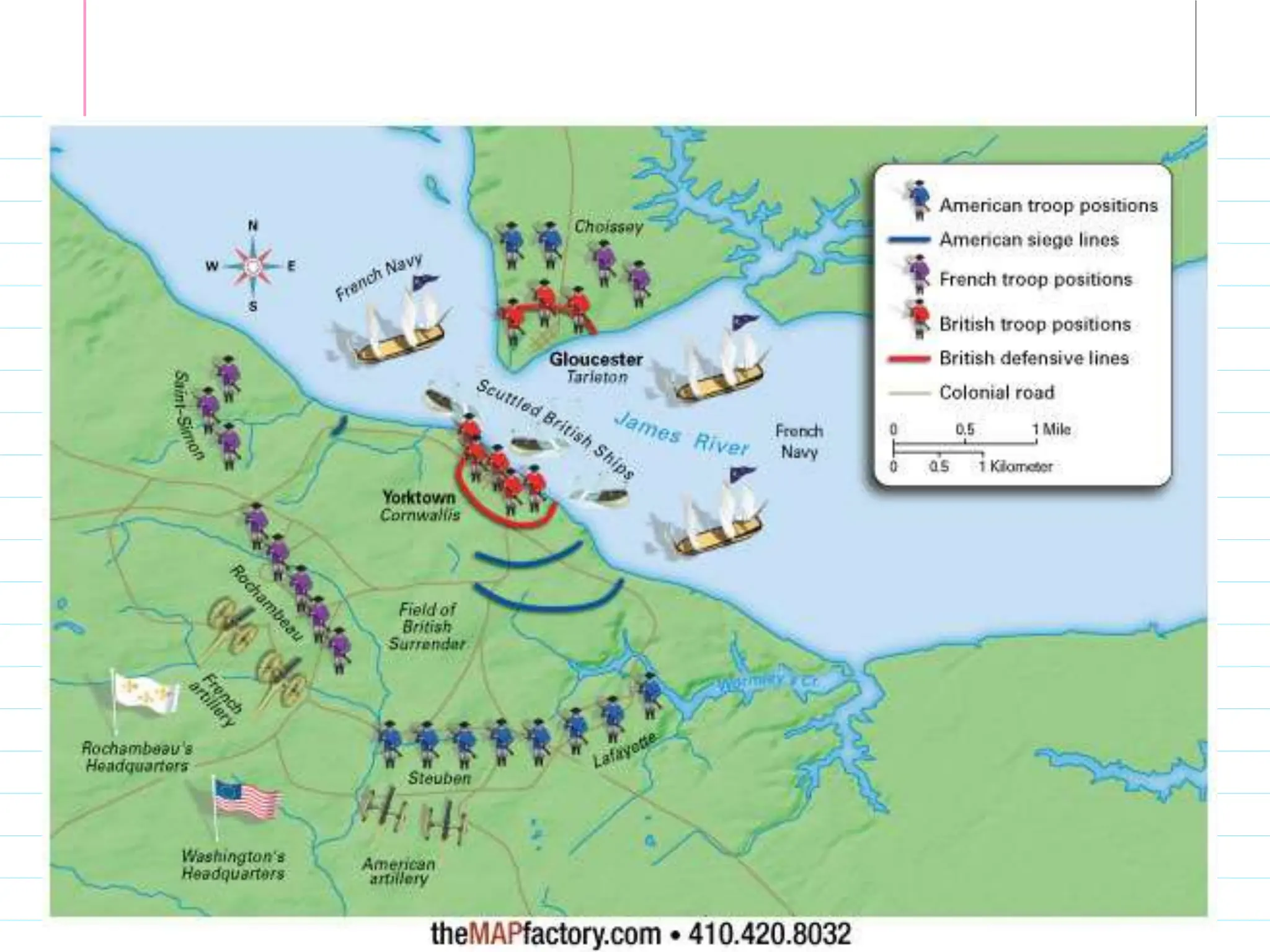
The American Revolutionary War began as a result of tensions between the American colonies and Britain following the French and Indian War. Britain imposed taxes on the colonies to help pay war debts, angering colonists who believed in "no taxation without representation." Protests and boycotts of British goods escalated, leading to armed conflict at Lexington and Concord in 1775. The Second Continental Congress formed the Continental Army under George Washington. Although the British captured New York, Washington later won key victories at Trenton and Saratoga. France entered the war as an American ally in 1778 following these successes. The British surrendered at Yorktown in 1781, leading to American independence and the 1783 Treaty of Paris.