This document summarizes different RAID levels:
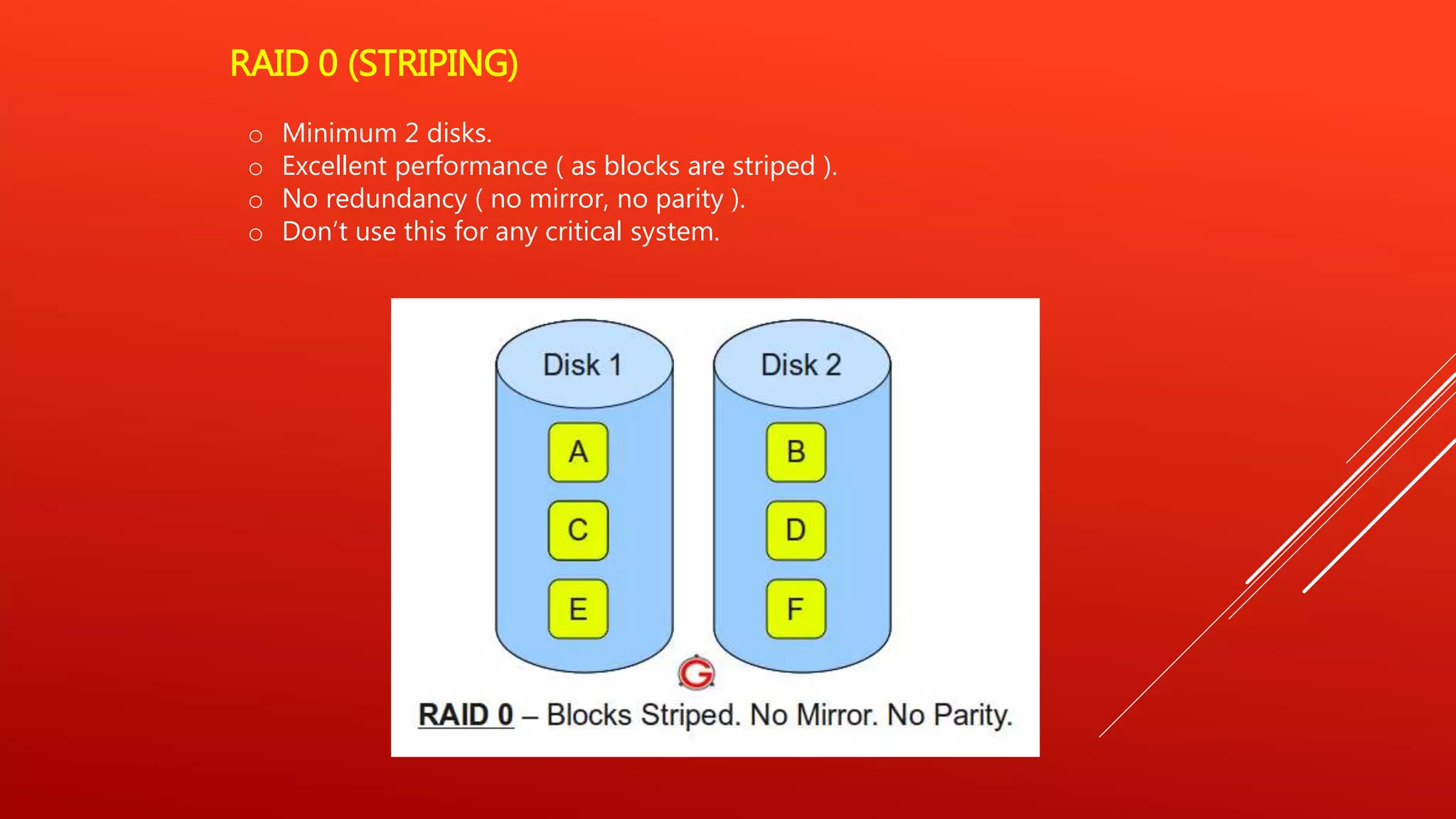
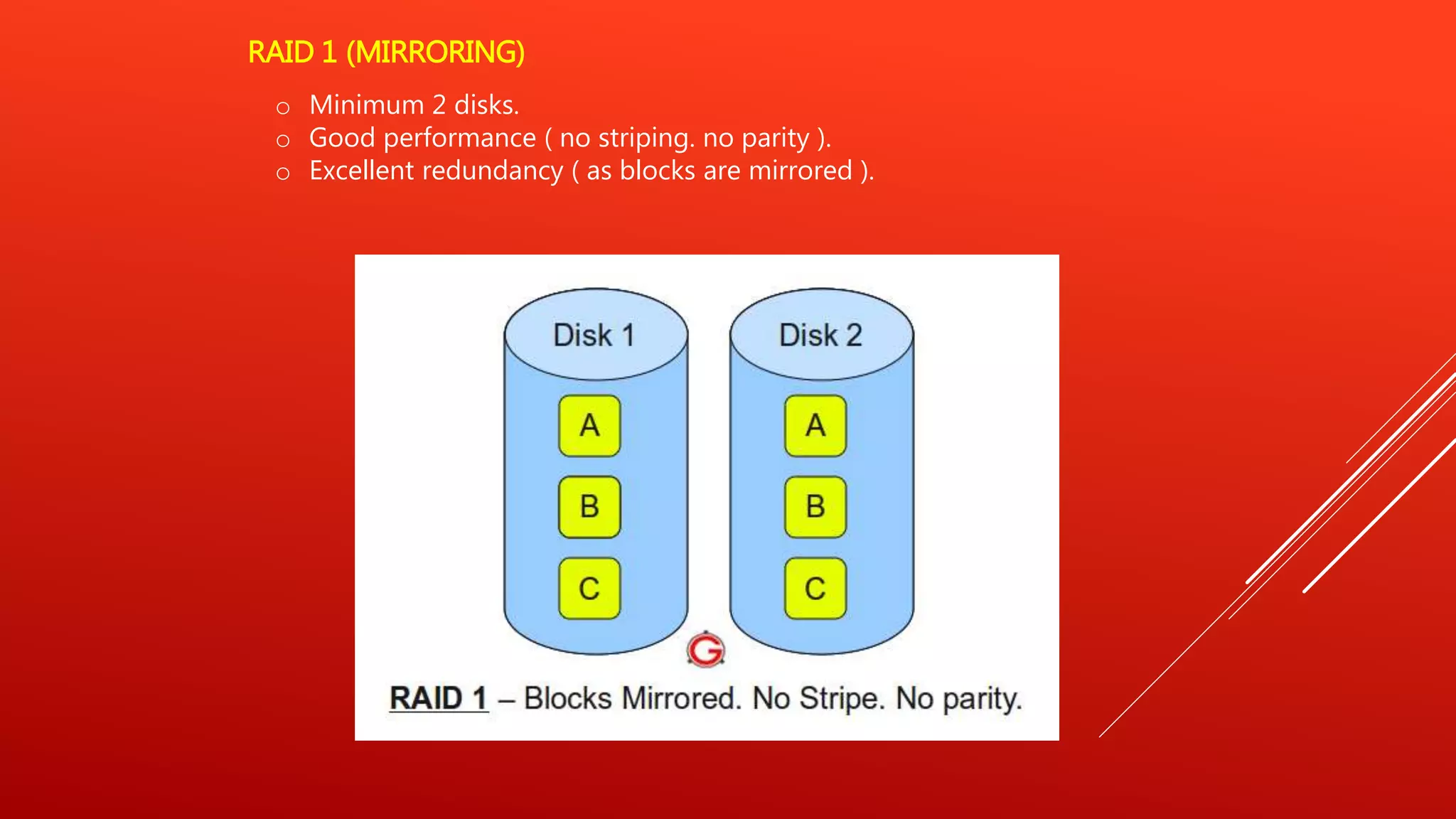
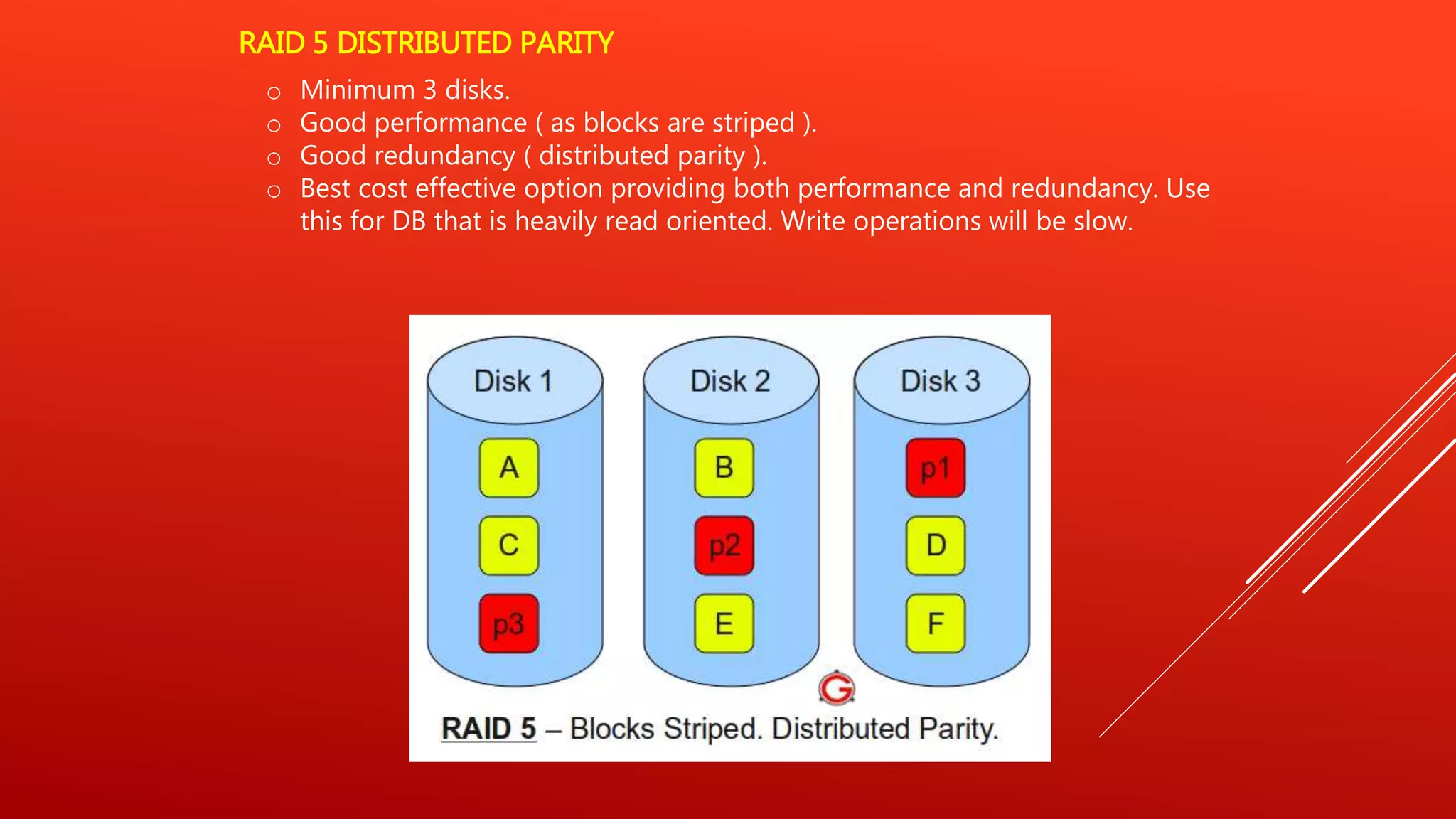
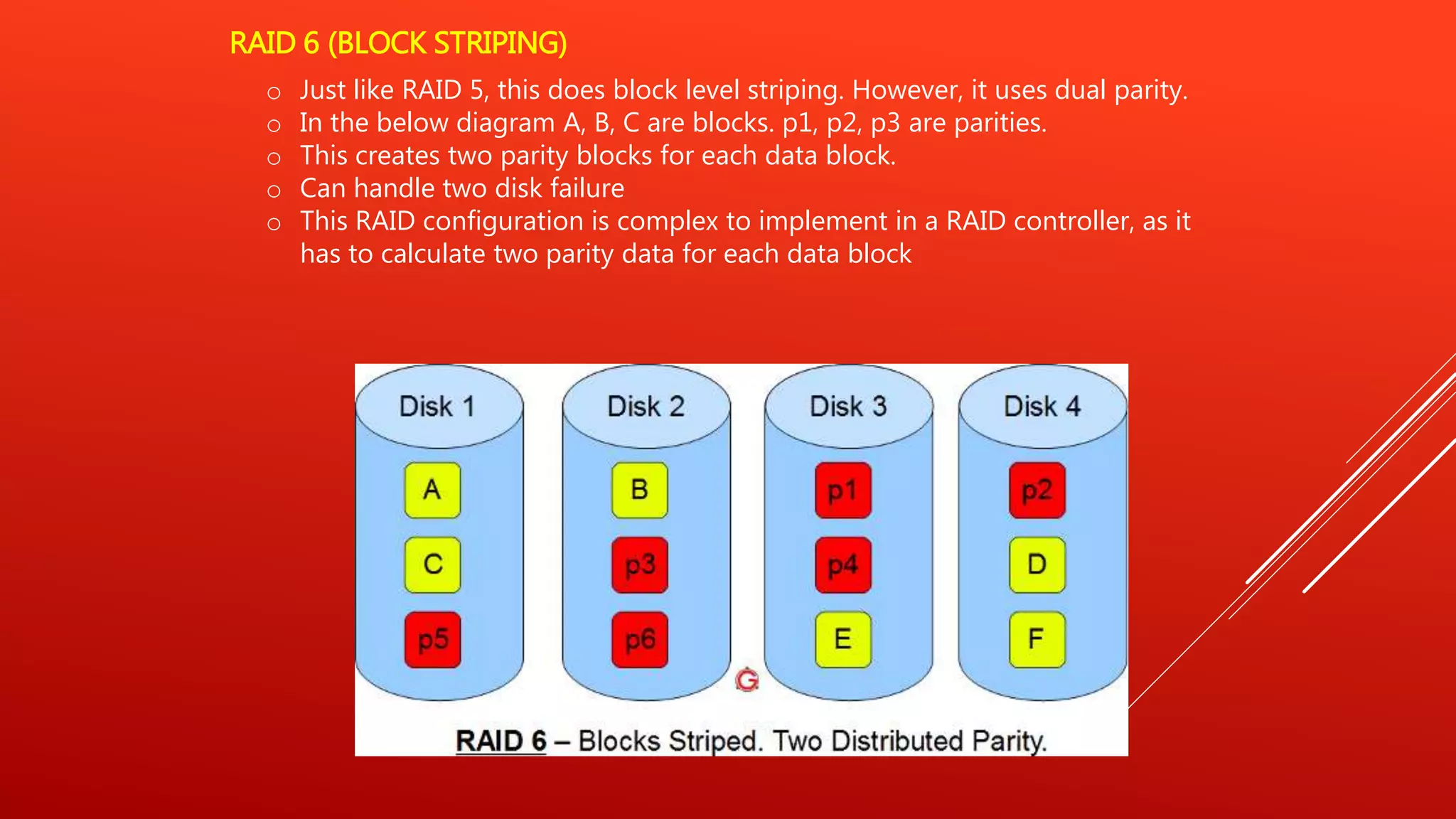
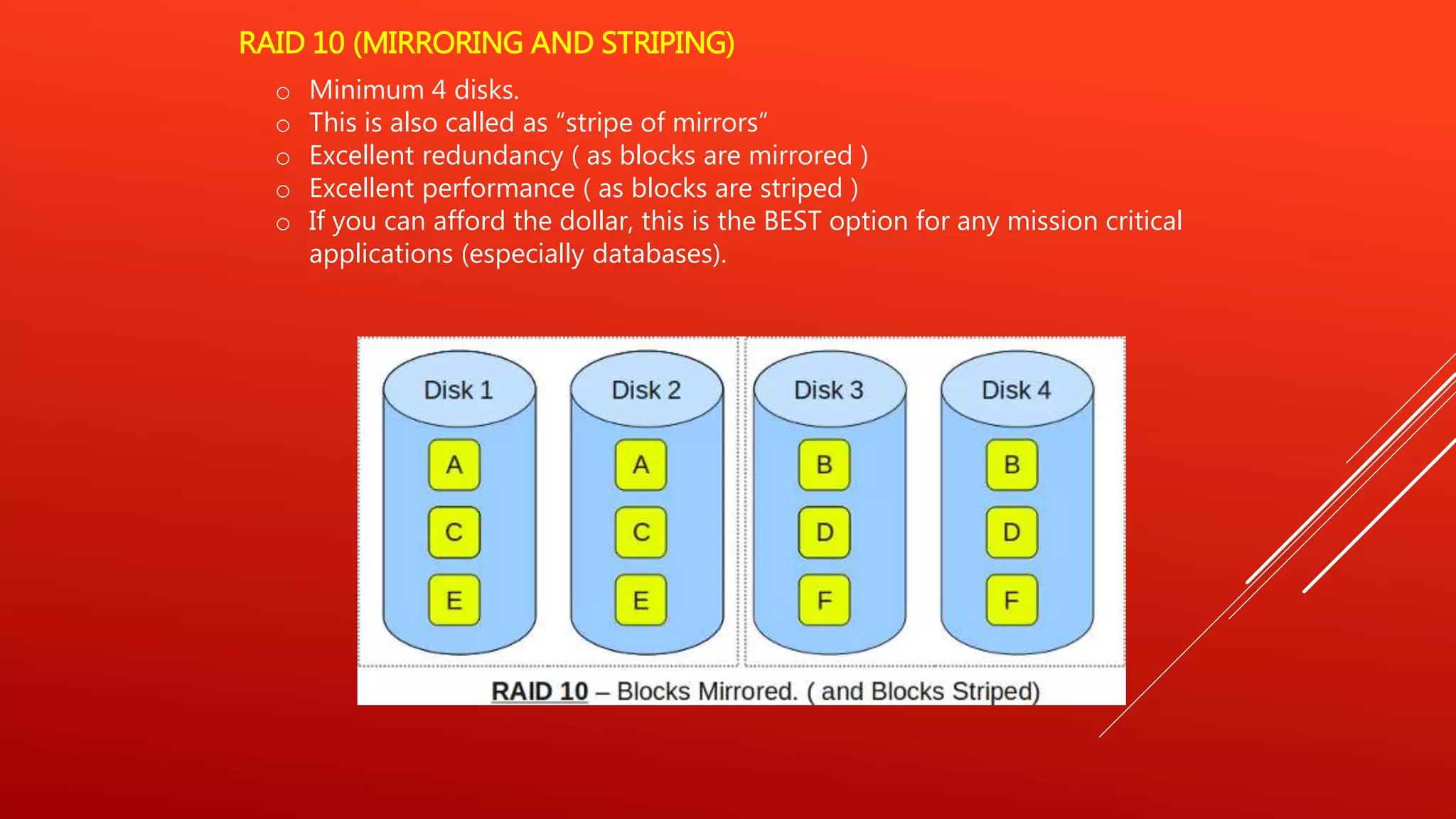
RAID 0 uses striping to improve performance but provides no redundancy. RAID 1 uses mirroring to provide redundancy but no performance benefits from striping. RAID 5 uses distributed parity to provide both performance from striping and redundancy, making it a good option for read-heavy databases. RAID 6 adds a second parity block to allow two disk failures but is more complex to implement. RAID 10 uses mirroring and striping to provide both high performance and redundancy, making it best for critical applications. RAID 0+1 mirrors stripes for data replication and sharing across disks.