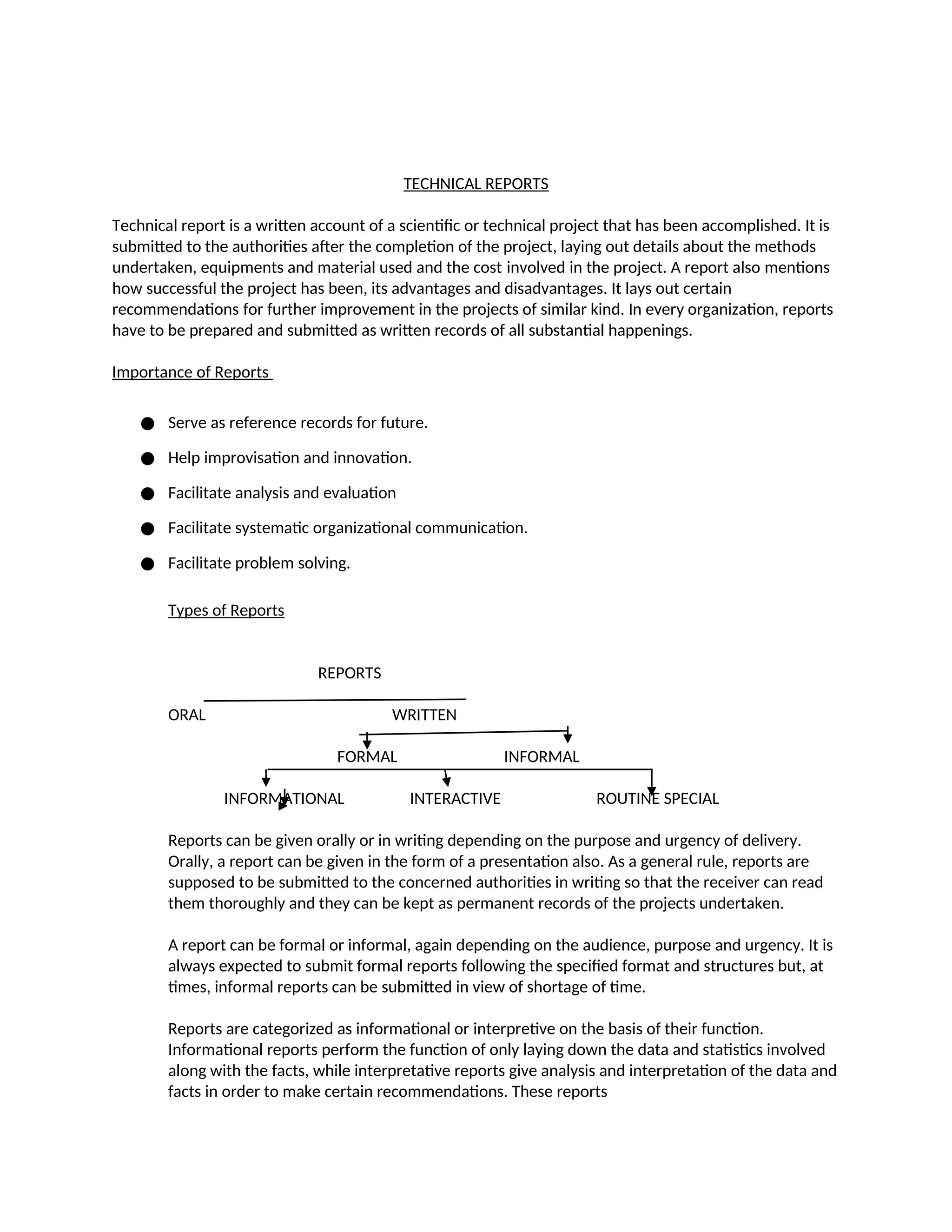
Technical reports document completed scientific or technical projects, outlining methods, materials, costs, and project outcomes, including recommendations for future improvements. Reports serve various functions, such as facilitating analysis, supporting organizational communication, and can be classified into types including informational and interpretive. Essential elements of report writing include accuracy, clarity, completeness, and adherence to specific formats, with structured components like title, methodology, findings, and recommendations.