Embed presentation
Downloaded 370 times


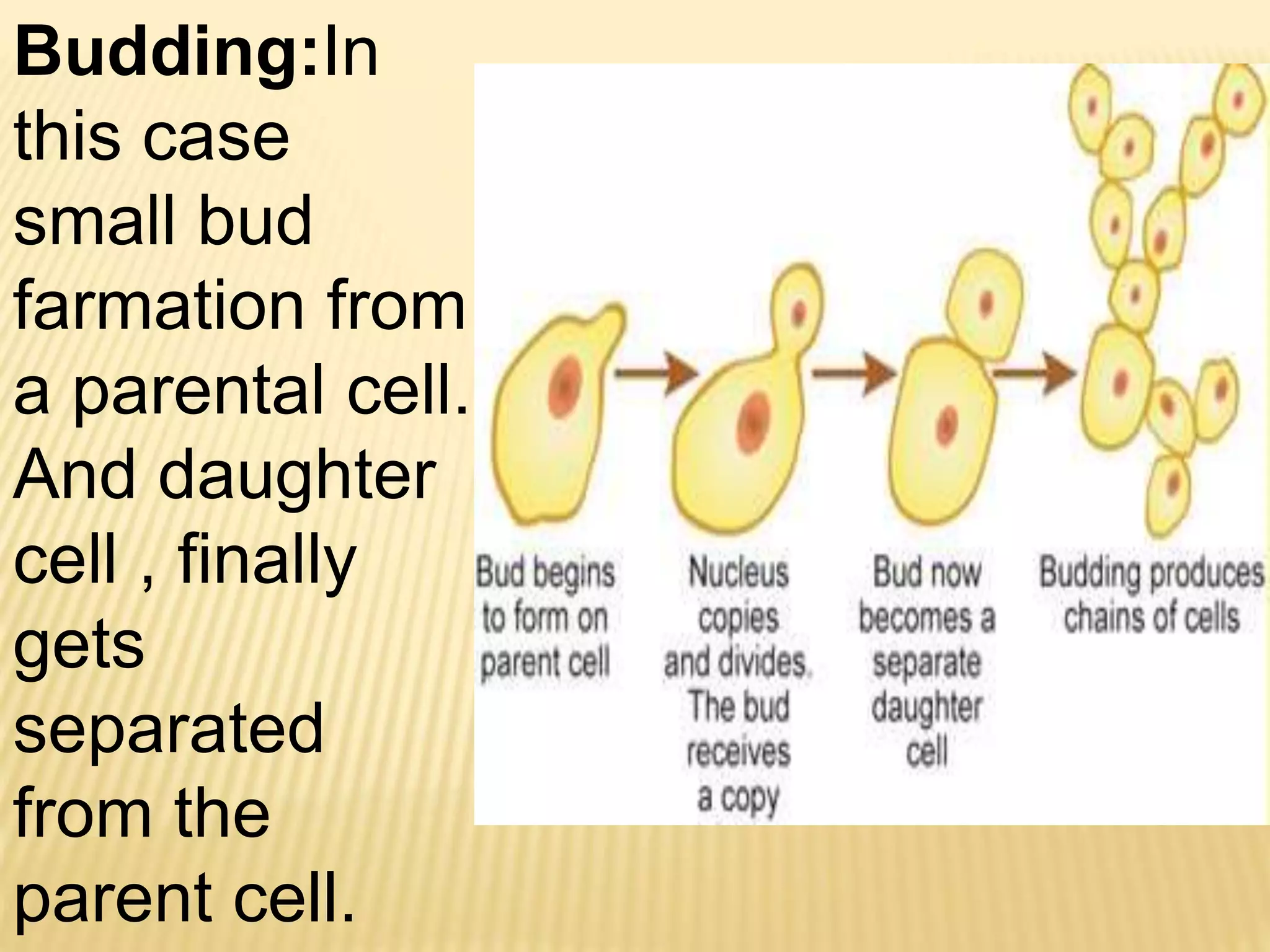

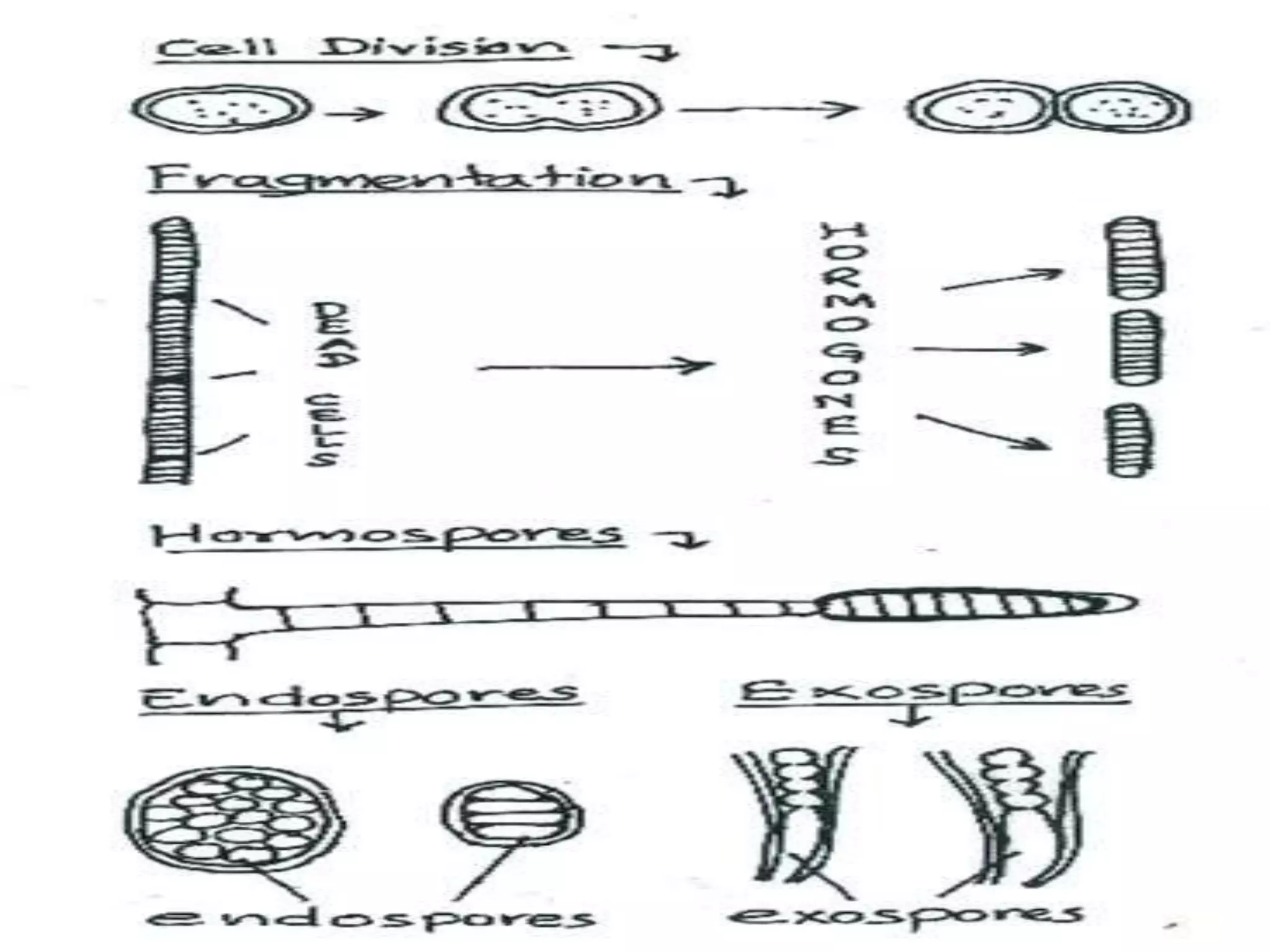

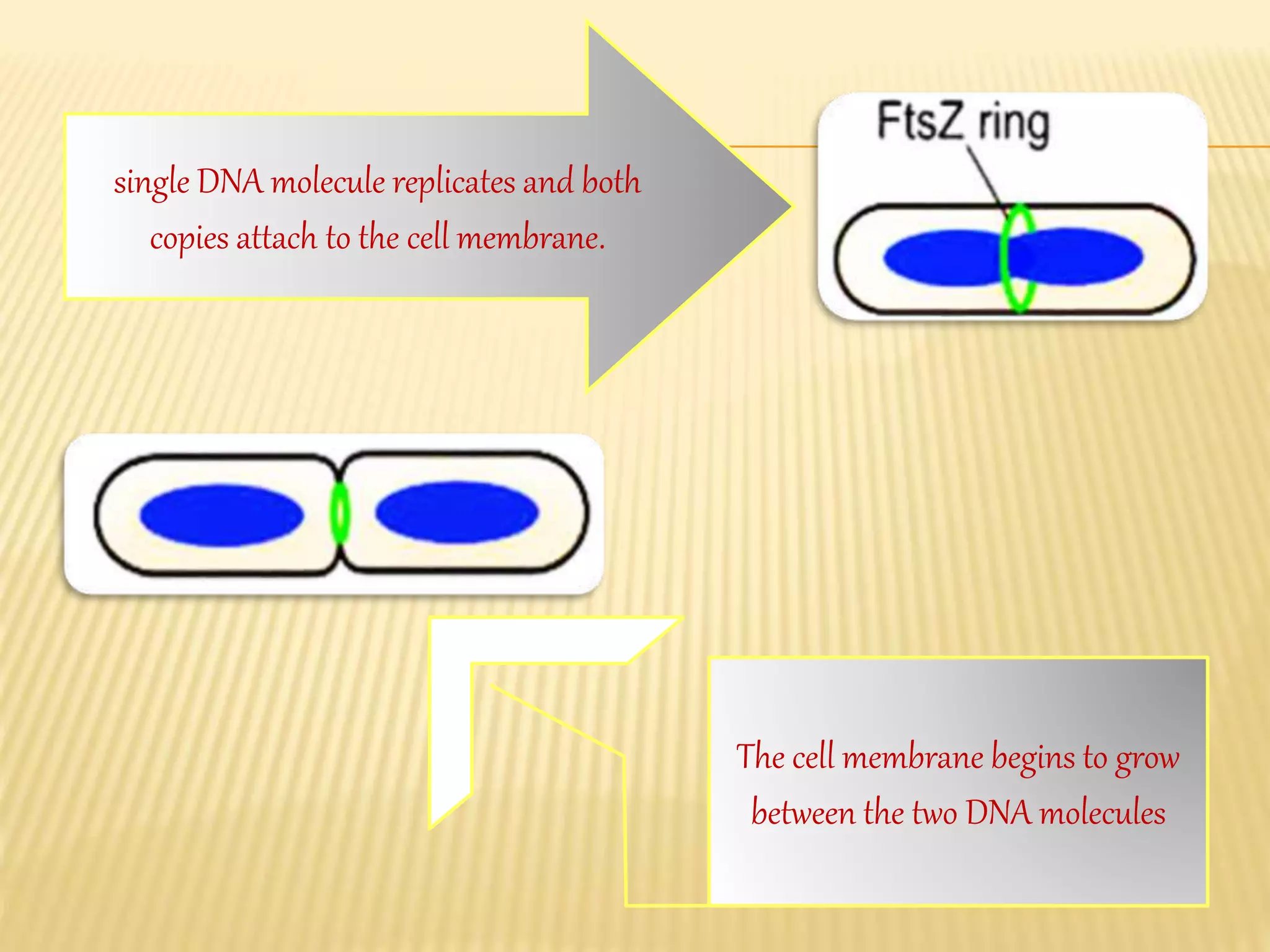
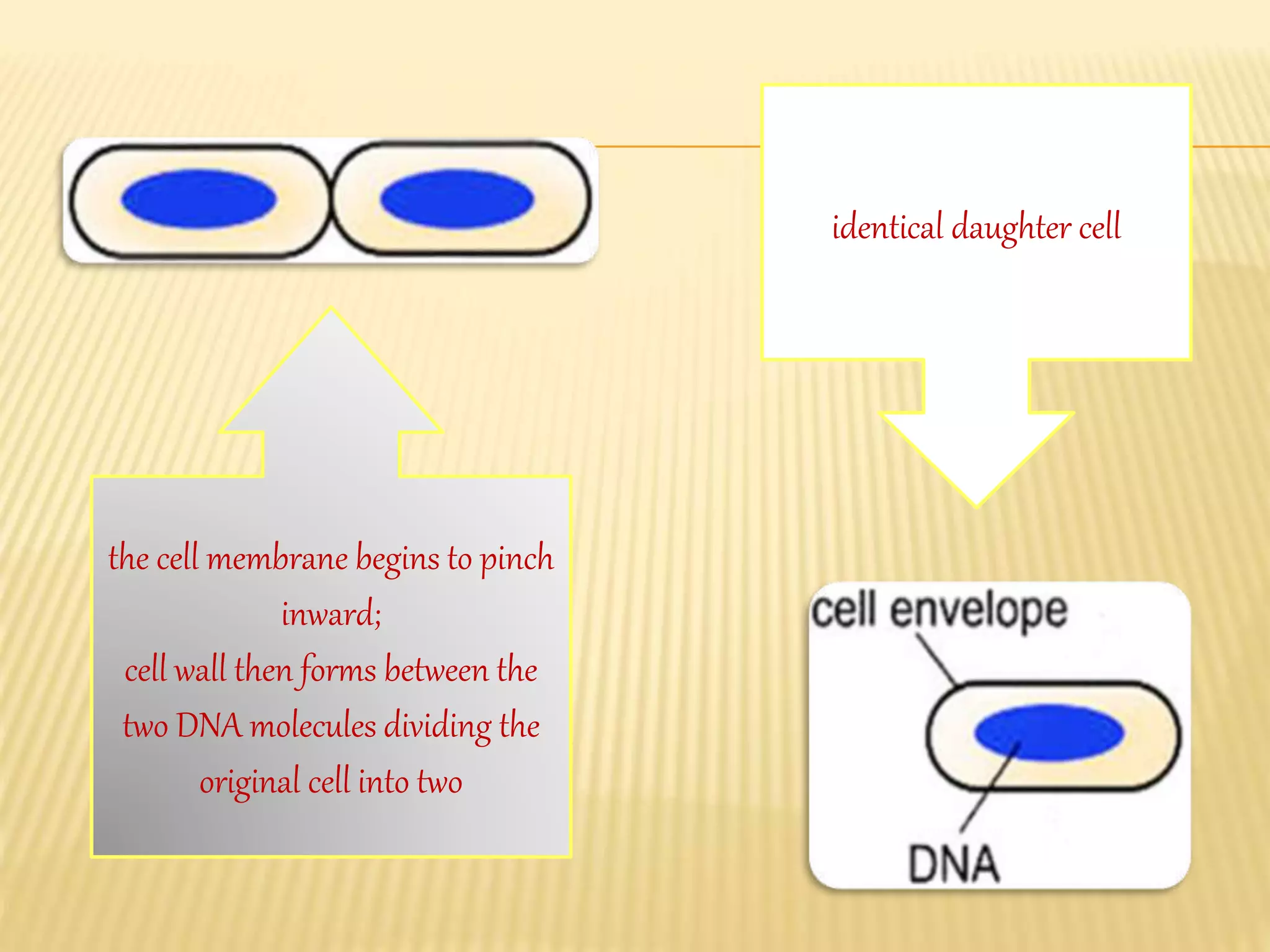
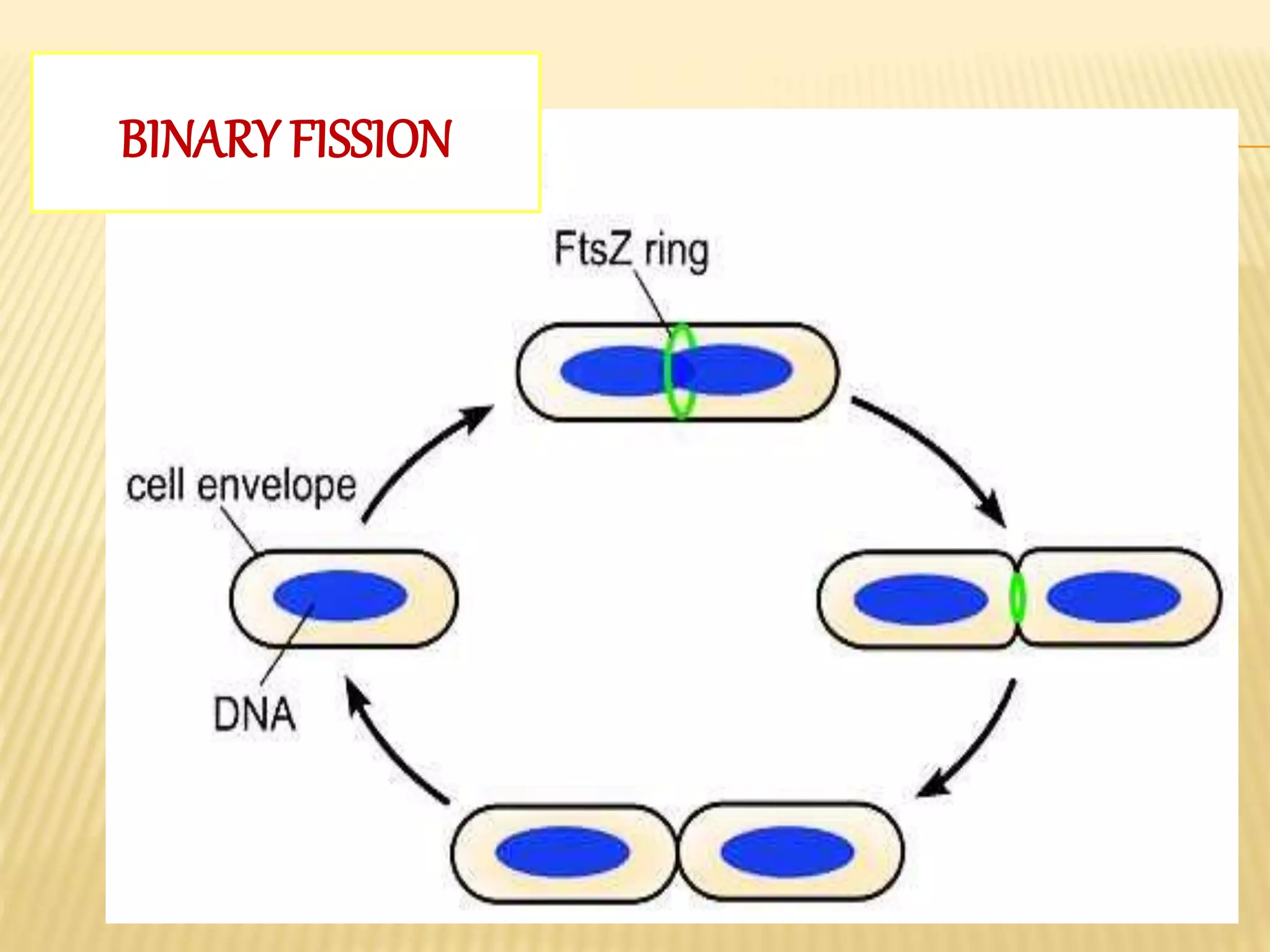




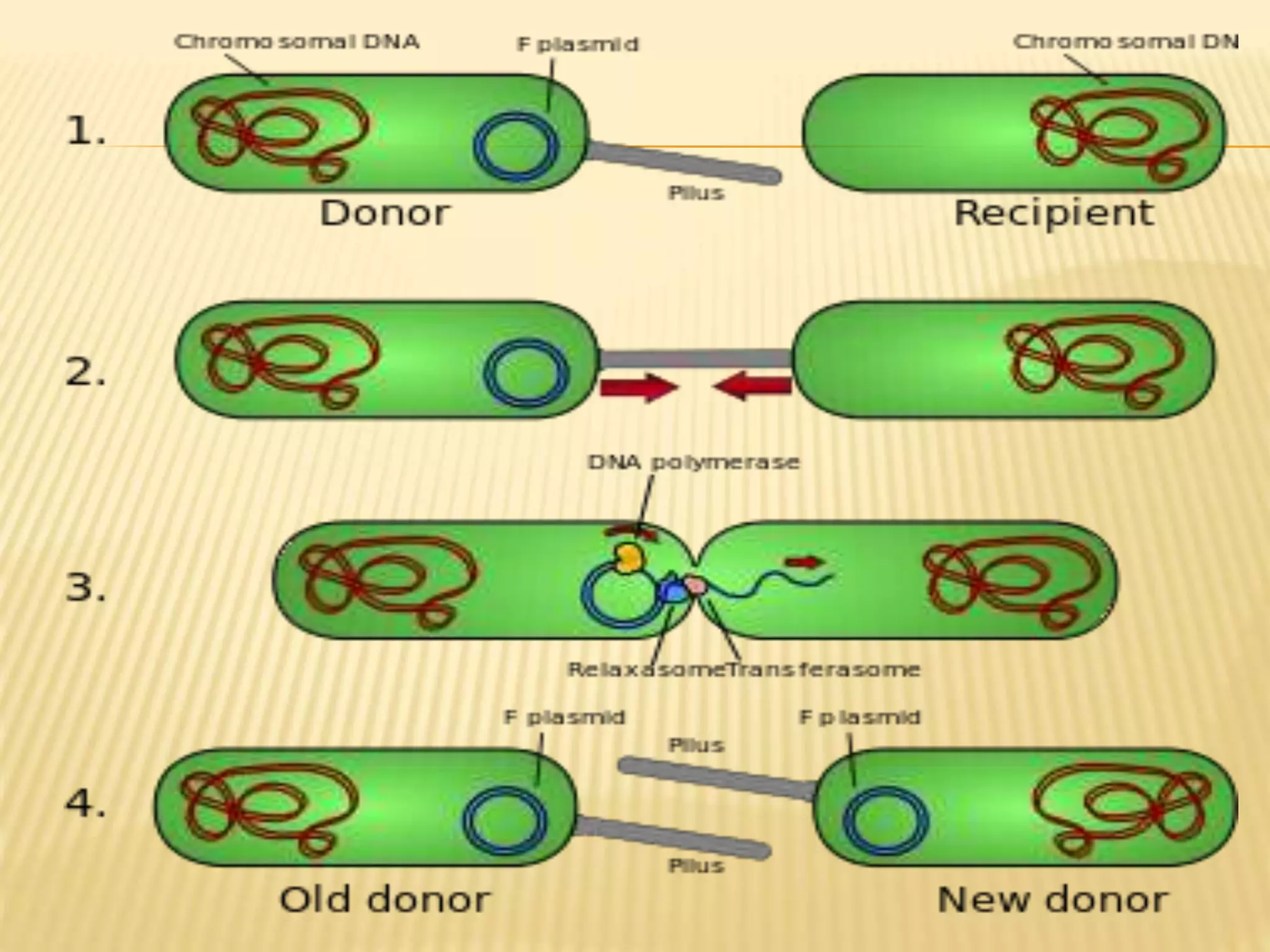

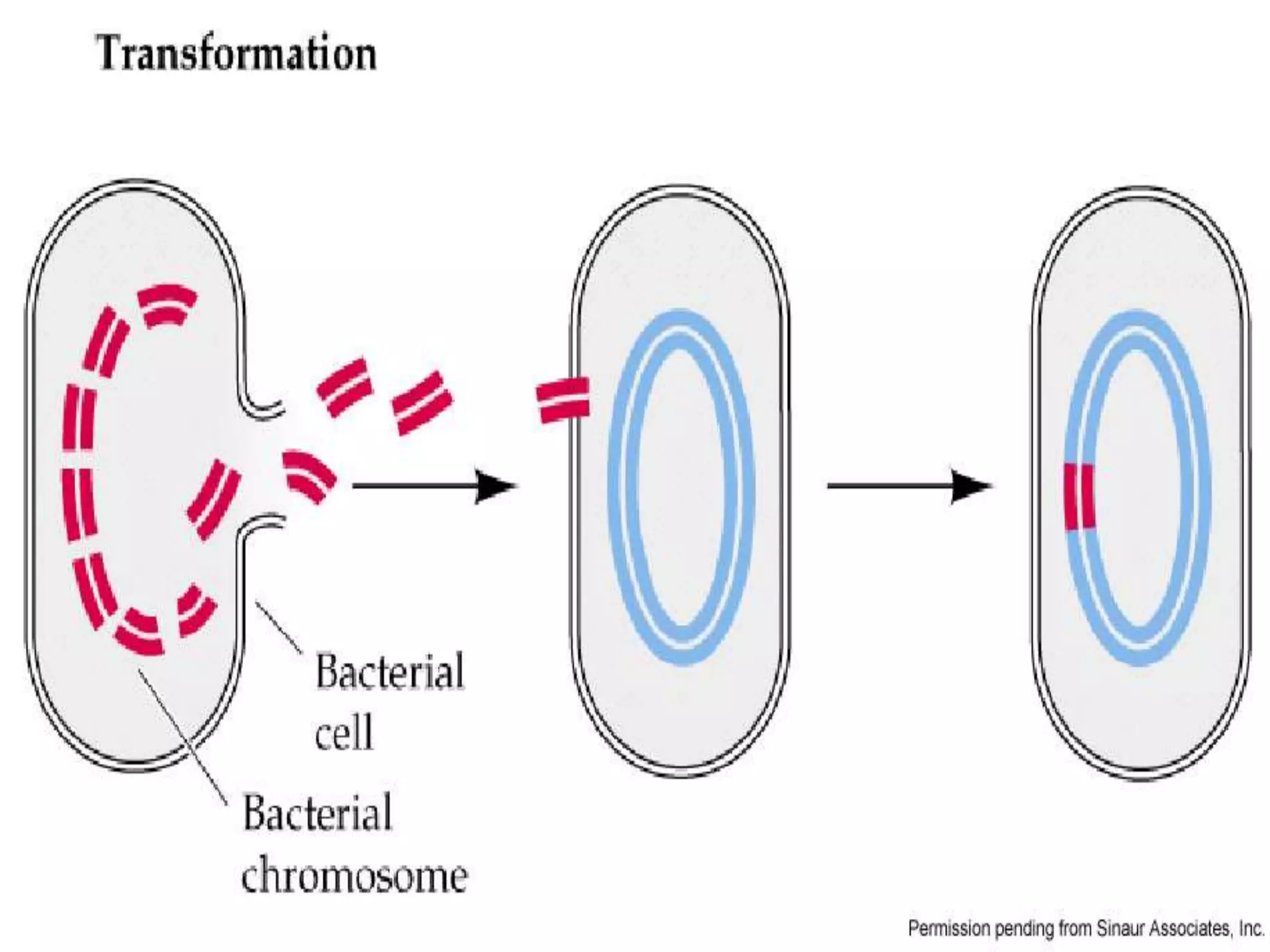

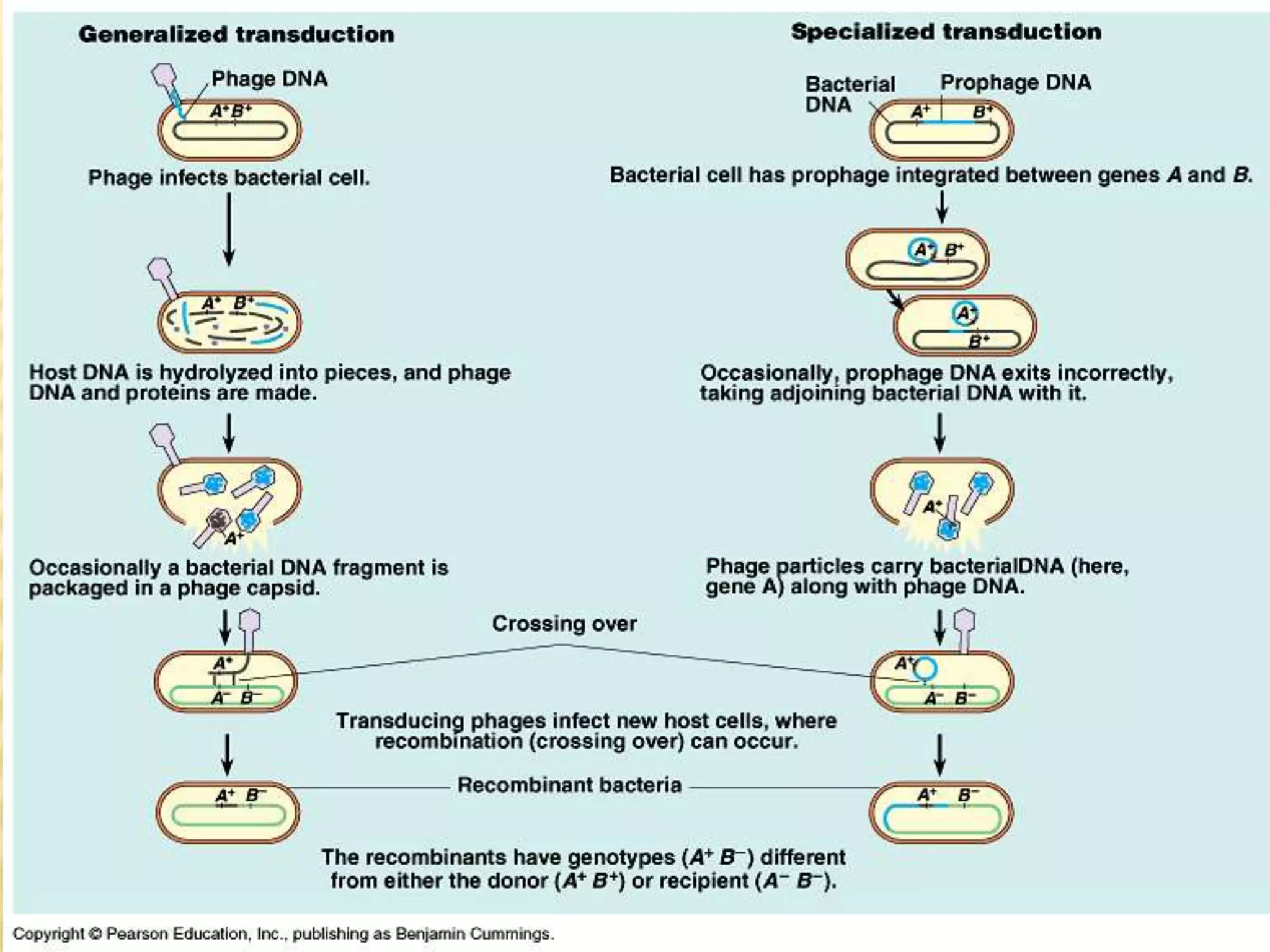




This document summarizes different types of asexual and sexual reproduction in bacteria. The main types of asexual reproduction discussed are budding, fragmentation, and binary fission. Binary fission involves the bacterial DNA replicating and the cell membrane dividing the original cell into two identical daughter cells. Sexual reproduction in bacteria can occur through conjugation, transformation, or transduction, which involves the transfer of genes between bacteria through direct contact, uptake of extracellular DNA, or bacteriophage transmission, respectively.





















