1. The document discusses selecting and formulating a research problem. It defines research as a process of observing phenomena repeatedly to collect data and draw conclusions.
2. A research problem is a question a researcher wants to answer or a problem they want to solve. It is the first step in the research process. Without a problem, research cannot proceed.
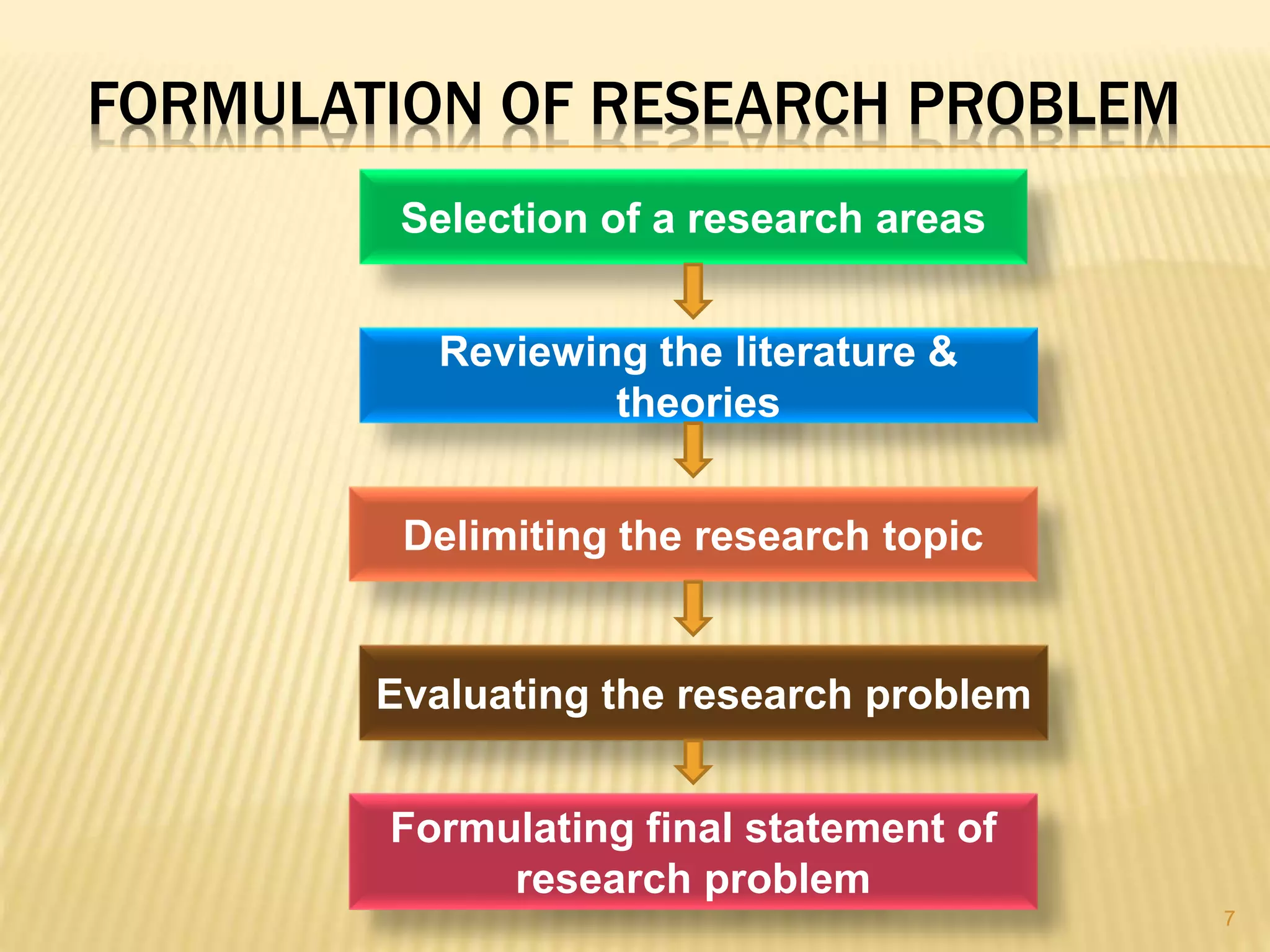
3. Formulating a research problem involves selecting a broad research topic, reviewing literature and theories, delimiting the topic to something more specific, evaluating the problem's significance and feasibility, and finally stating the problem in declarative or interrogative format.