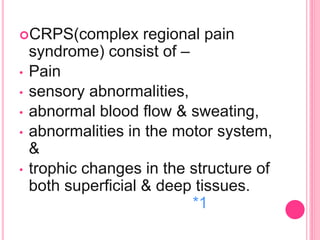
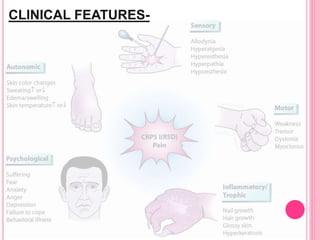
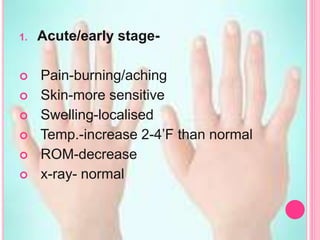
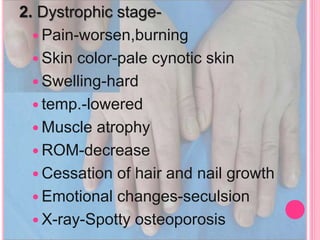
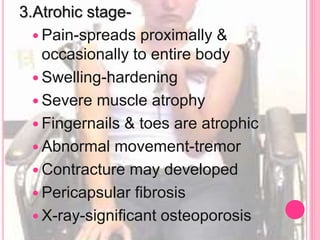
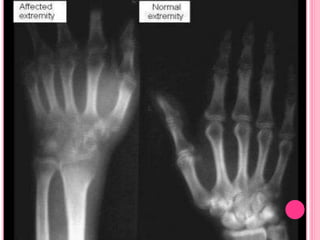
RSD, also known as complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), is a chronic pain condition that usually affects the limbs. It is characterized by pain, sensory abnormalities, changes in skin temperature and color, abnormal sweating, and motor and trophic changes. RSD typically develops after an injury or trauma and causes pain severely disproportionate to the inciting event. It is diagnosed based on patient history and symptoms, with supportive tests like bone scans and MRI. Treatment involves a multidisciplinary approach including medications, physical therapy, psychological support, and potentially nerve blocks or spinal cord stimulation.