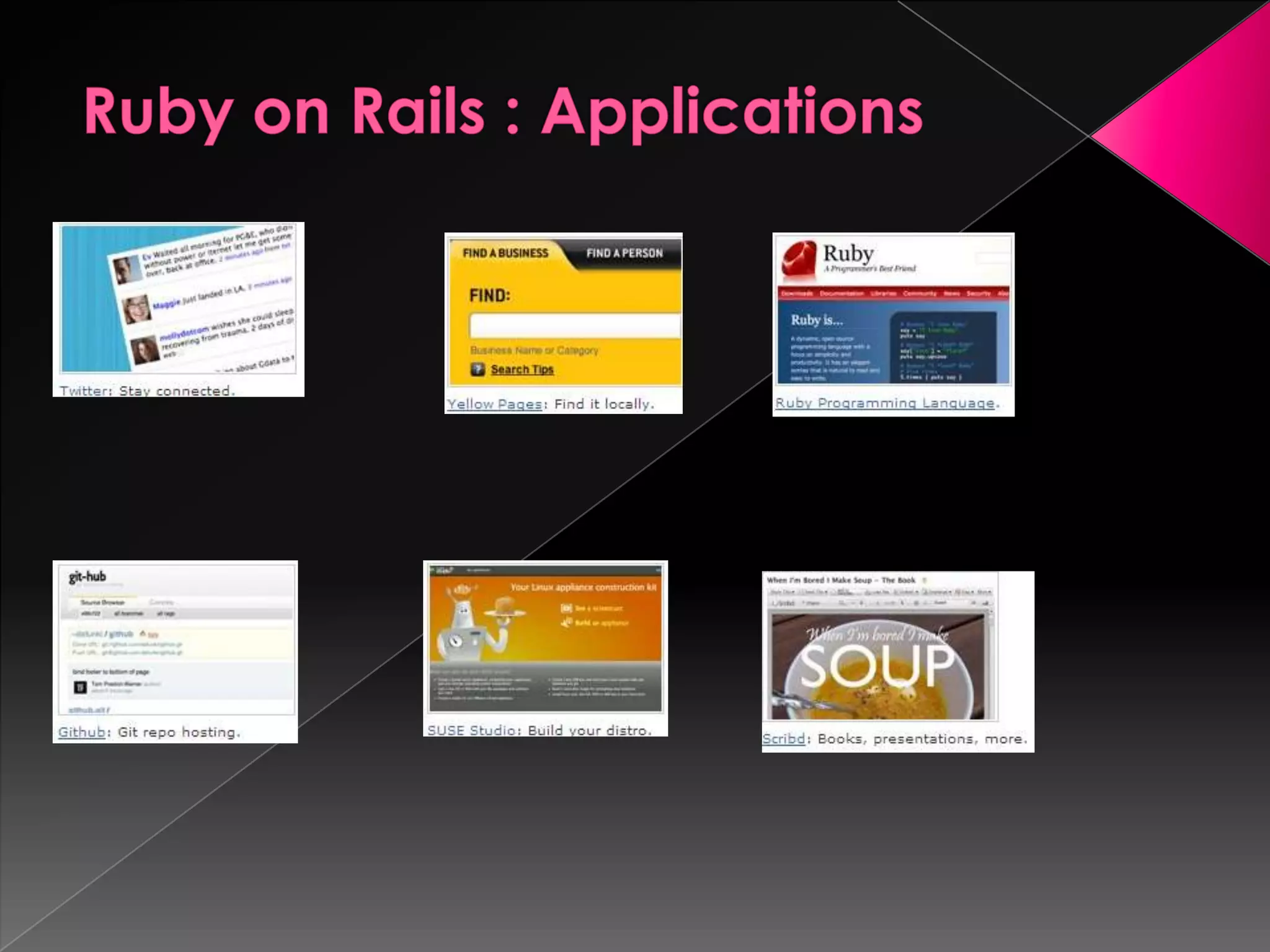
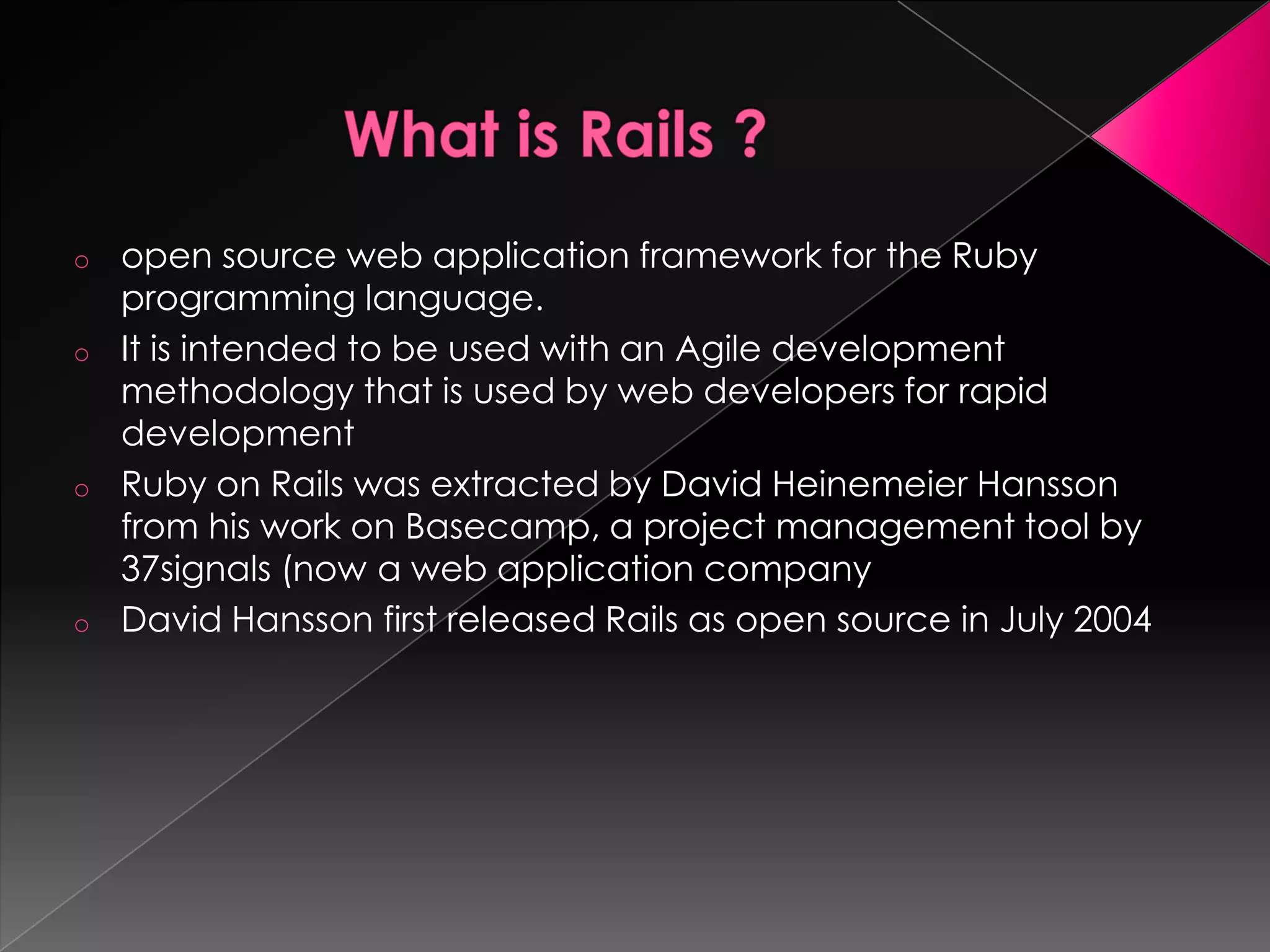
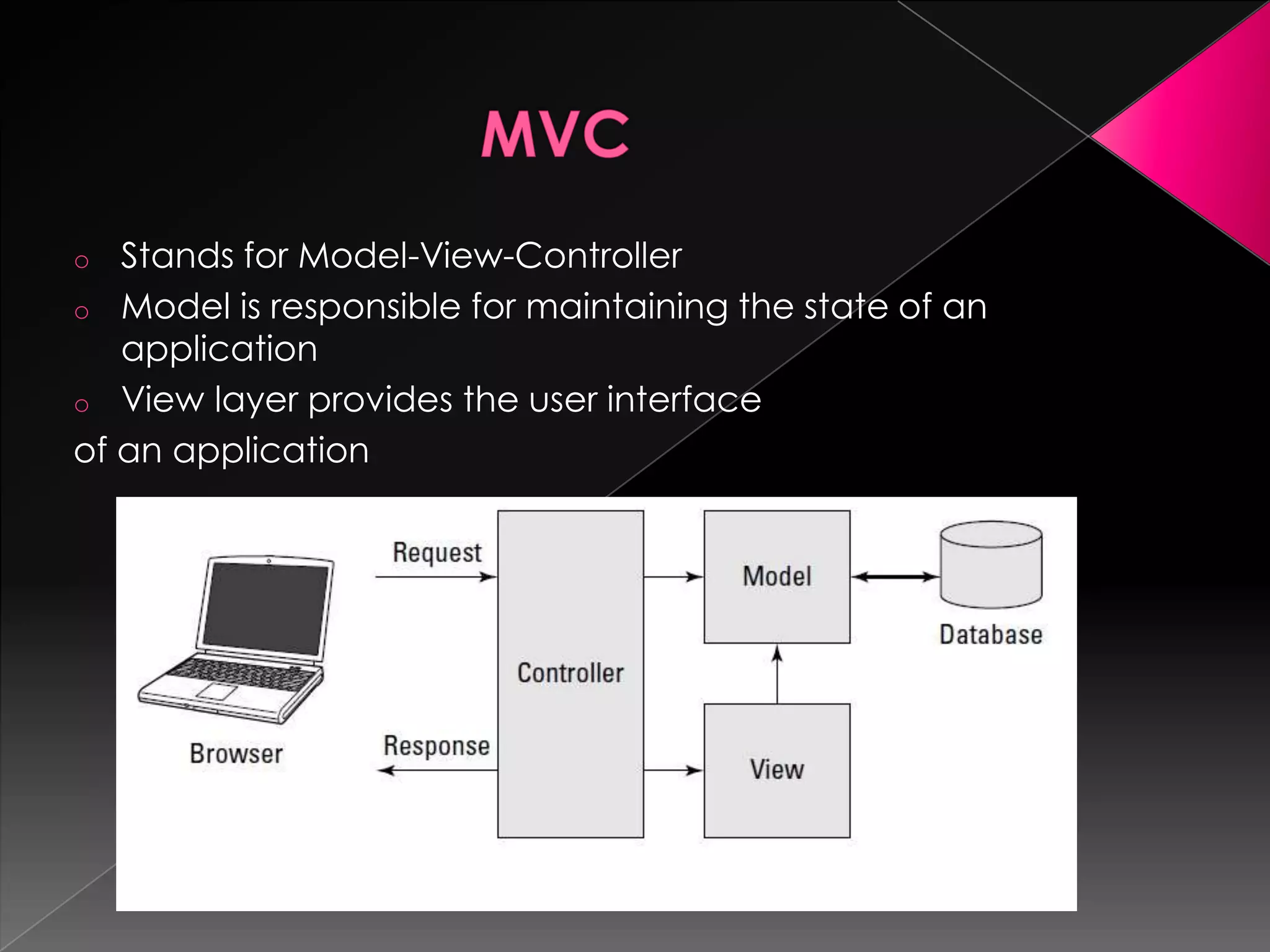
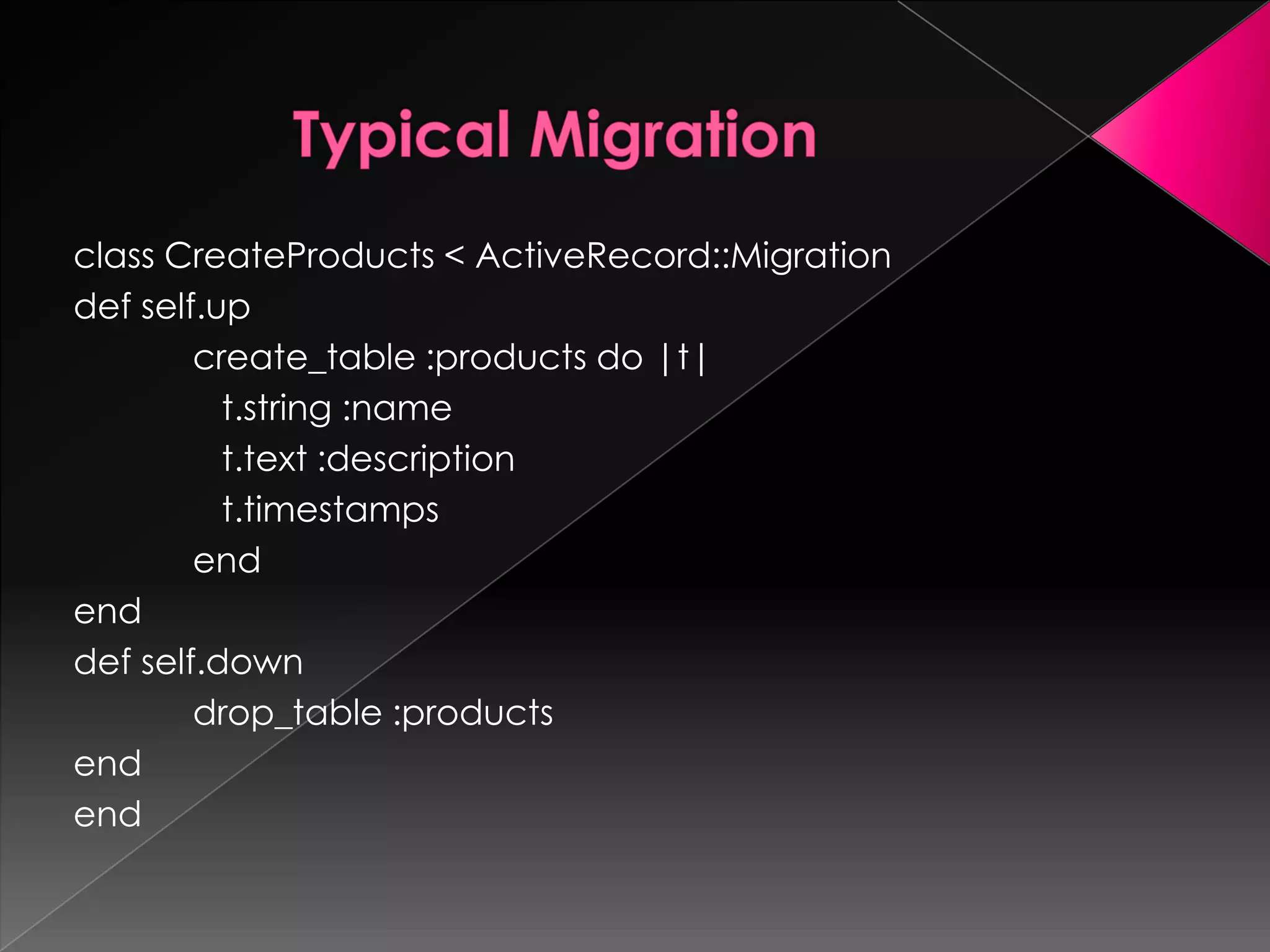
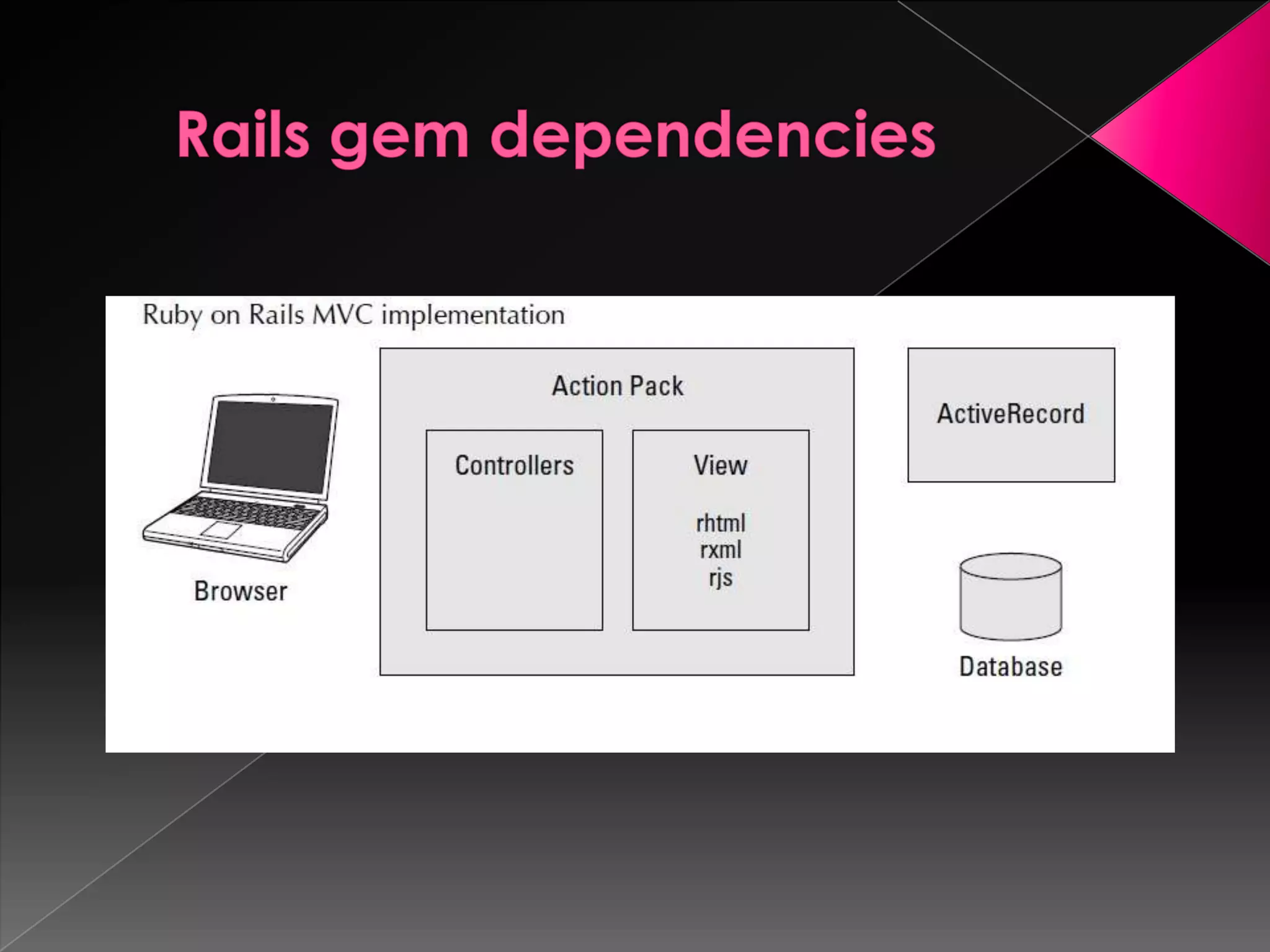
Ruby is a dynamic, reflective, and general-purpose object-oriented programming language designed by Yukihiro Matsumoto, inspired by languages like Perl and Smalltalk. It supports multiple programming paradigms and has led to the development of Ruby on Rails, a web application framework that emphasizes rapid development and agile methodologies. The document further explores key Ruby concepts, the MVC paradigm, and practical tools for database management within Rails applications.