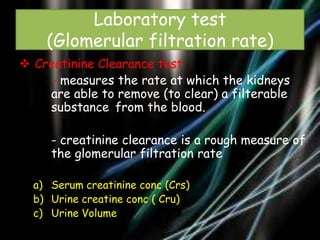
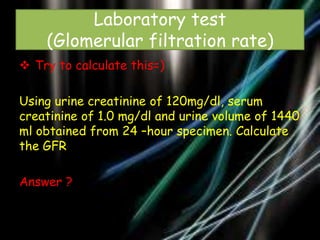
This document discusses renal function tests. It begins by outlining the objectives of renal function tests which are to detect possible renal damage, assess severity, observe progress of renal disease, and monitor safe drug use. It then discusses causes of kidney disorders which can be pre-renal, renal, or post-renal. The main tests of renal function described are urine examination, tests of excretory function like creatinine clearance, and estimating blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels. The document provides details on how to perform and interpret these tests.






![Laboratory test
(Glomerular filtration rate)
Formula;
Creatinine clearance
= (Cru x V/t) / Crs
= [120mg/dl x 1440ml / (24H x 60min)]
1.0mg/dl
=120 x 1440ml / 1440min
1.0
=120ml/min](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/renalfunctiontest-140226082926-phpapp02/85/Renal-function-test-11-320.jpg)

