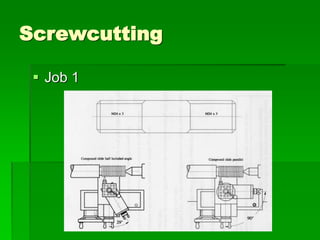
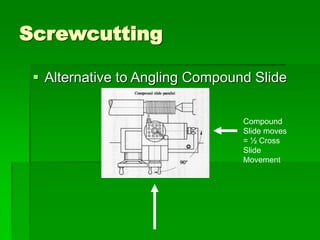
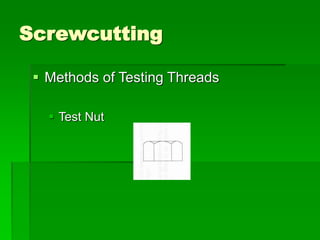
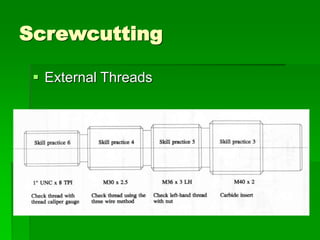
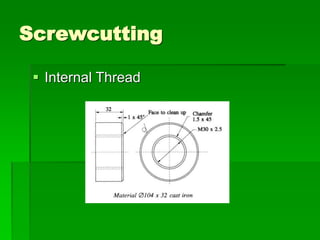
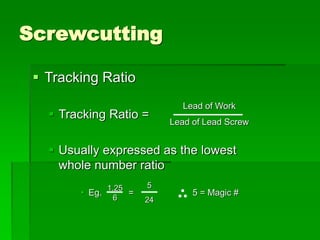
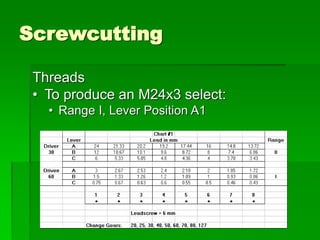
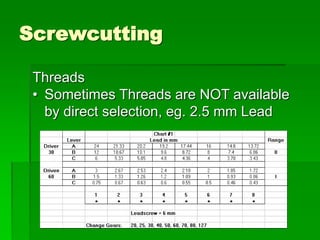
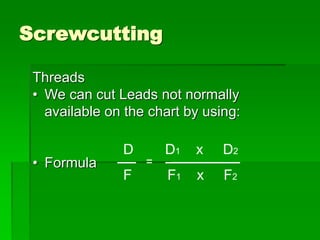
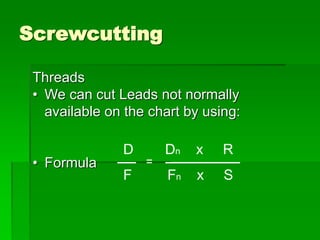
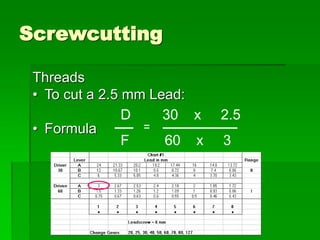
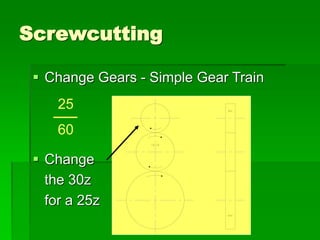
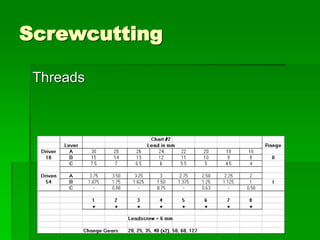
The document discusses different types of screw threads including Vee threads, buttress threads, square threads, and trapezoidal threads. It also covers screw thread terminology such as pitch, lead, and starts. Additionally, it describes methods of screw cutting including how to calculate the number of starts and testing threads using methods such as a test nut, thread calipers, or three wire method. Tracking ratios and various methods for tracking threads are also outlined.