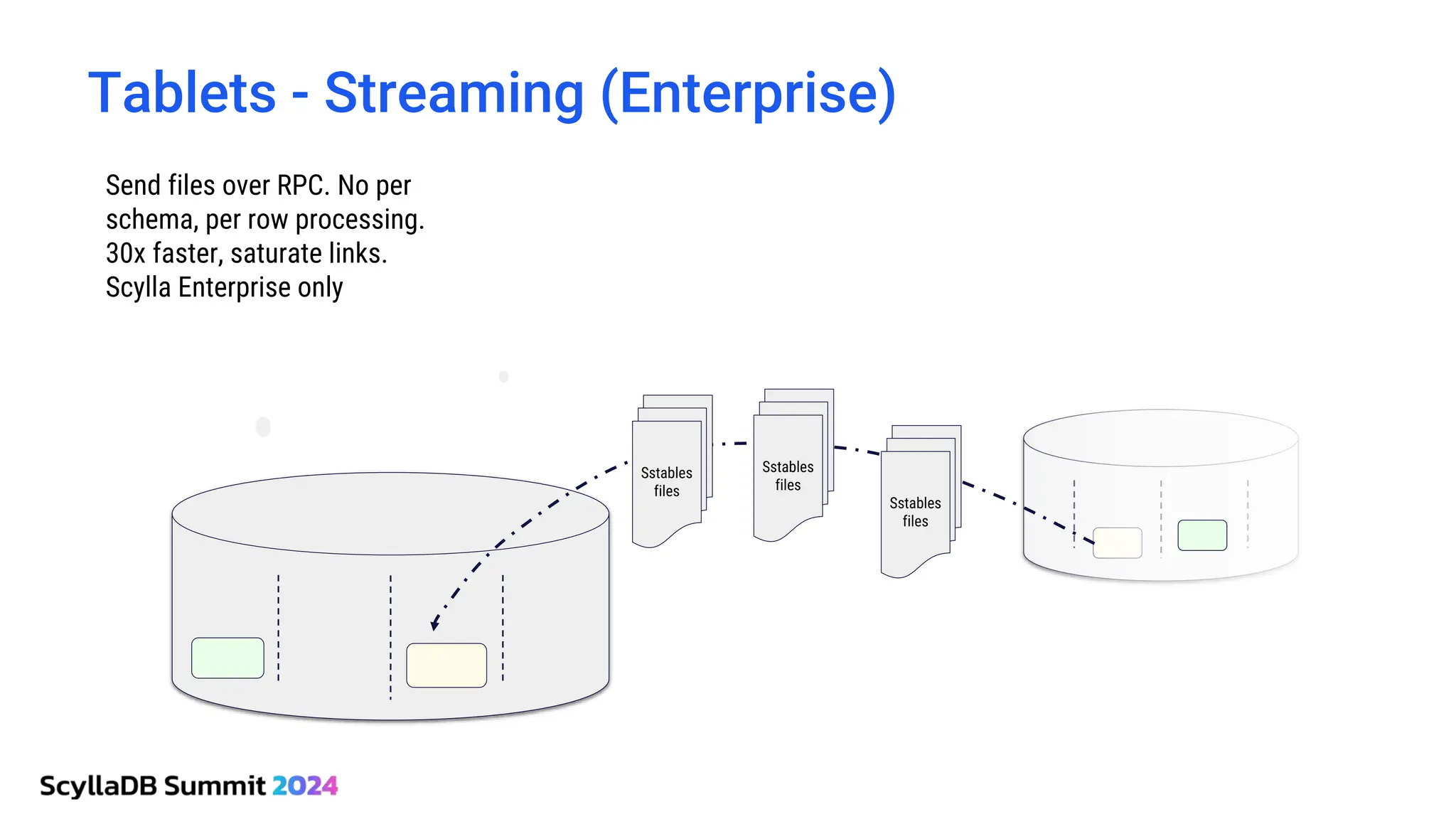
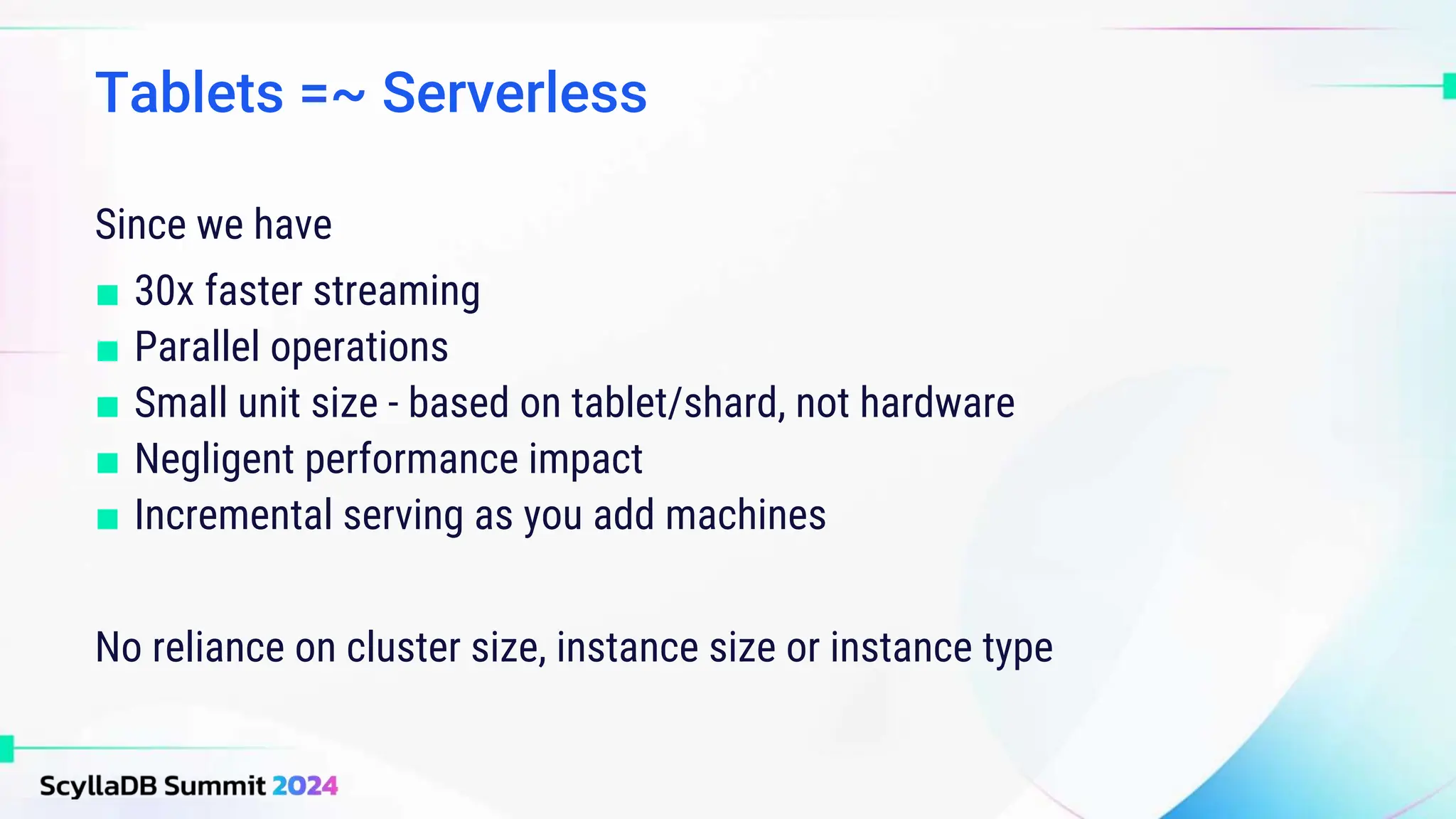
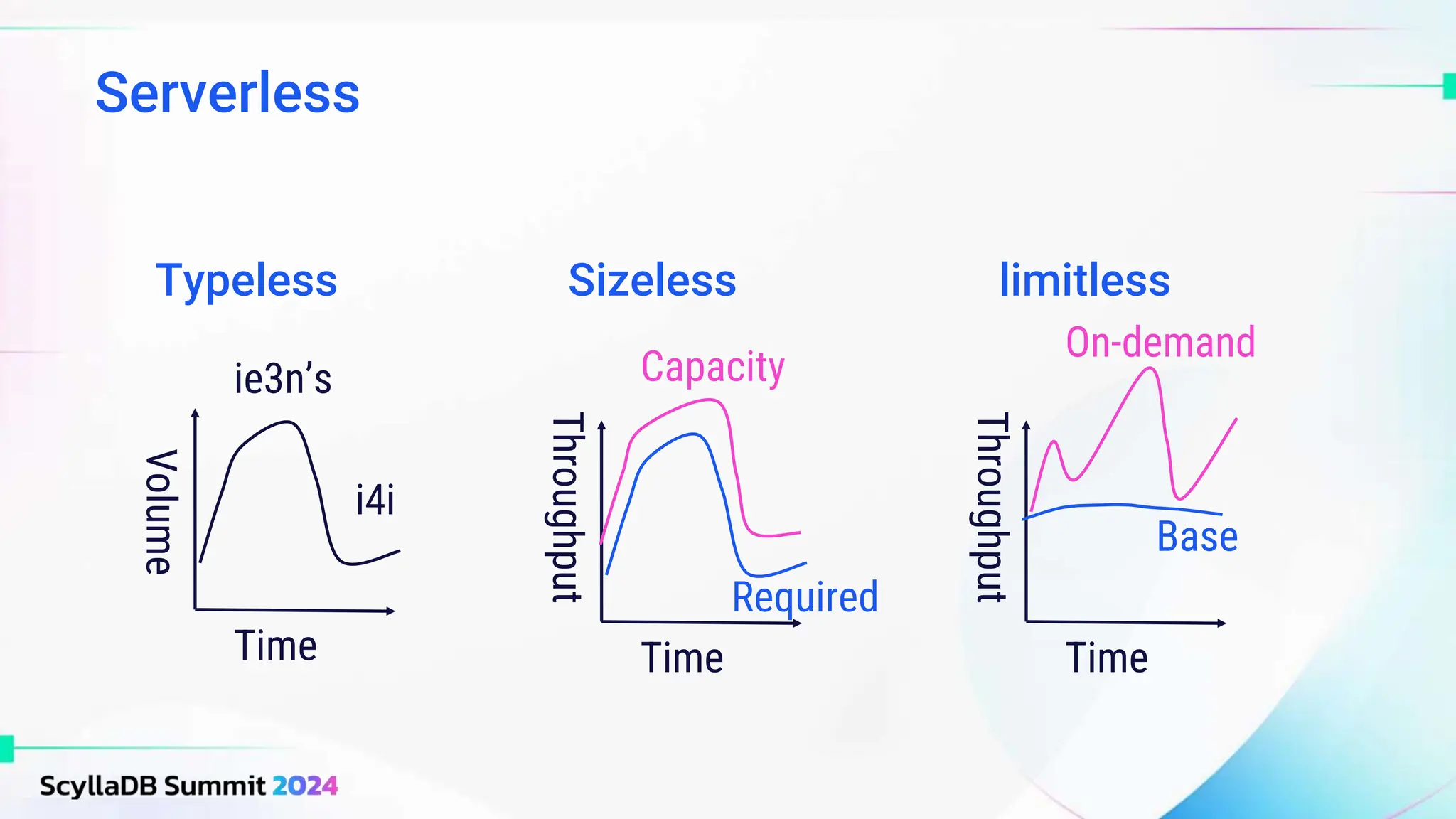
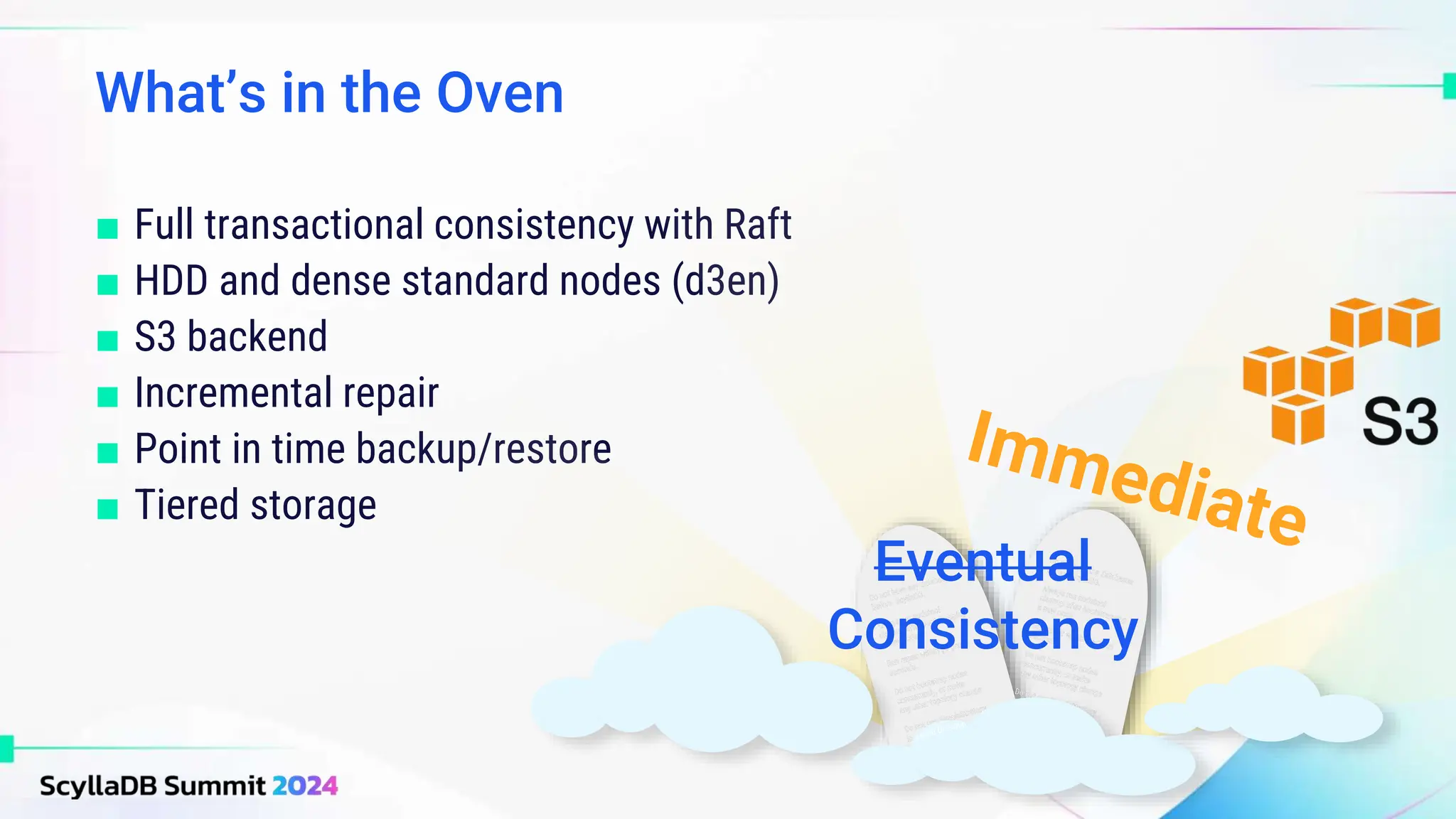
ScyllaDB, co-founded by Dor Laor, is highlighting its advancements in database technology, emphasizing high availability, disaster recovery, and scalability, while maintaining compatibility with Cassandra and DynamoDB. The document outlines new features in ScyllaDB 6.0 and upcoming innovations, including consistency improvements, efficient data ingestion, and enhanced performance benchmarks comparing ScyllaDB with MongoDB. The focus is on providing robust solutions for various industries while simplifying database operations and maintenance.