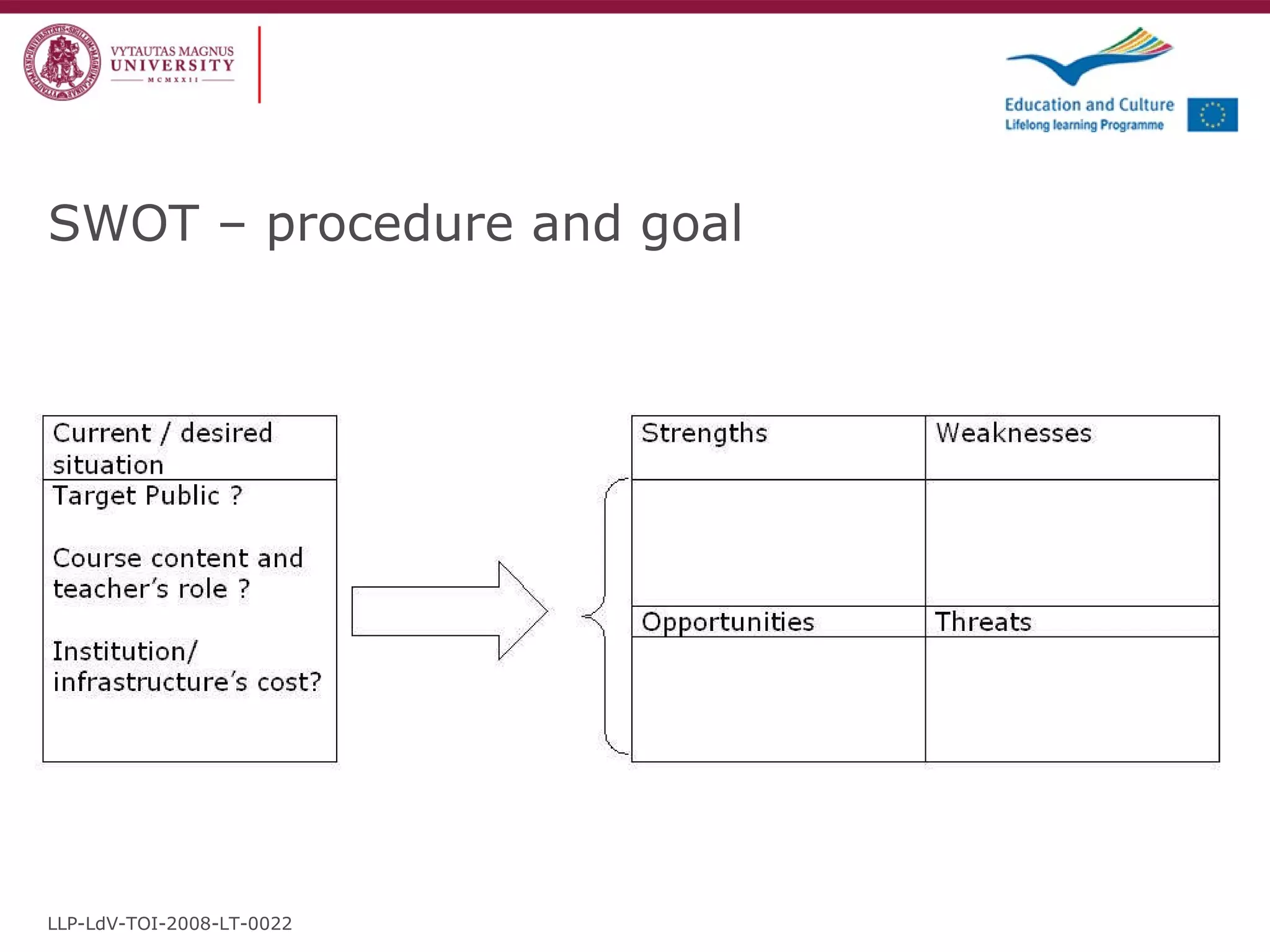
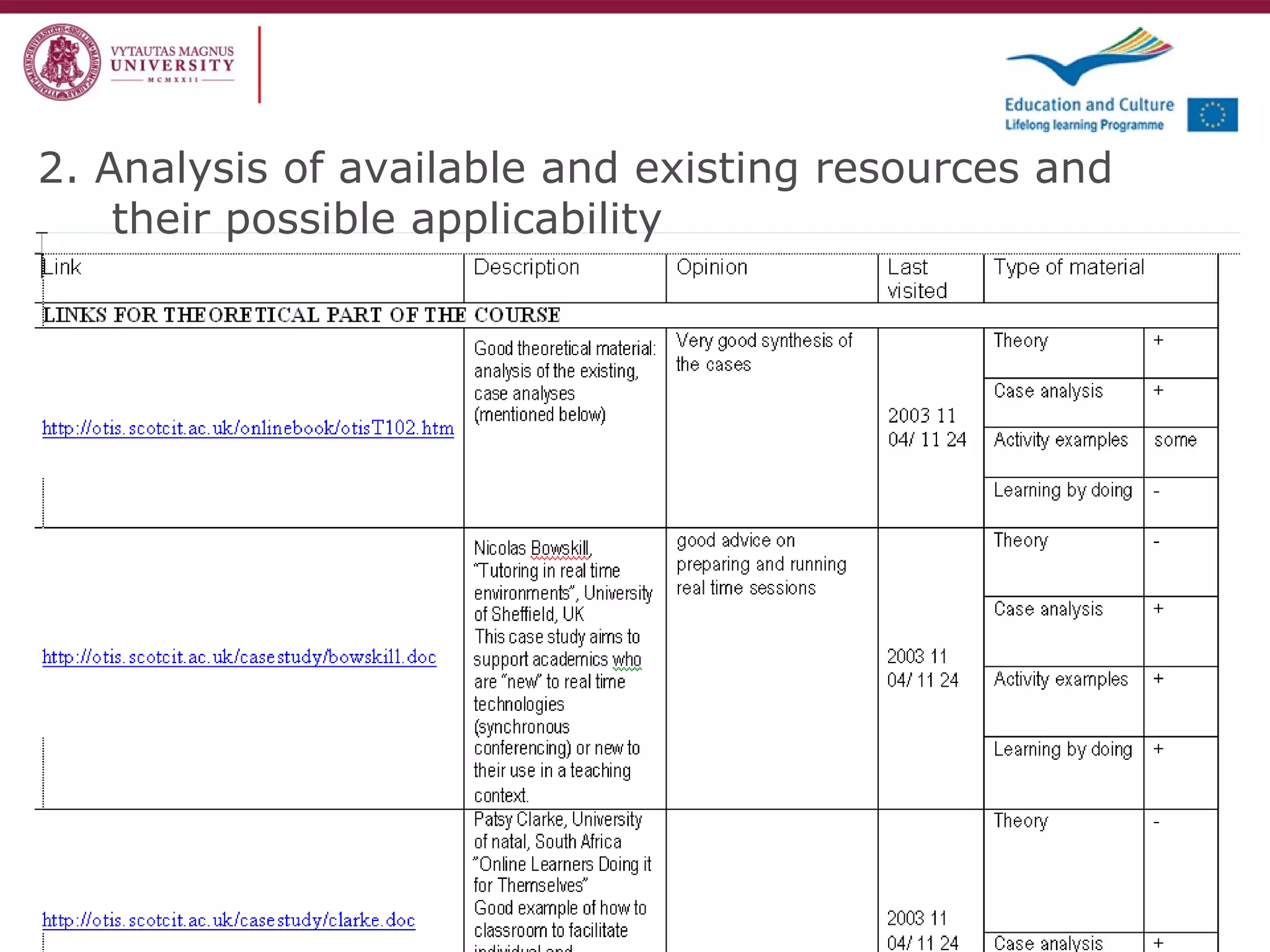
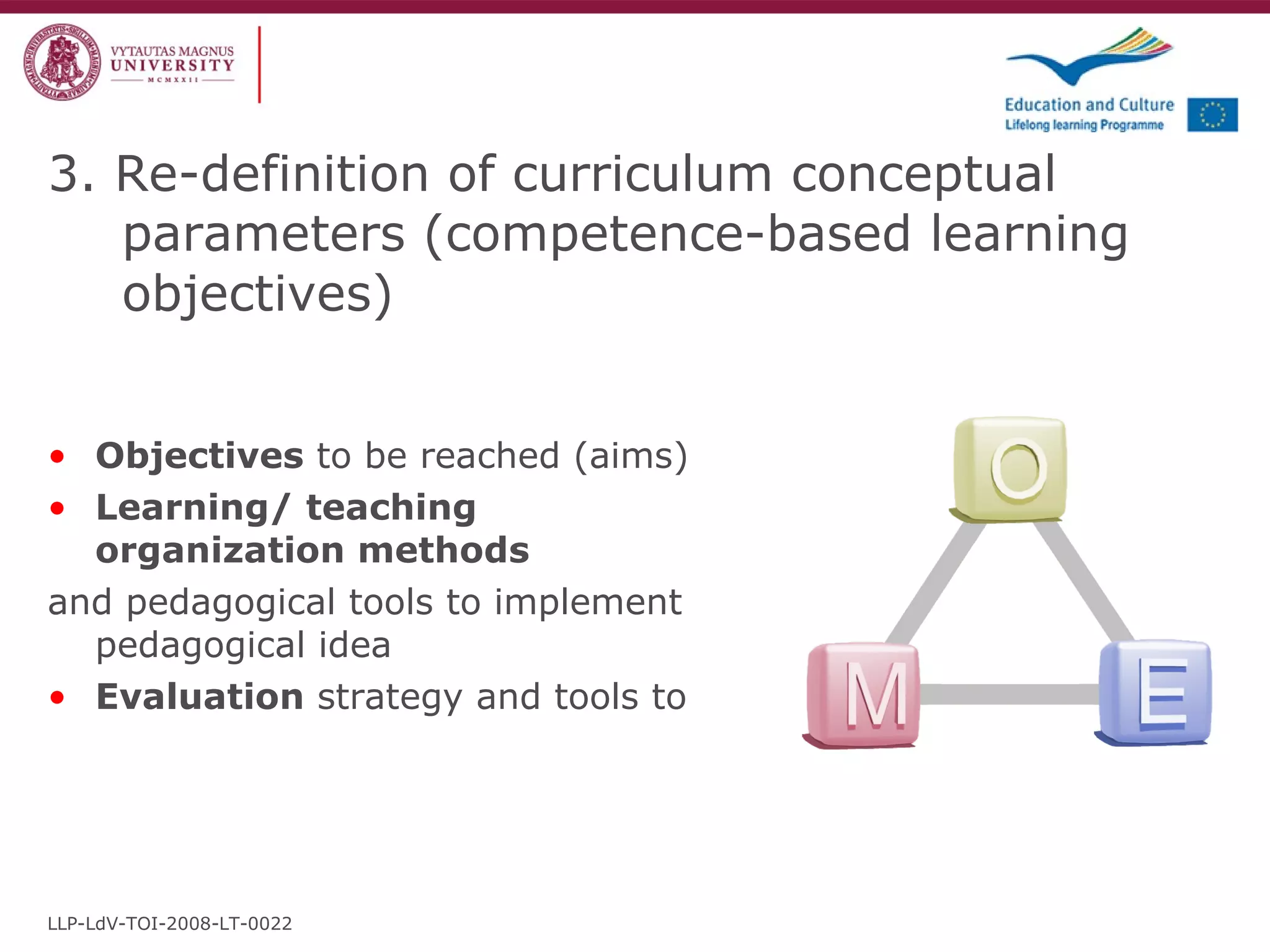
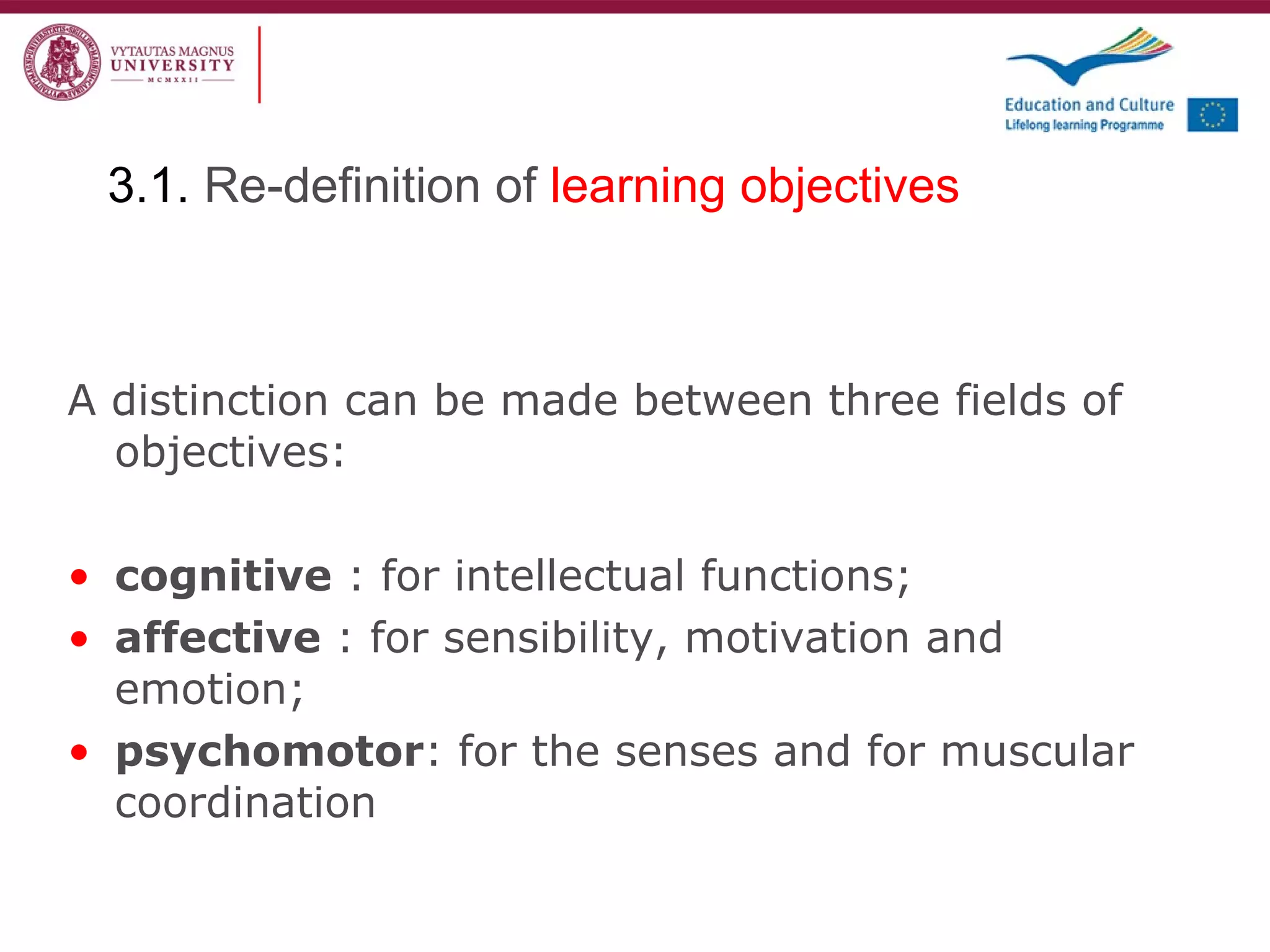
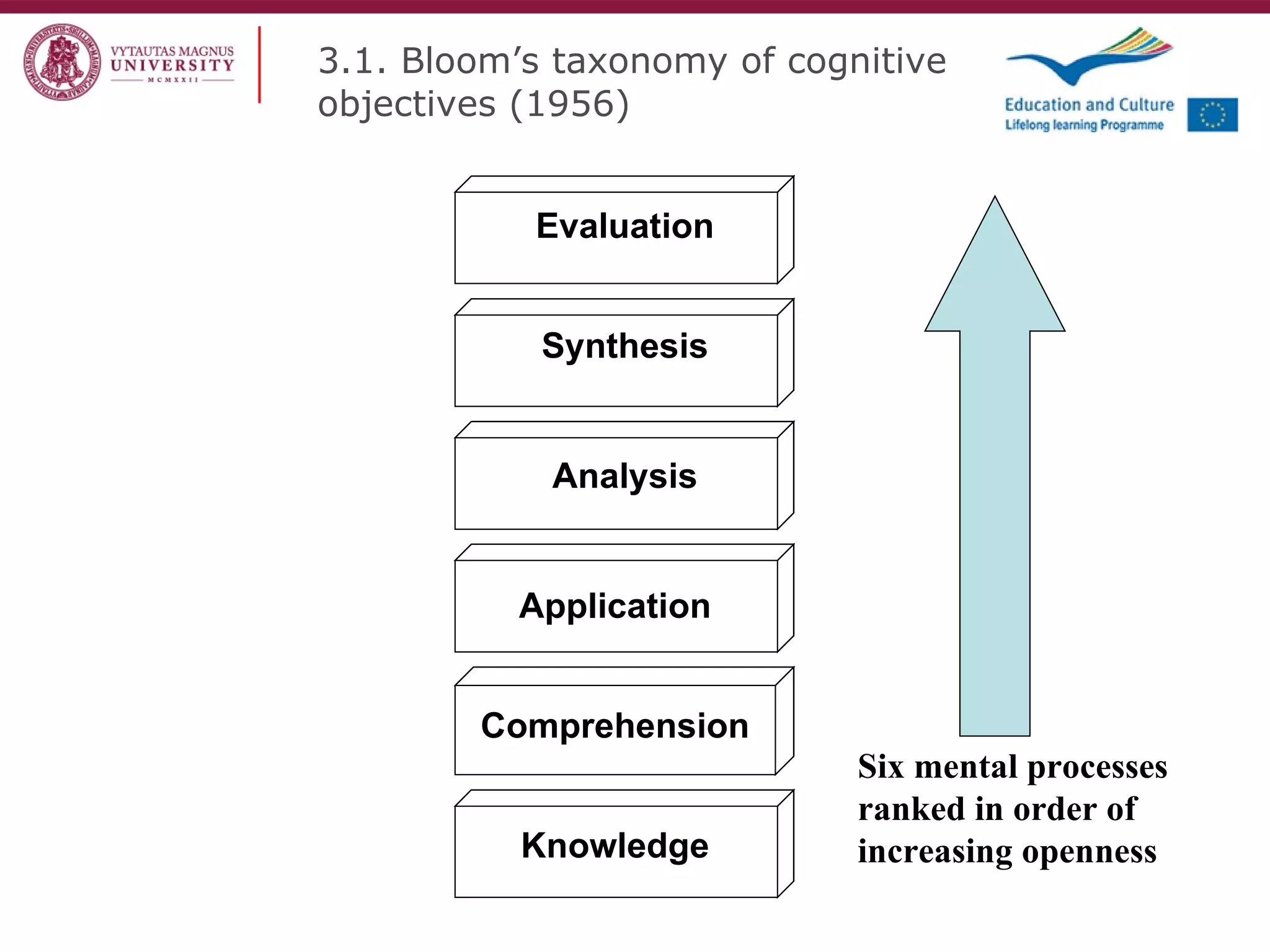
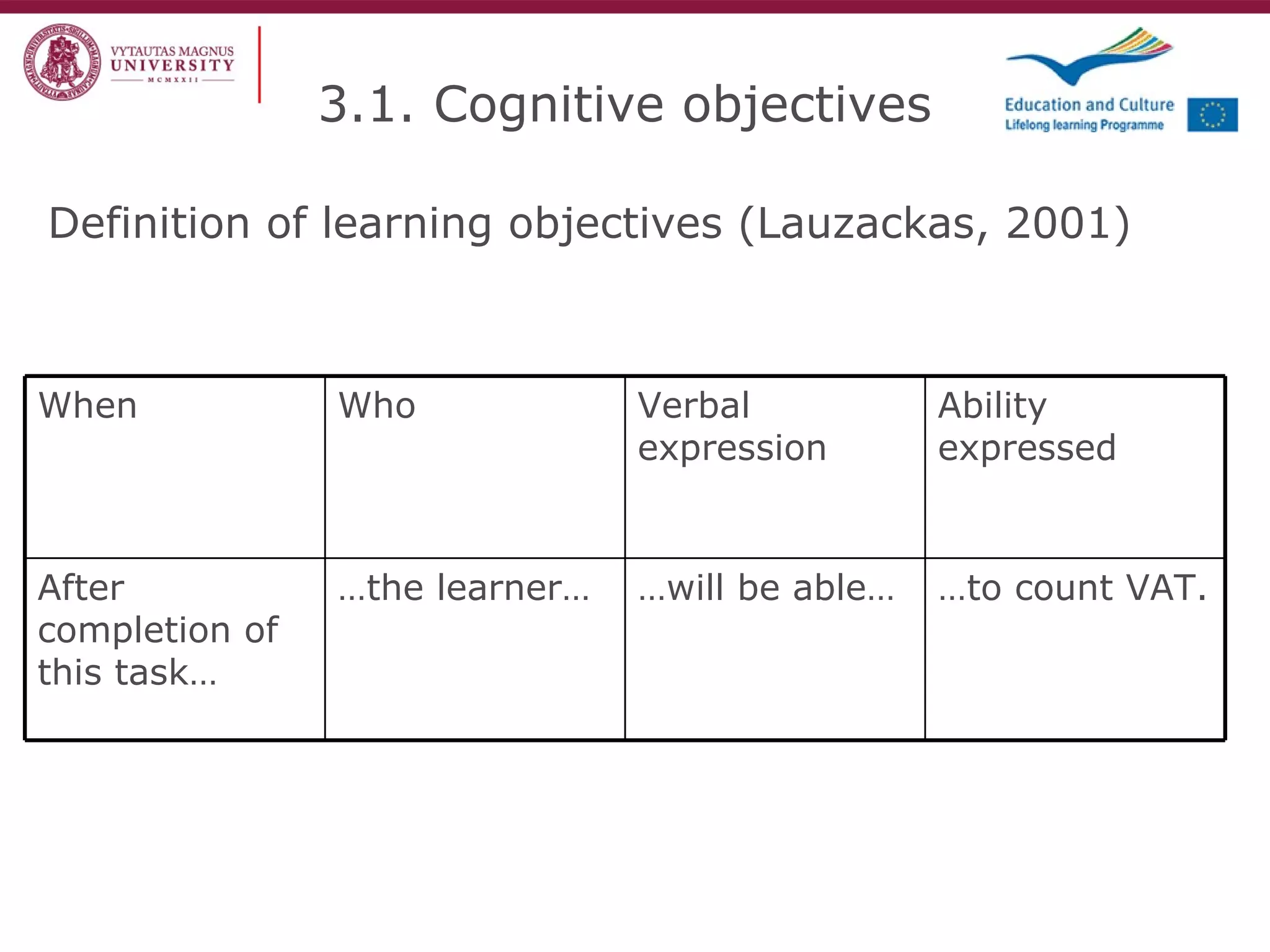
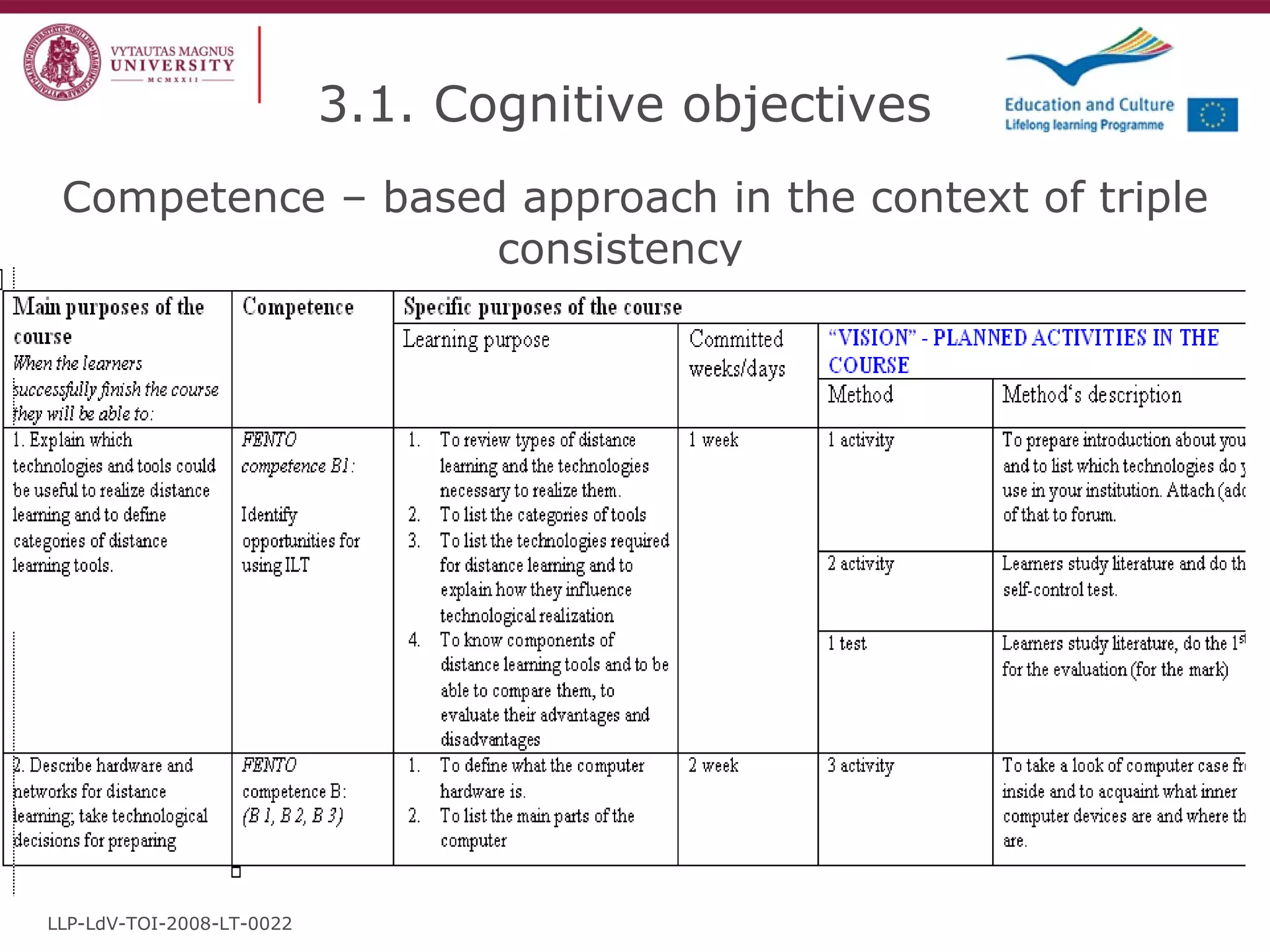
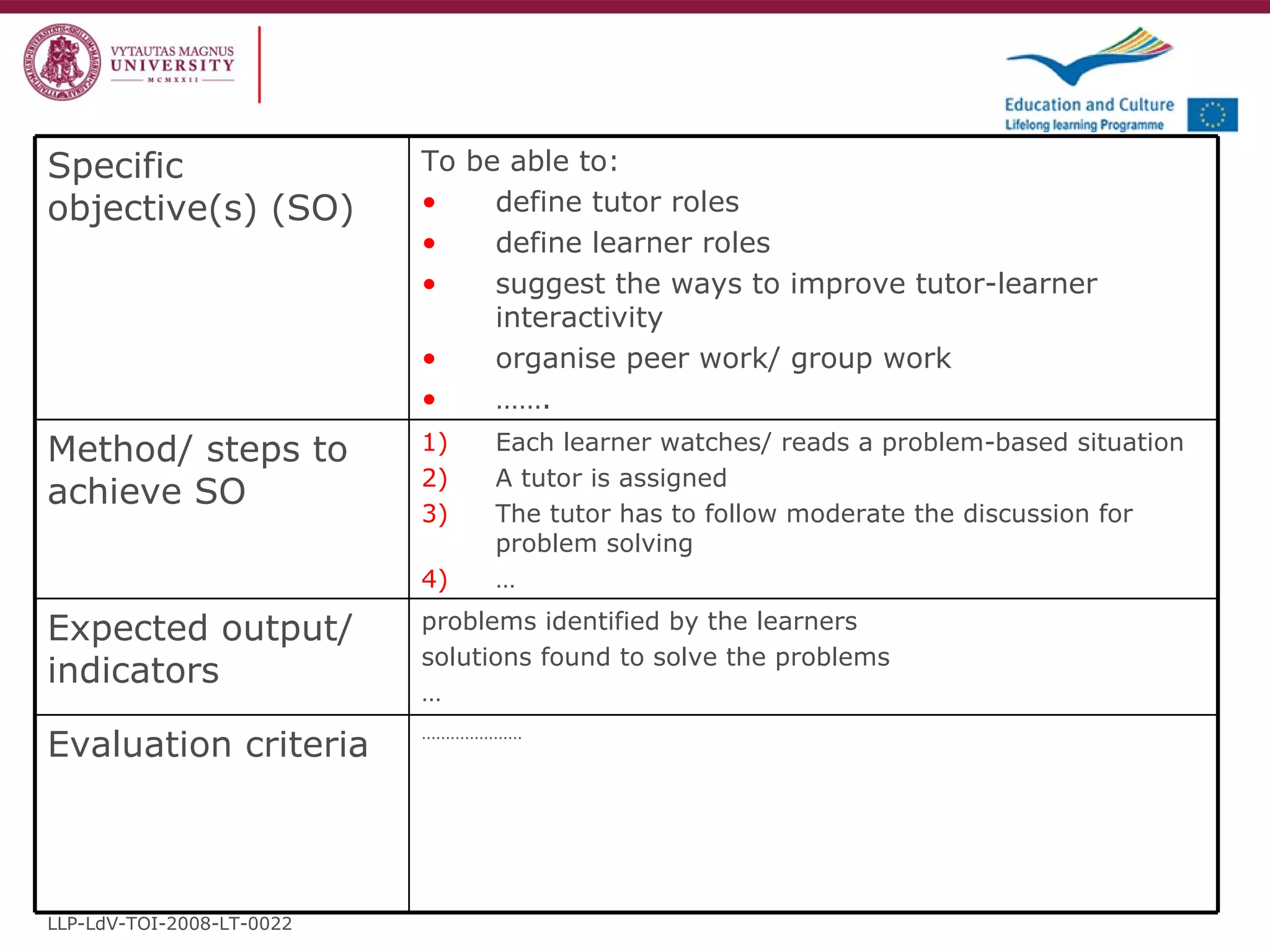
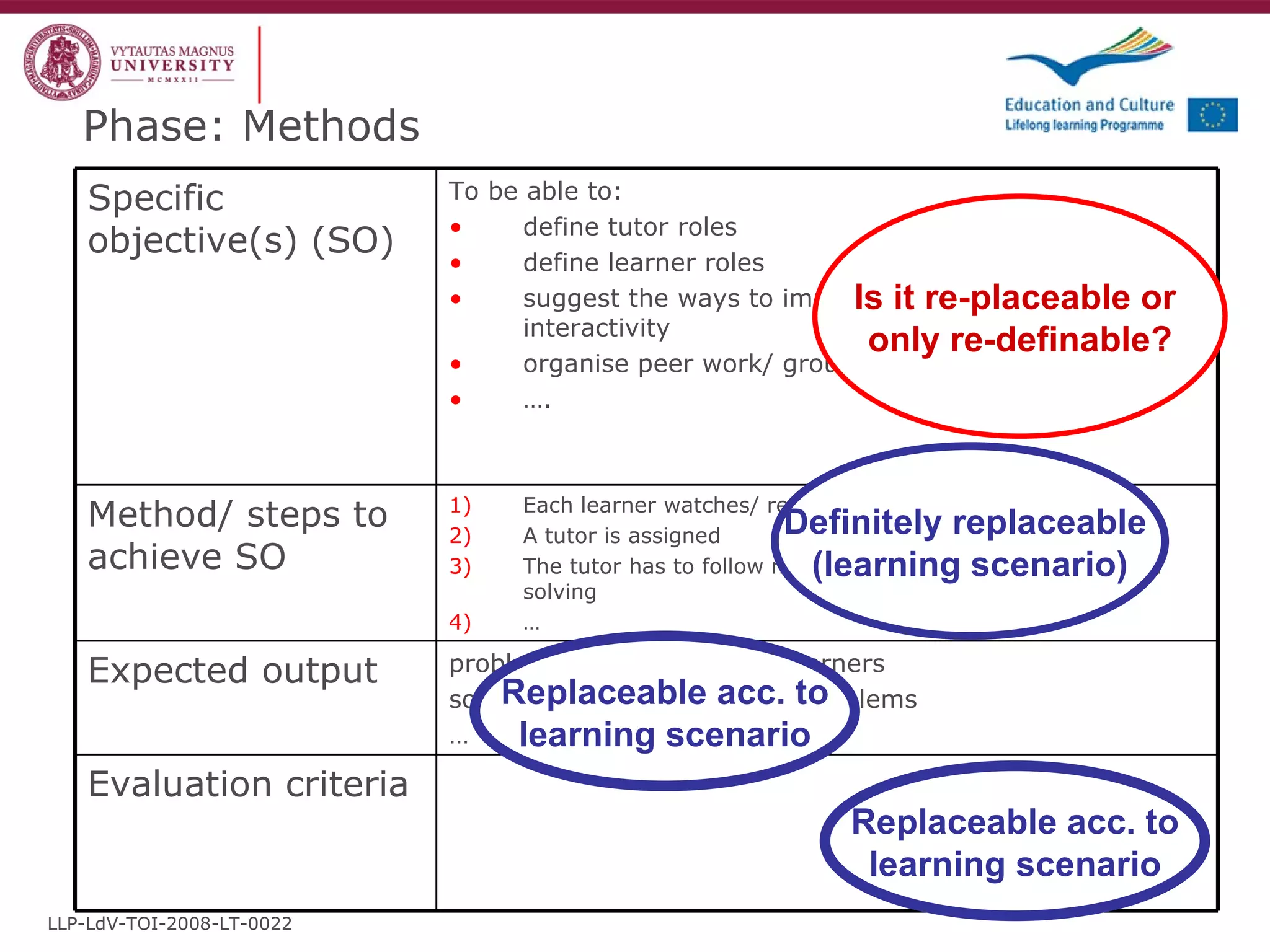
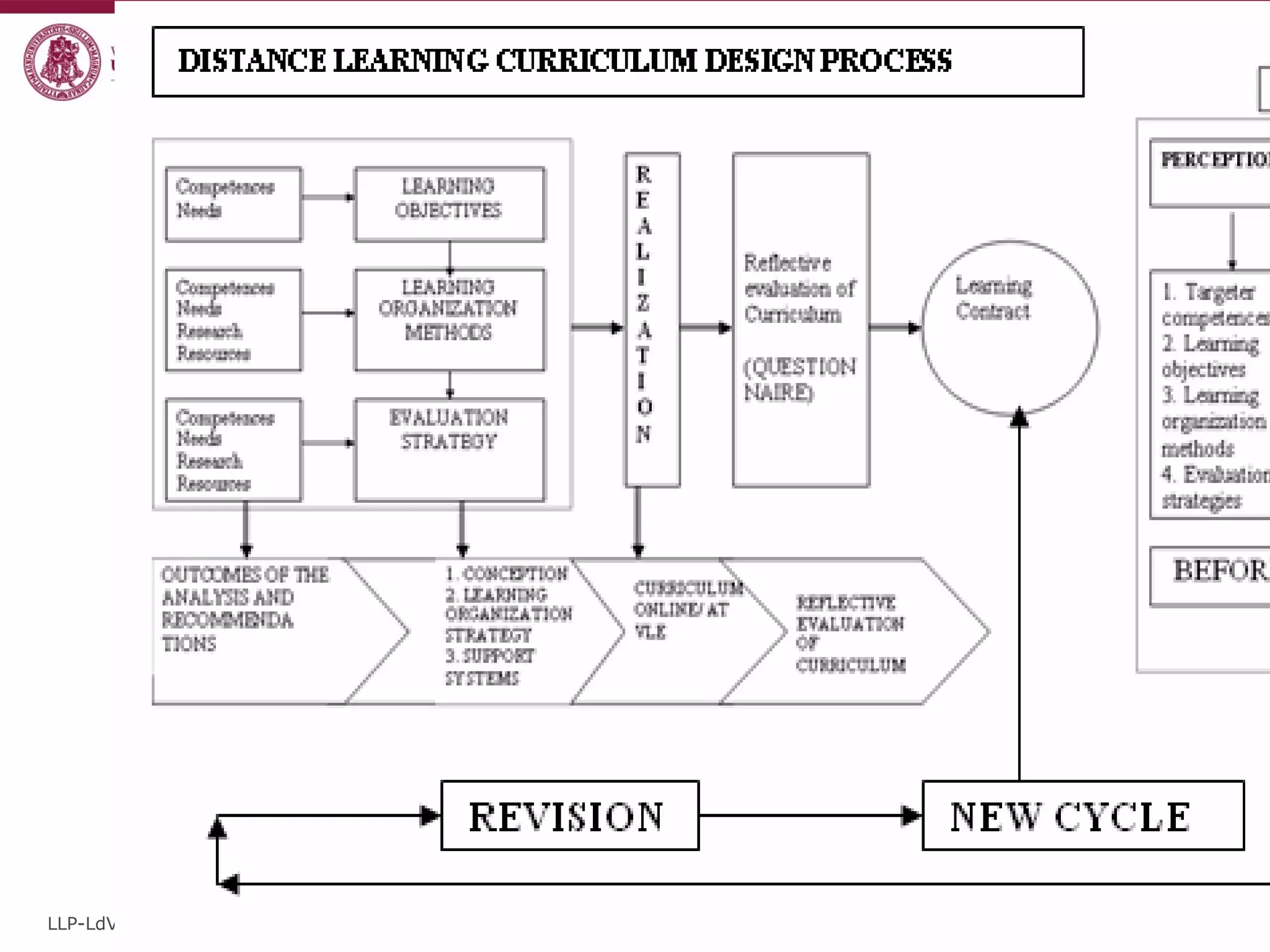
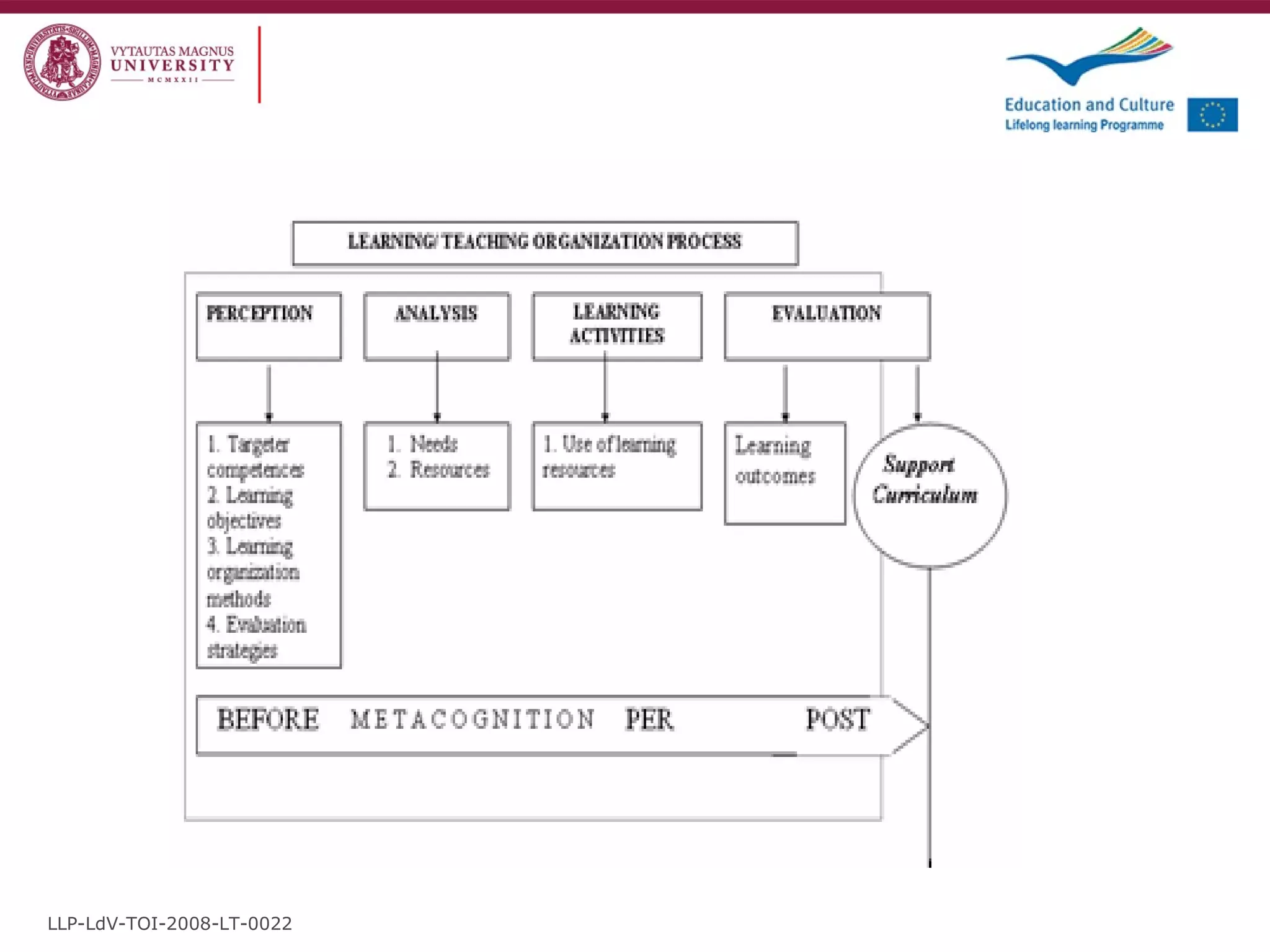
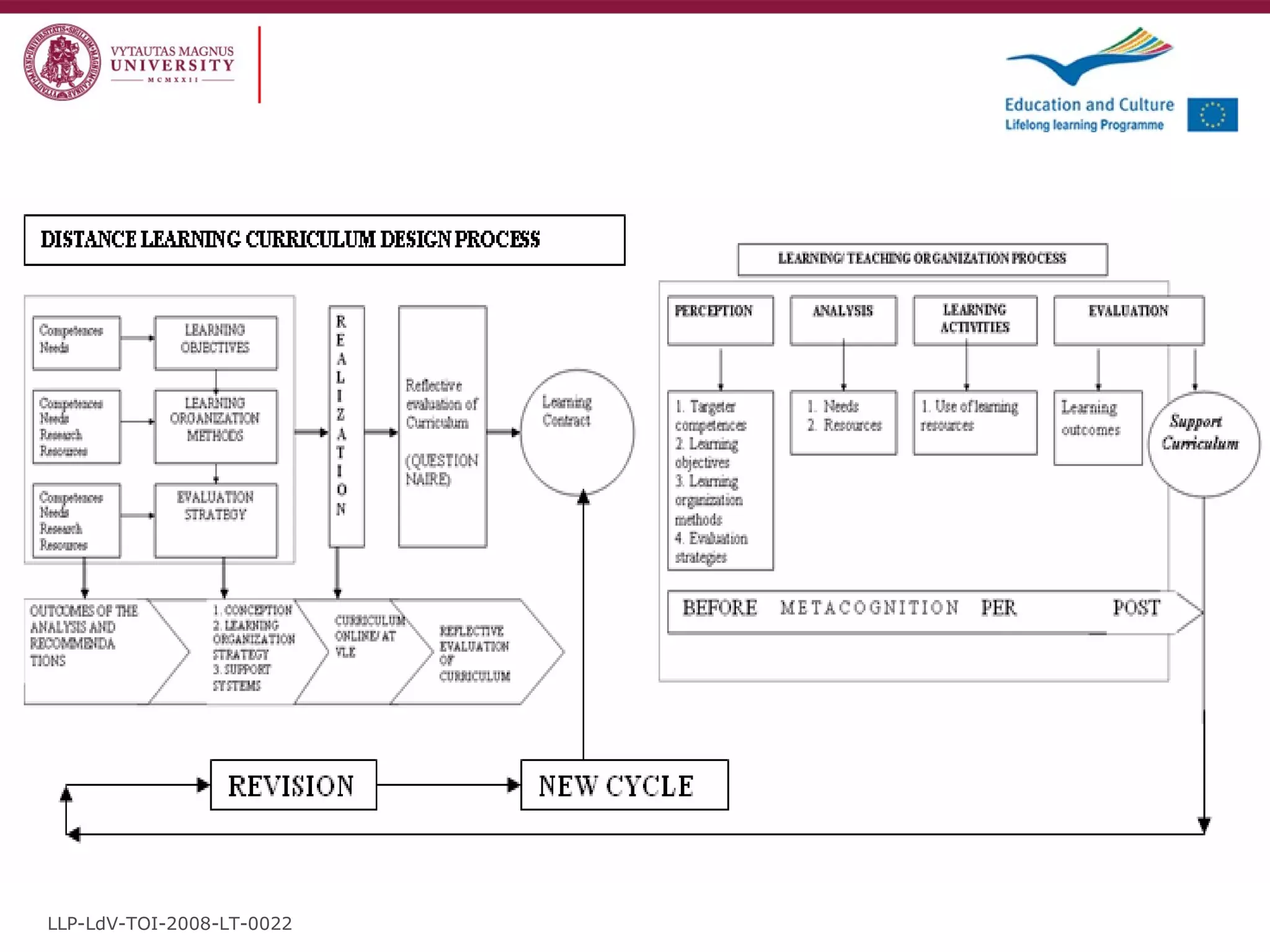
The document discusses the REVIVE project which aims to review and revive existing vocational education and training (VET) curriculum. Specifically, it seeks to:
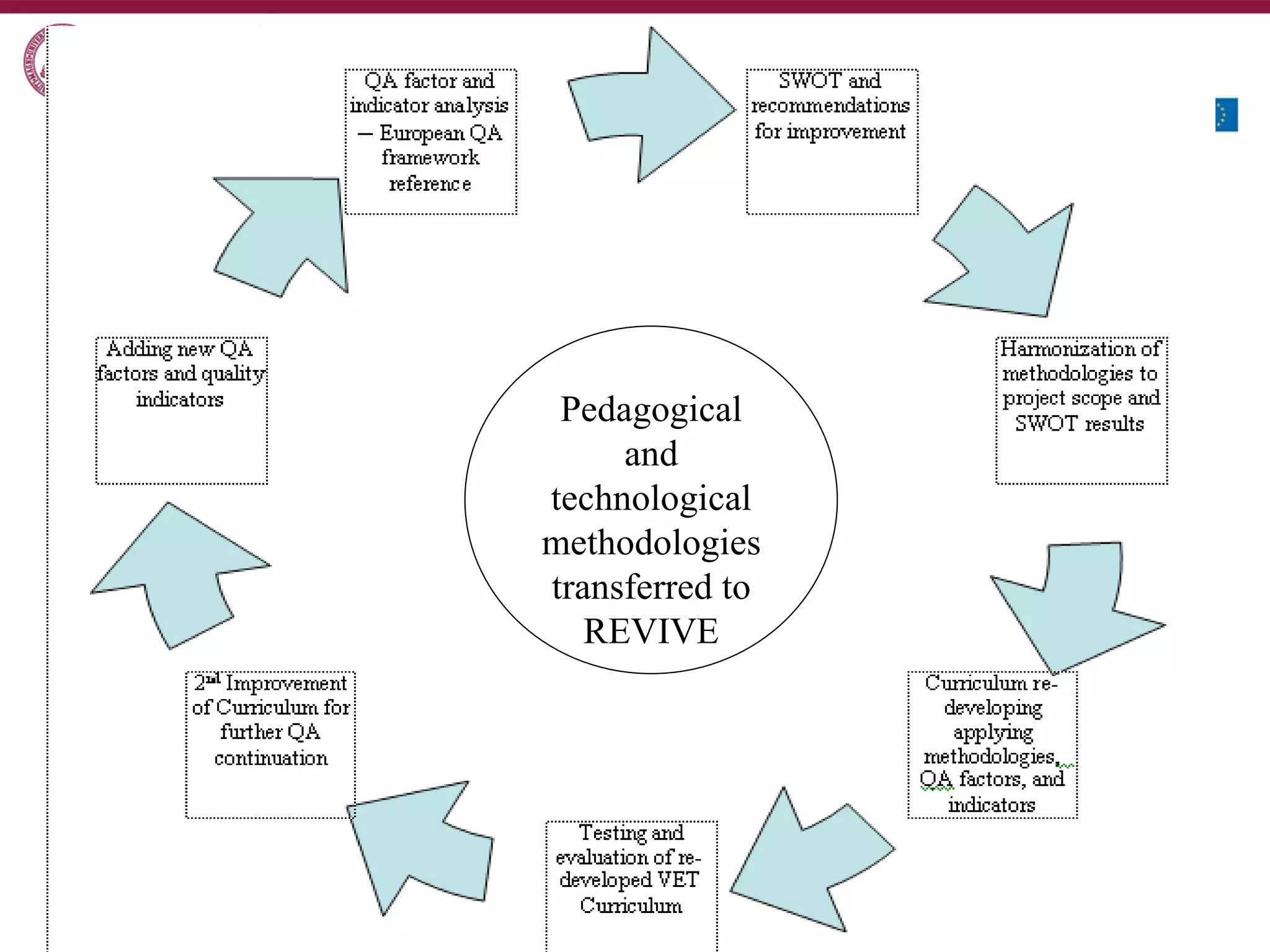
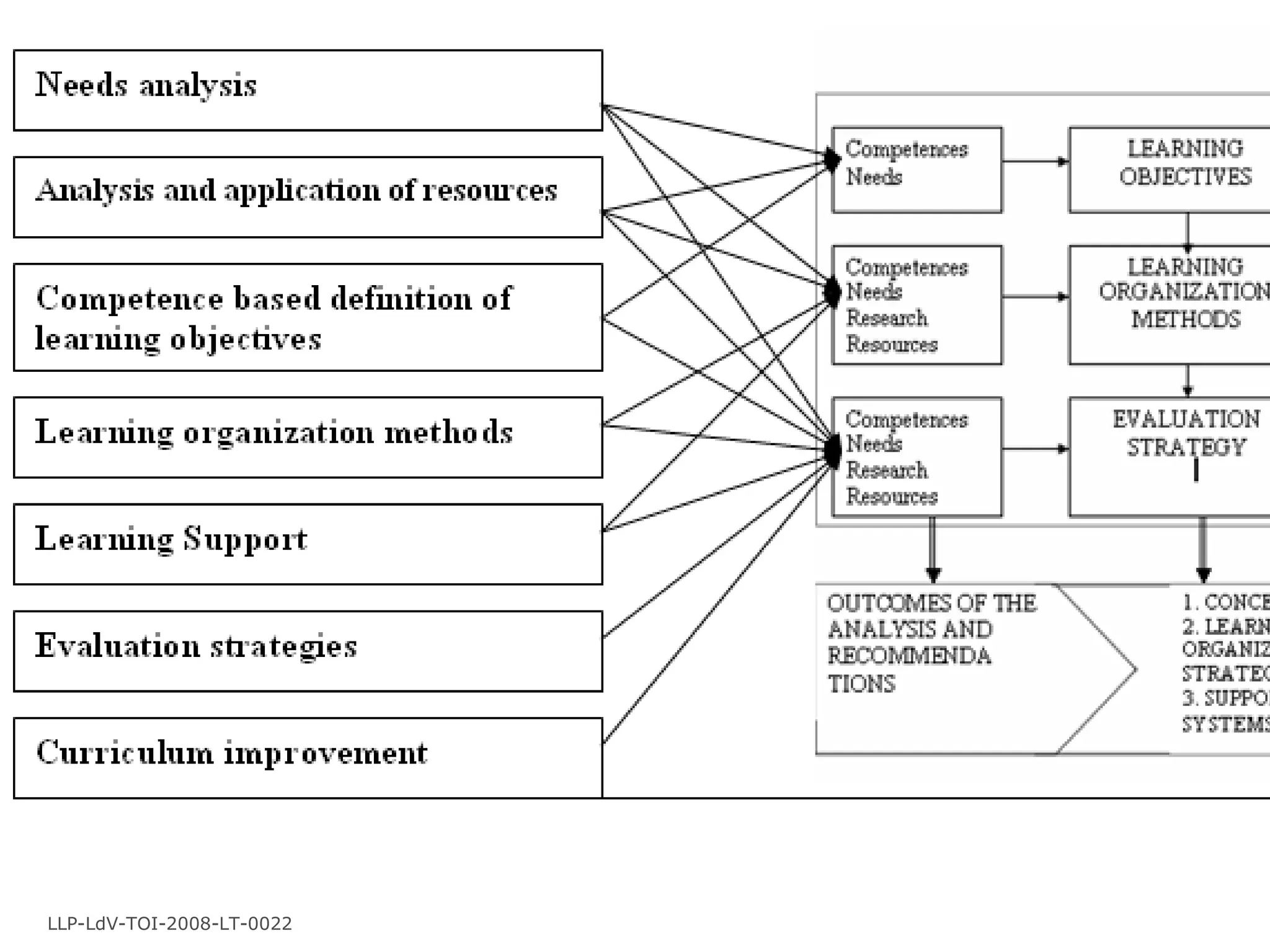
1) Apply a methodology to ensure quality of VET curriculum at the institutional level.
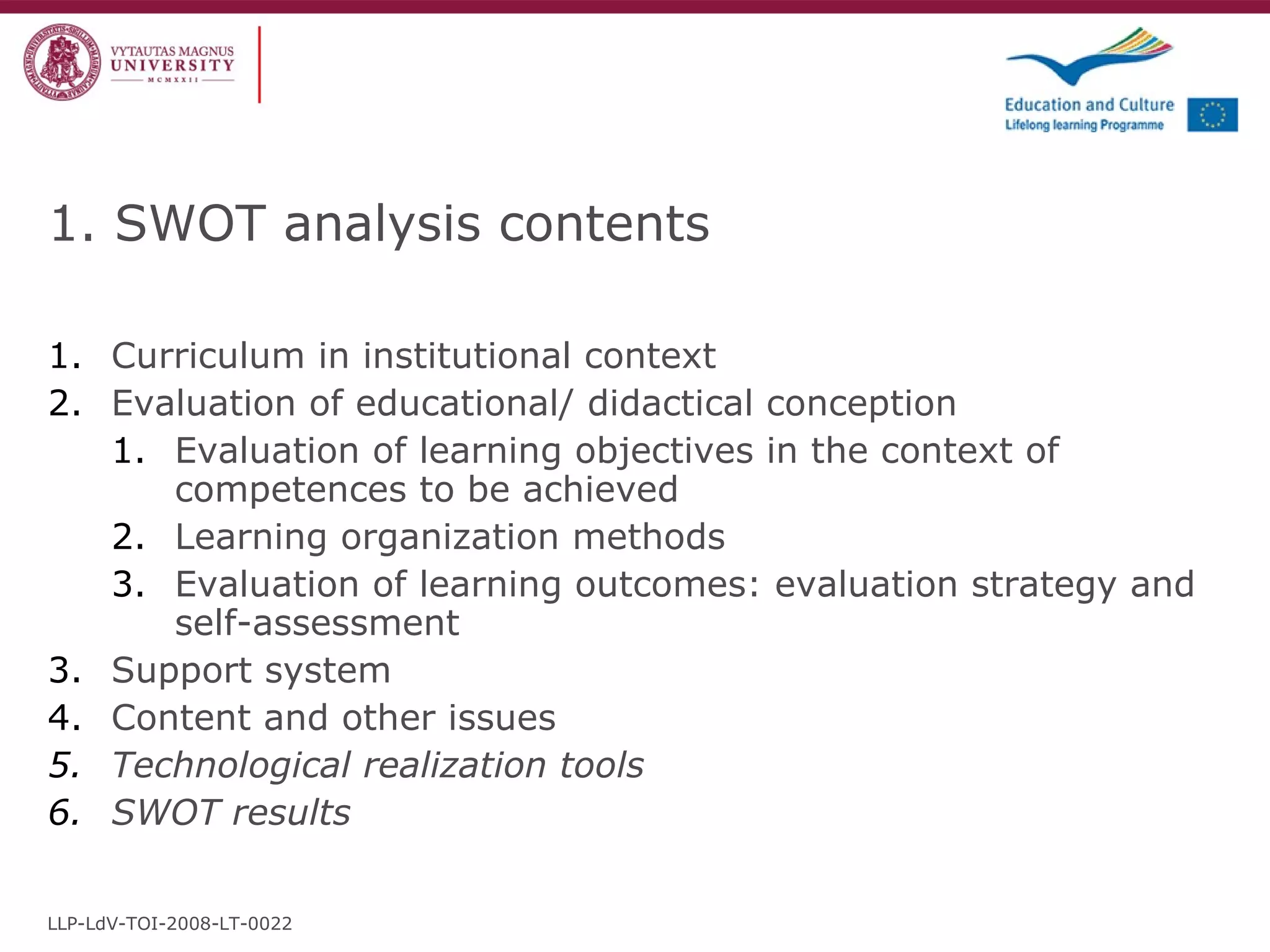
2) Develop recommendations to improve curriculum quality based on didactic and technological methodology.
3) Involve VET institutions, teachers, and trainers to select curriculum in need of improvement and provide recommendations after analysis.