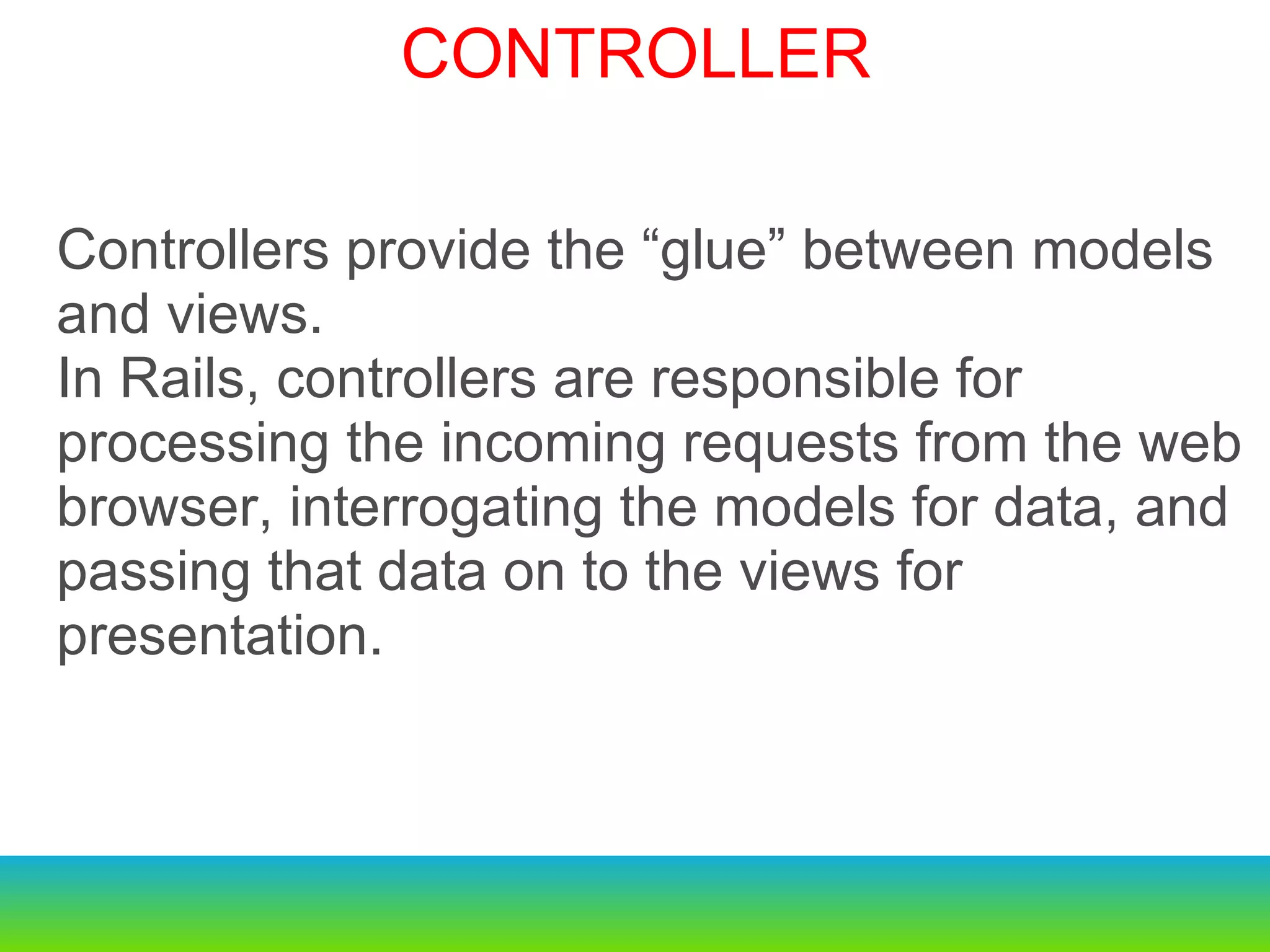
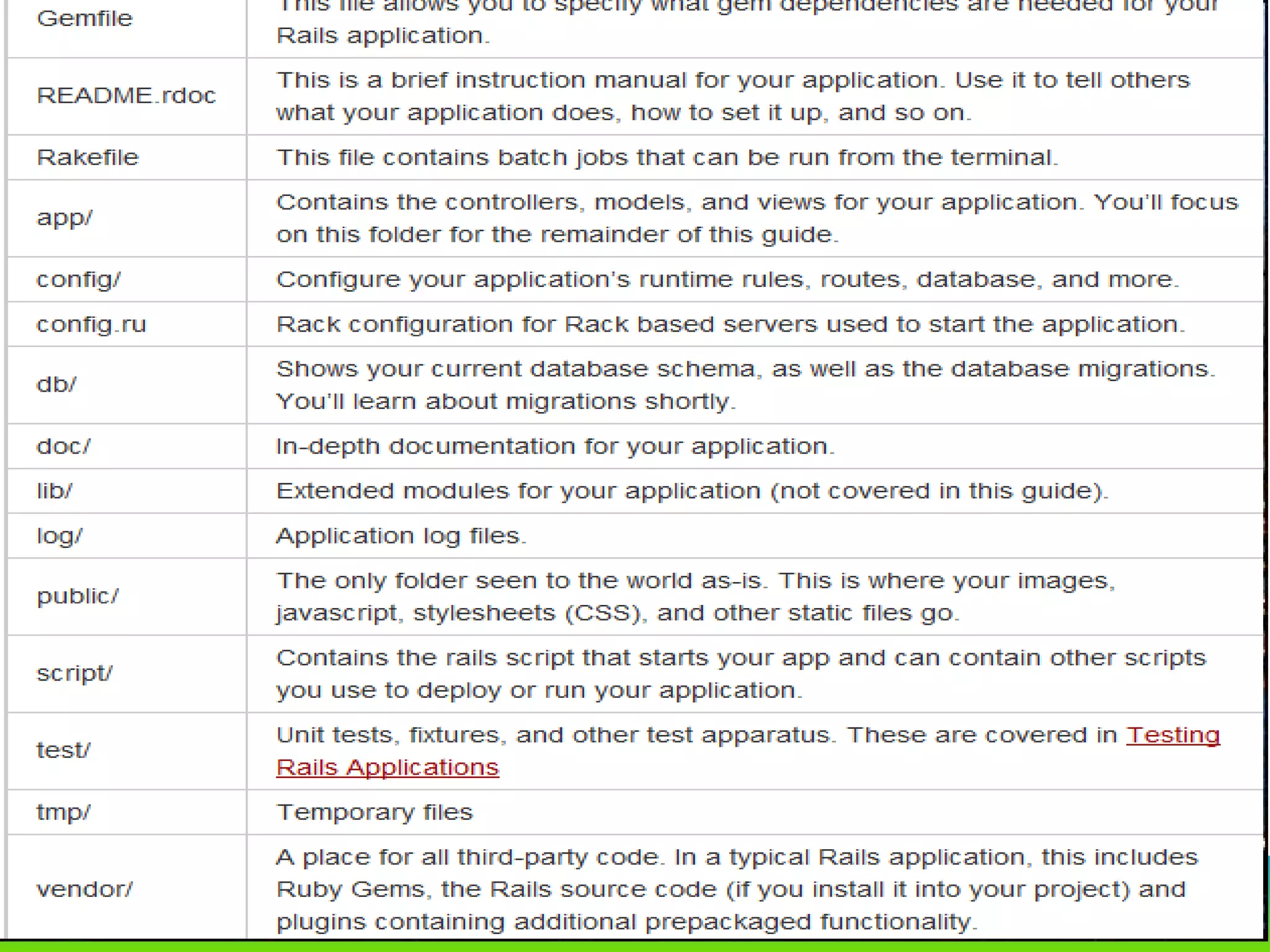
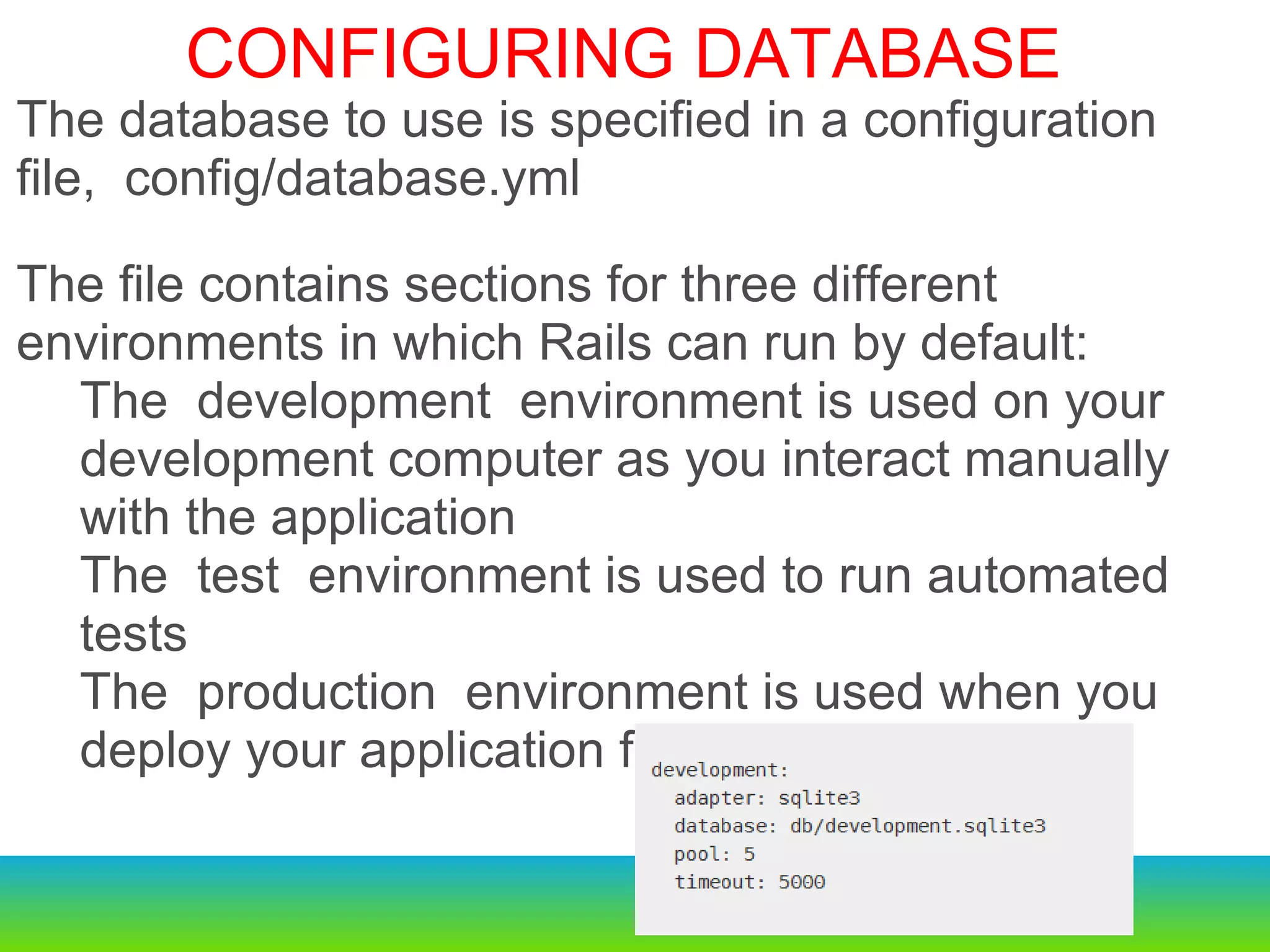
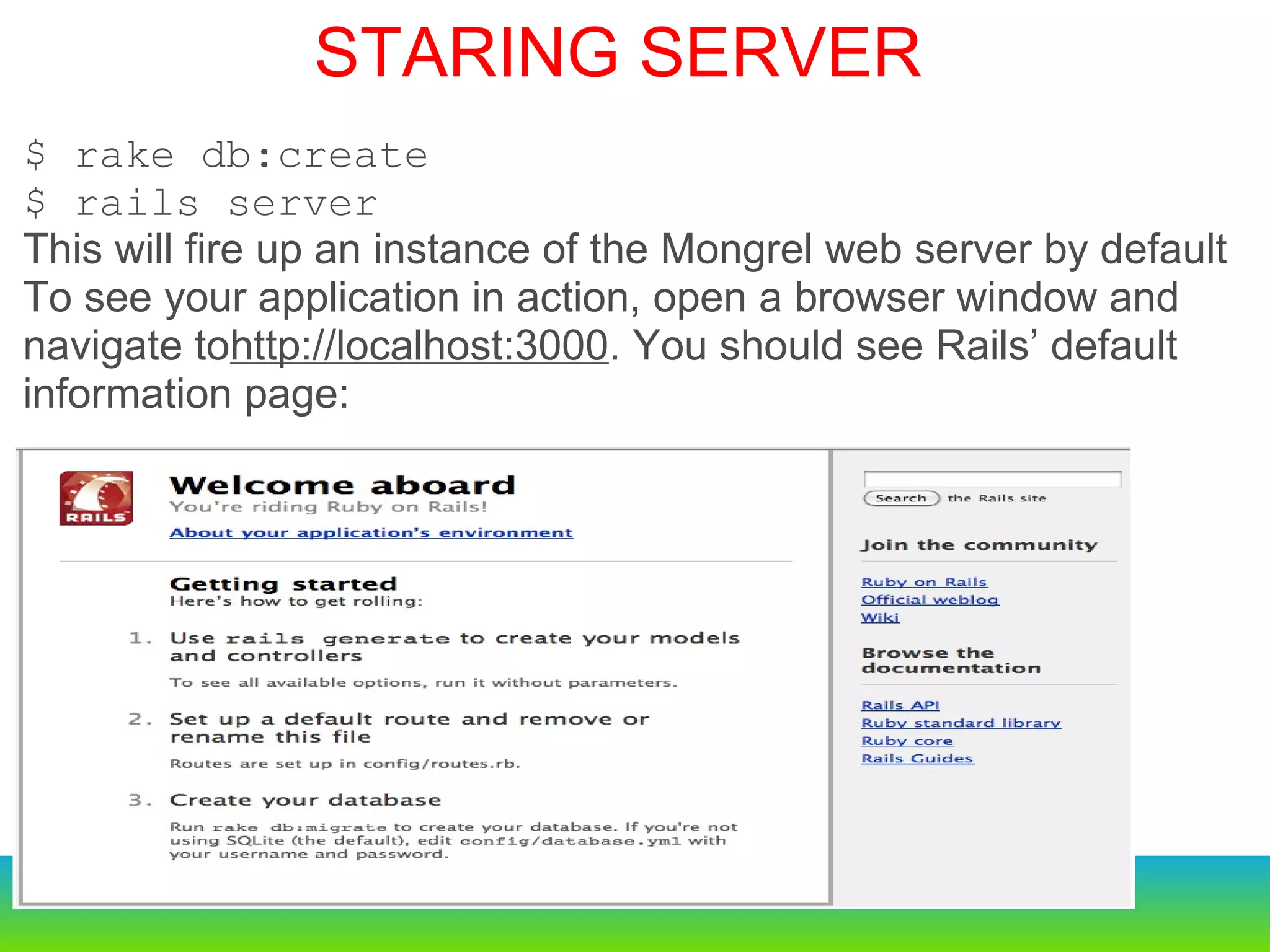
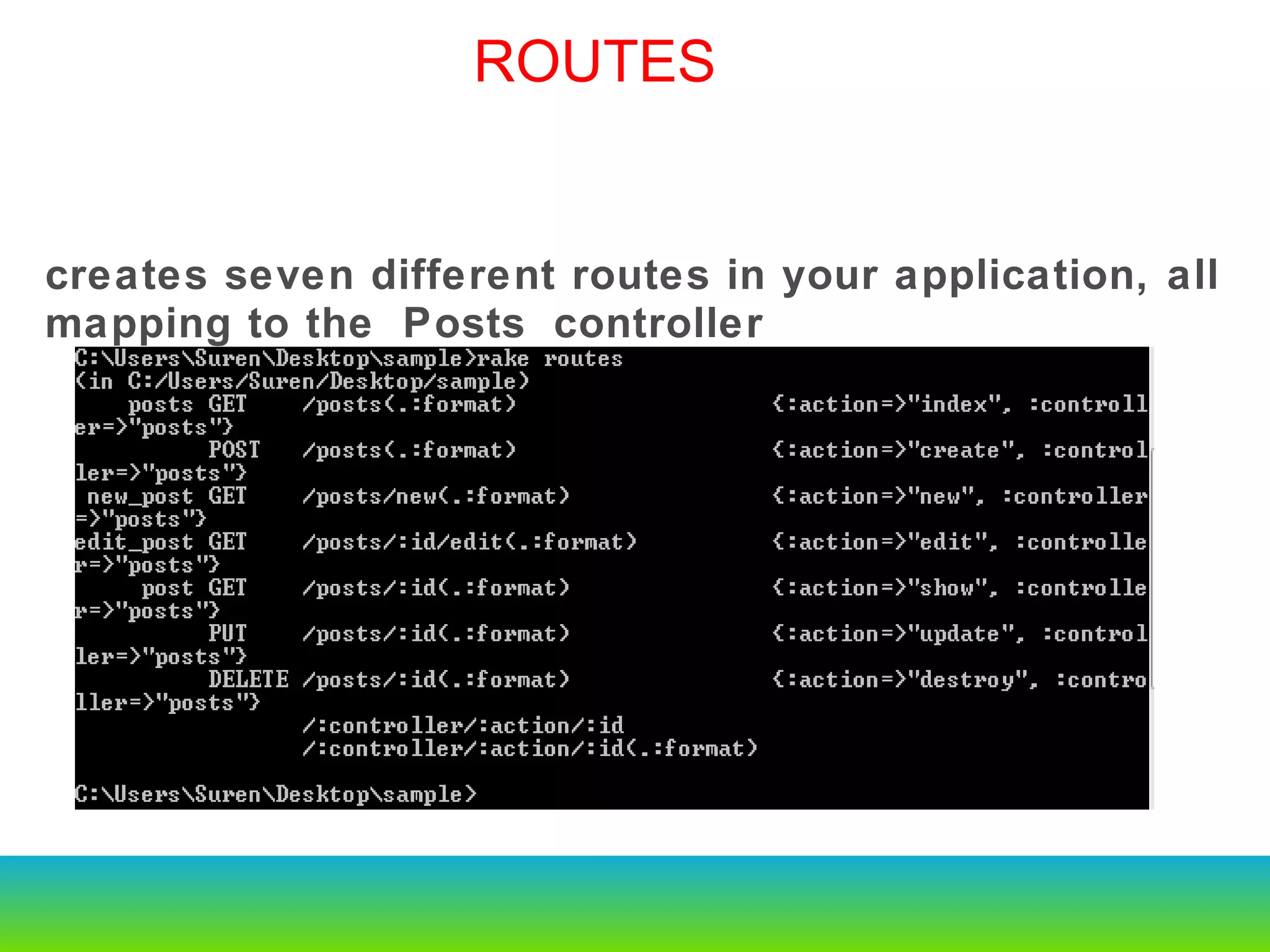
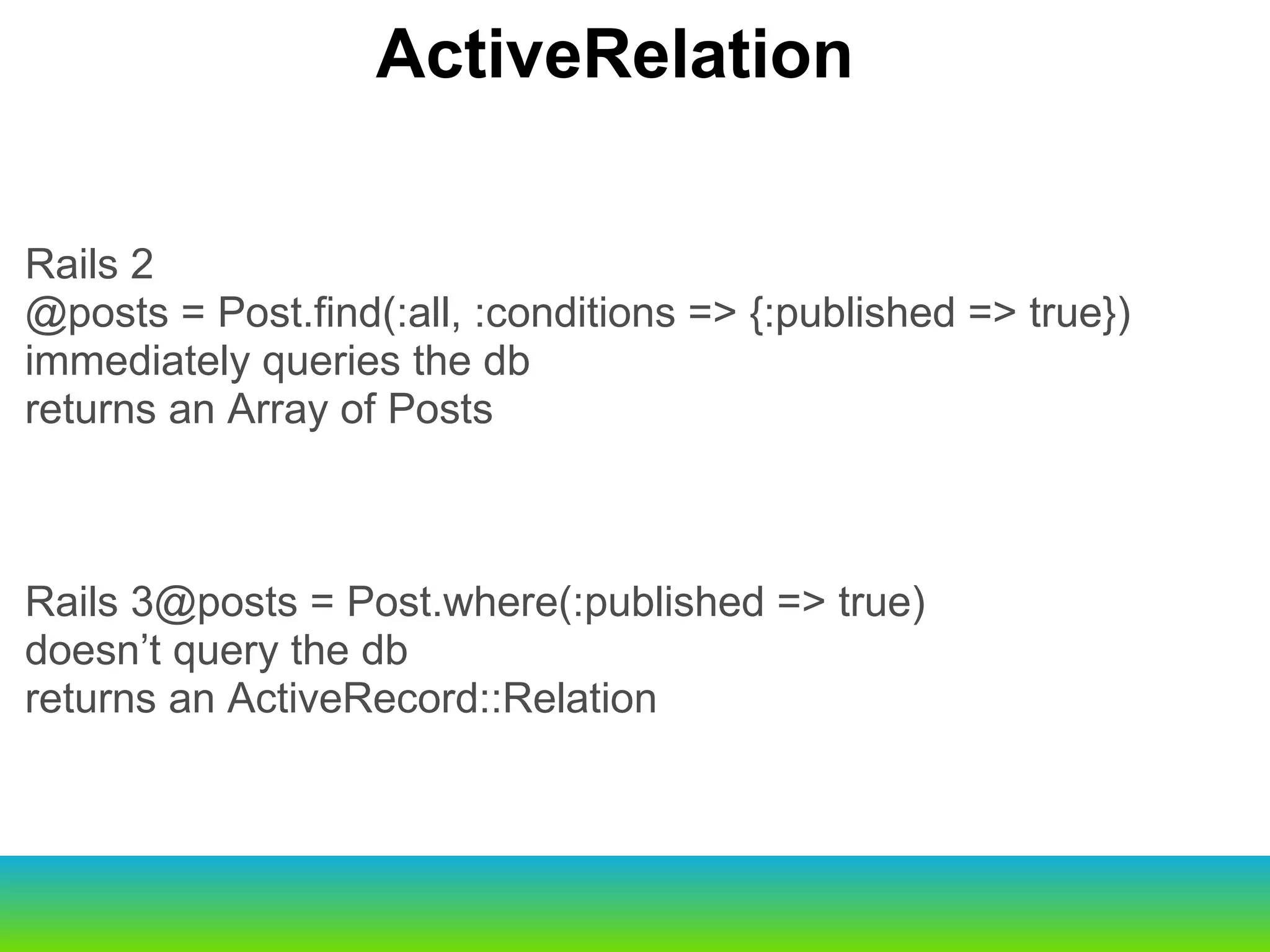
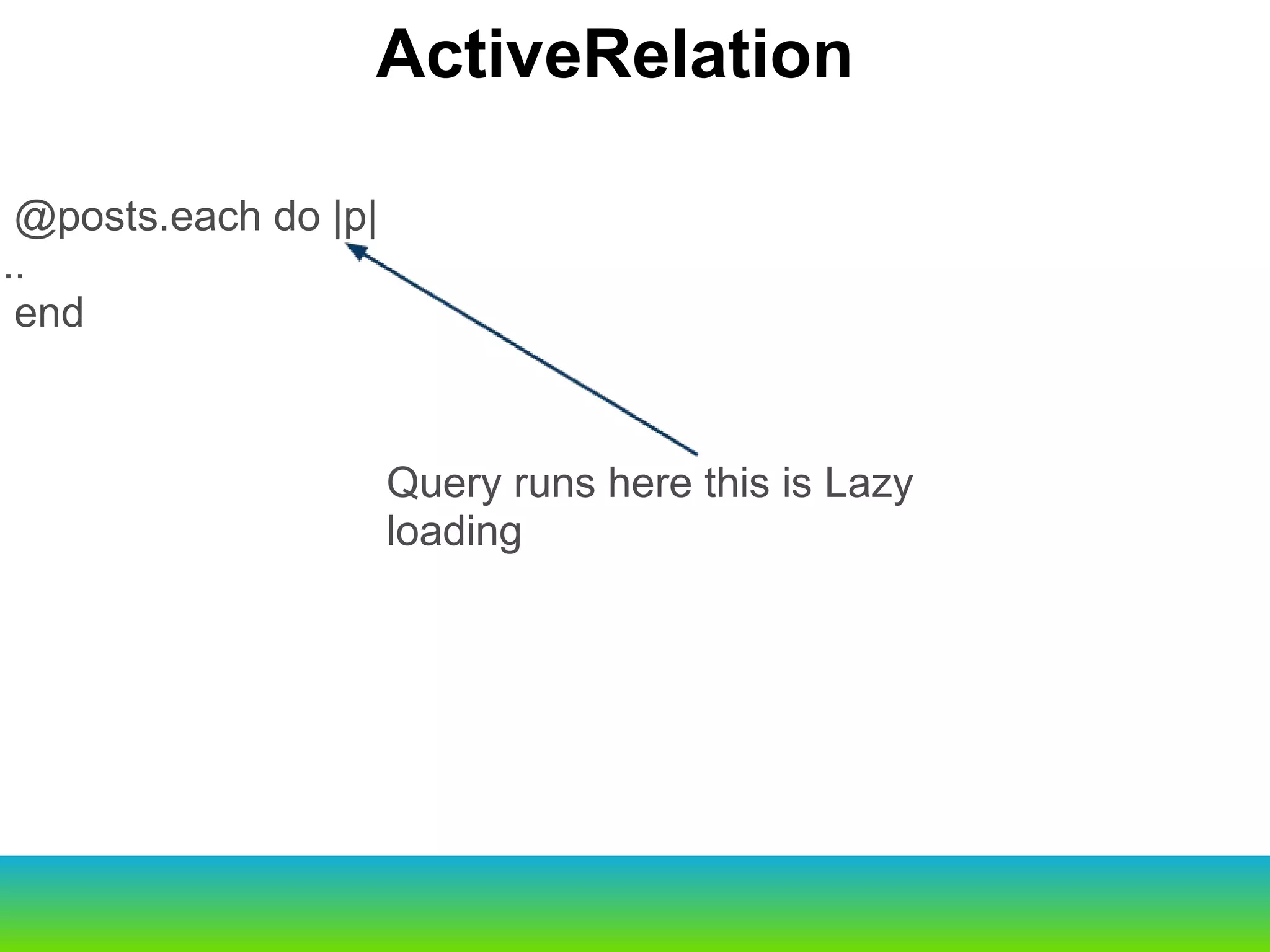
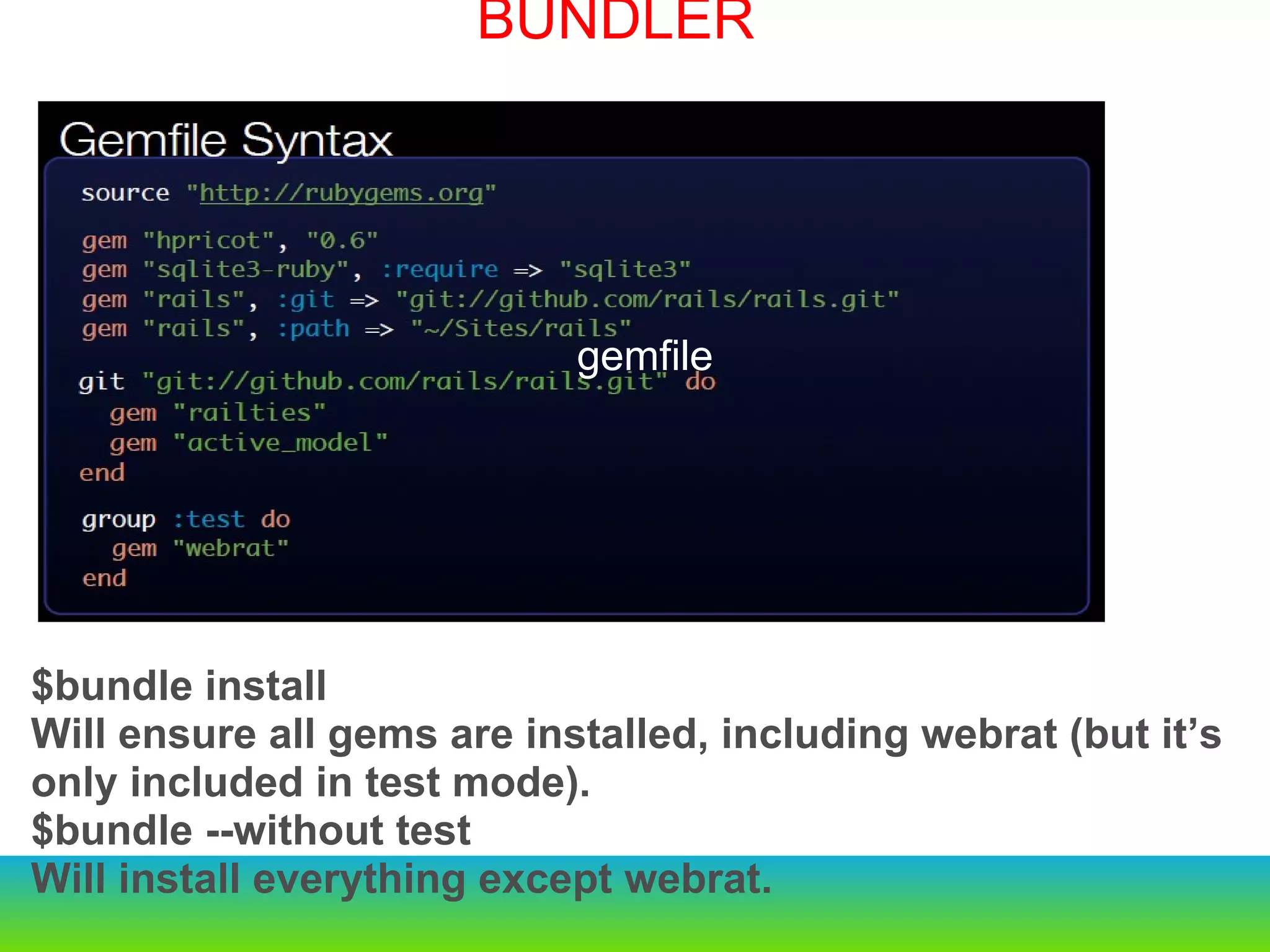
This document provides an overview of the key changes and improvements in Rails 3 compared to Rails 2. It discusses updates to generators, models, migrations, routes, controllers, views, databases, and adopting unobtrusive JavaScript. New features like ActiveRelation and Turbolinks are also covered.










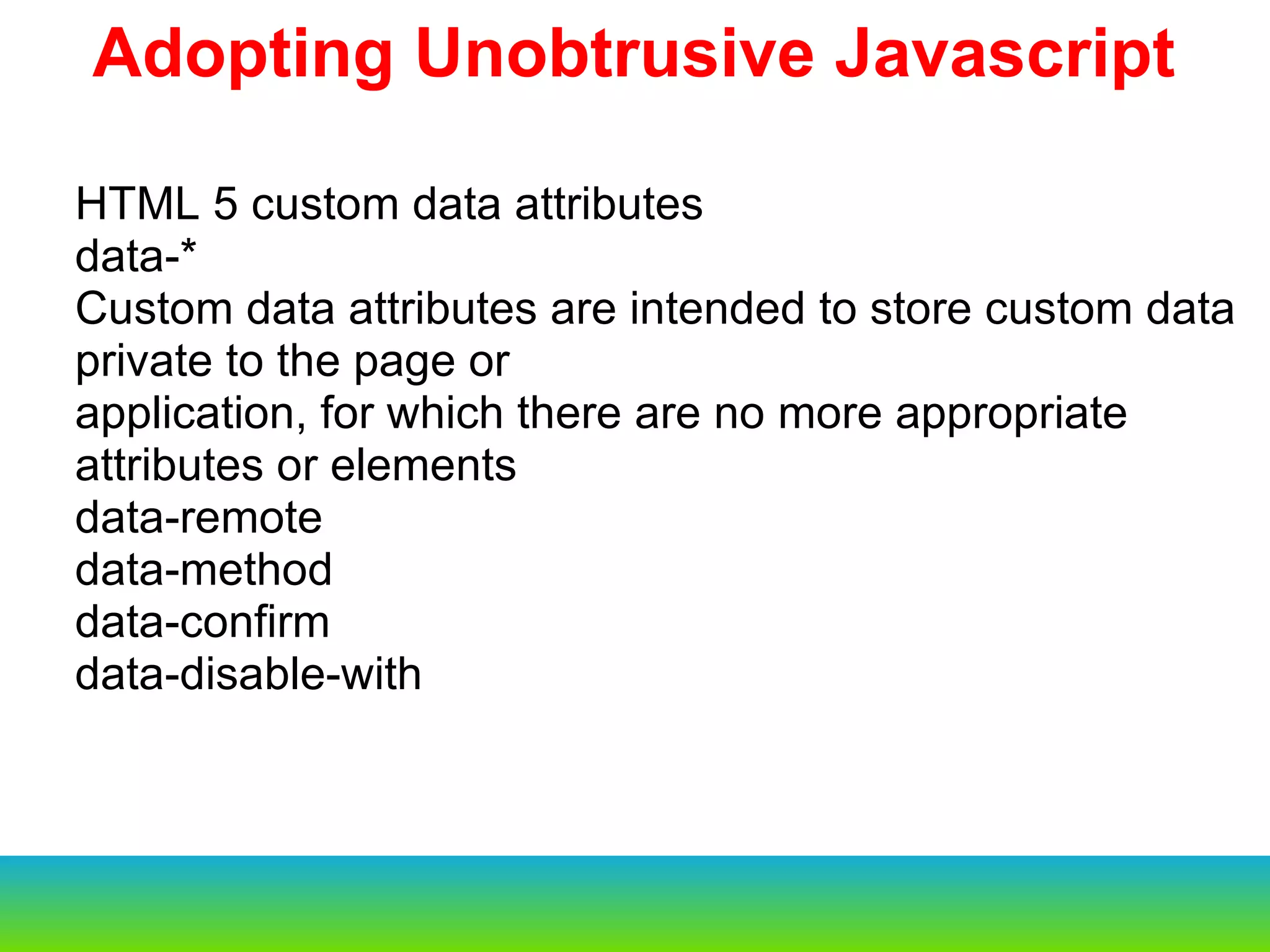

![Adopting Unobtrusive Javascript document.observe("dom:loaded", function() { $(document.body).observe("click", function(event) { var message = event.element().readAttribute('data-confirm'); if (message) { // ... Do a confirm box } var element = event.findElement("a[data-remote=true]"); if (element) { // ... Do the AJAX call } var element = event.findElement("a[data-method]"); if (element) { // ... Create a form } })](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rail3intro29thsepsurendran-100930070826-phpapp02/75/Rail3-intro-29th_sep_surendran-30-2048.jpg)
![http://github.com/rails/jquery-uj $('a[data-confirm],input[data-confirm]').live('click', function () { // ... Do a confirm box }); $('form[data-remote="true"]').live('submit', function (e) { // ... Do an AJAX call }); jQuery in Rails?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rail3intro29thsepsurendran-100930070826-phpapp02/75/Rail3-intro-29th_sep_surendran-31-2048.jpg)
