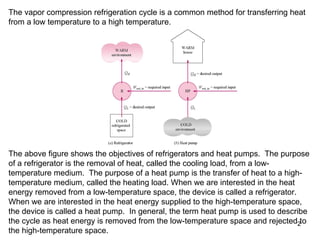
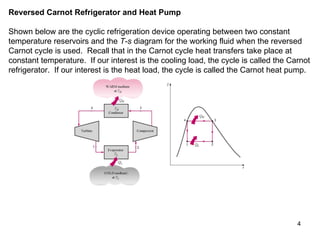
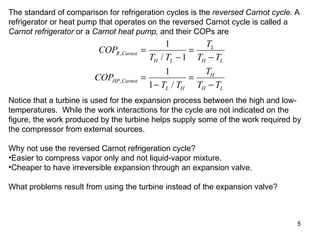
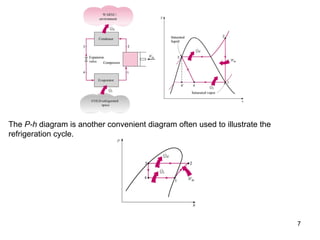
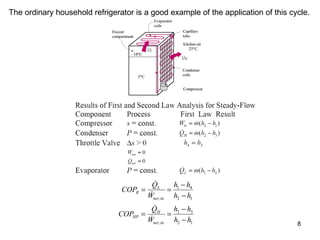
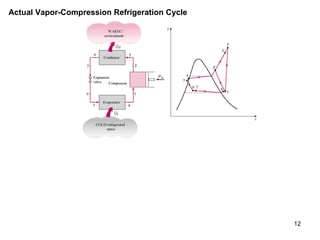
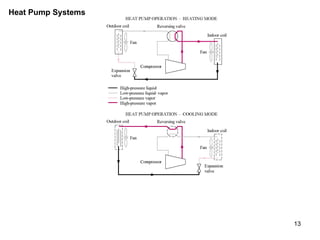
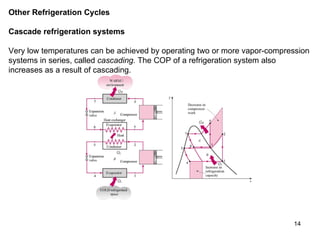
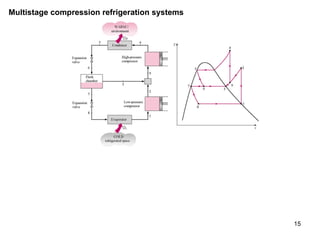
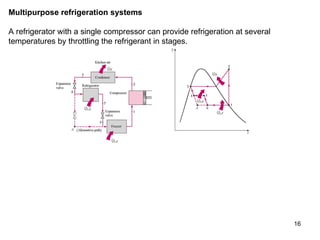
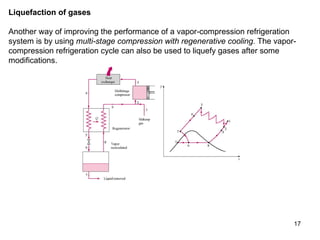
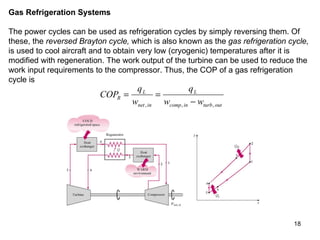
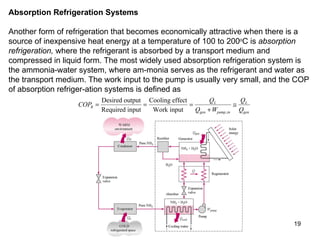
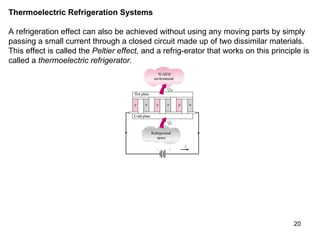
The vapor compression refrigeration cycle is commonly used to transfer heat from a low temperature medium to a high temperature medium. It involves four main processes: (1) compression of a refrigerant vapor, (2) heat rejection in a condenser, (3) expansion of the refrigerant through a throttle valve, and (4) heat absorption in an evaporator. The coefficient of performance (COP) is used to measure the efficiency of refrigerators and heat pumps. Actual vapor compression cycles are less efficient than the ideal Carnot cycle due to irreversibilities.