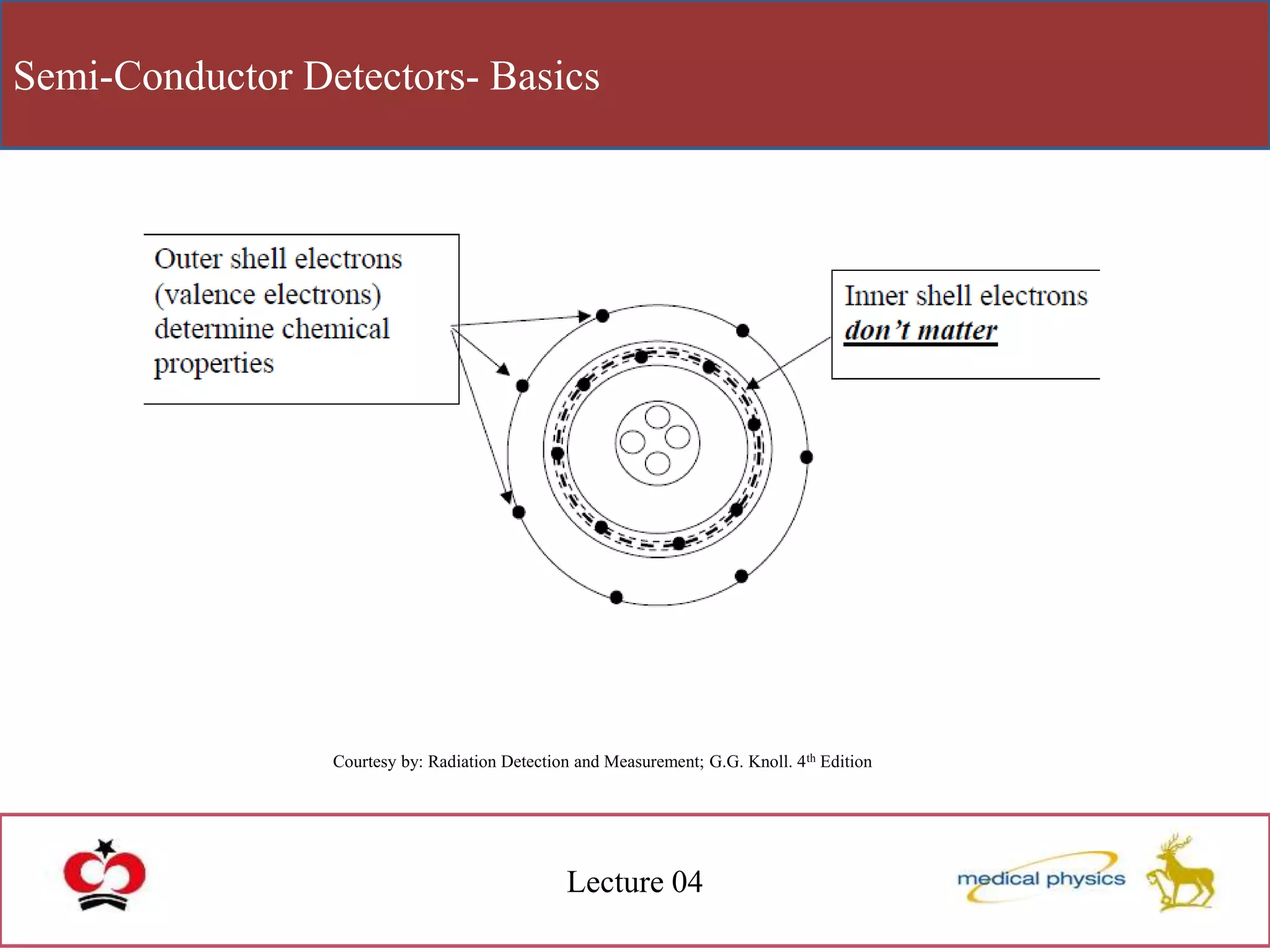
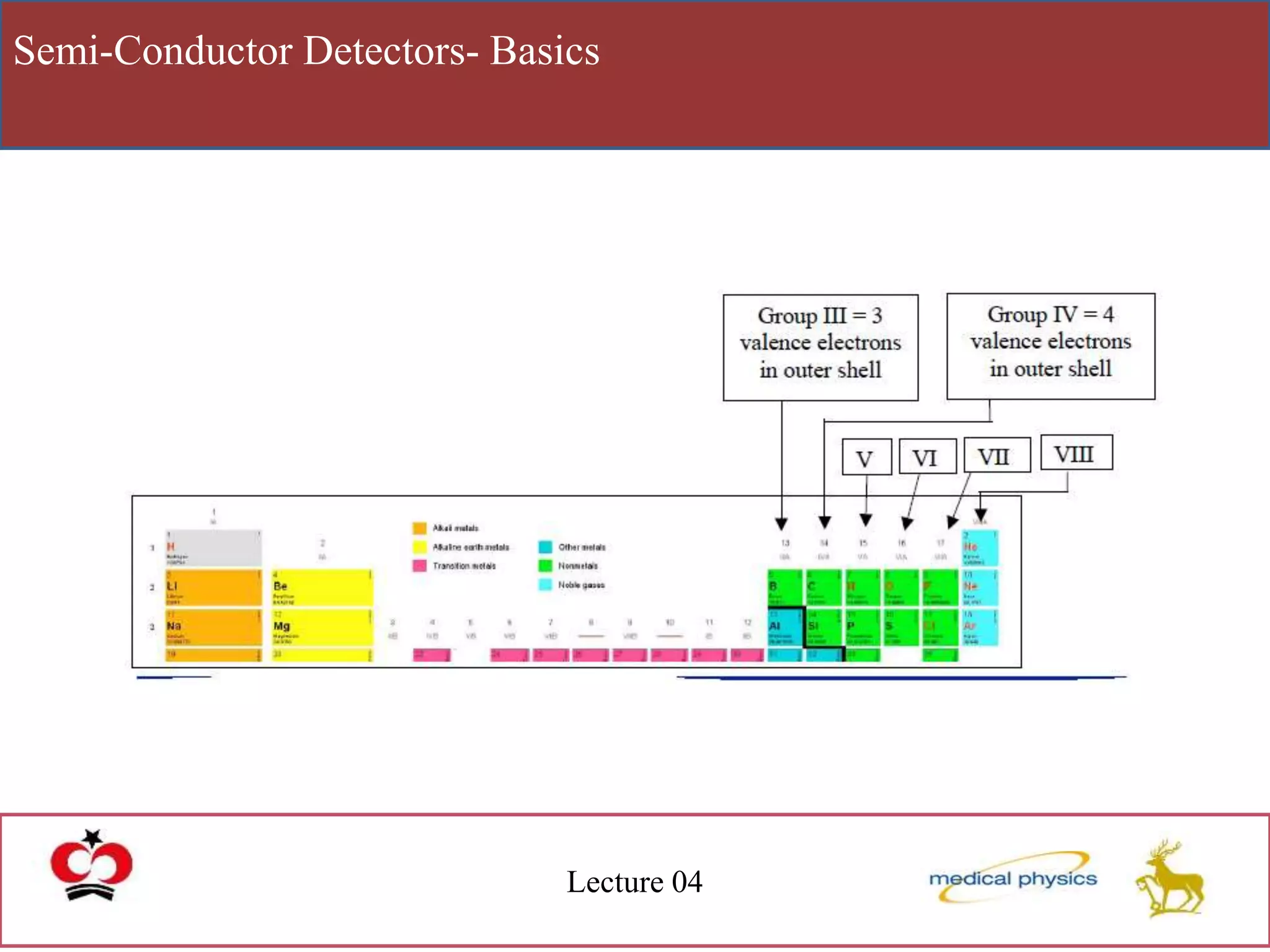
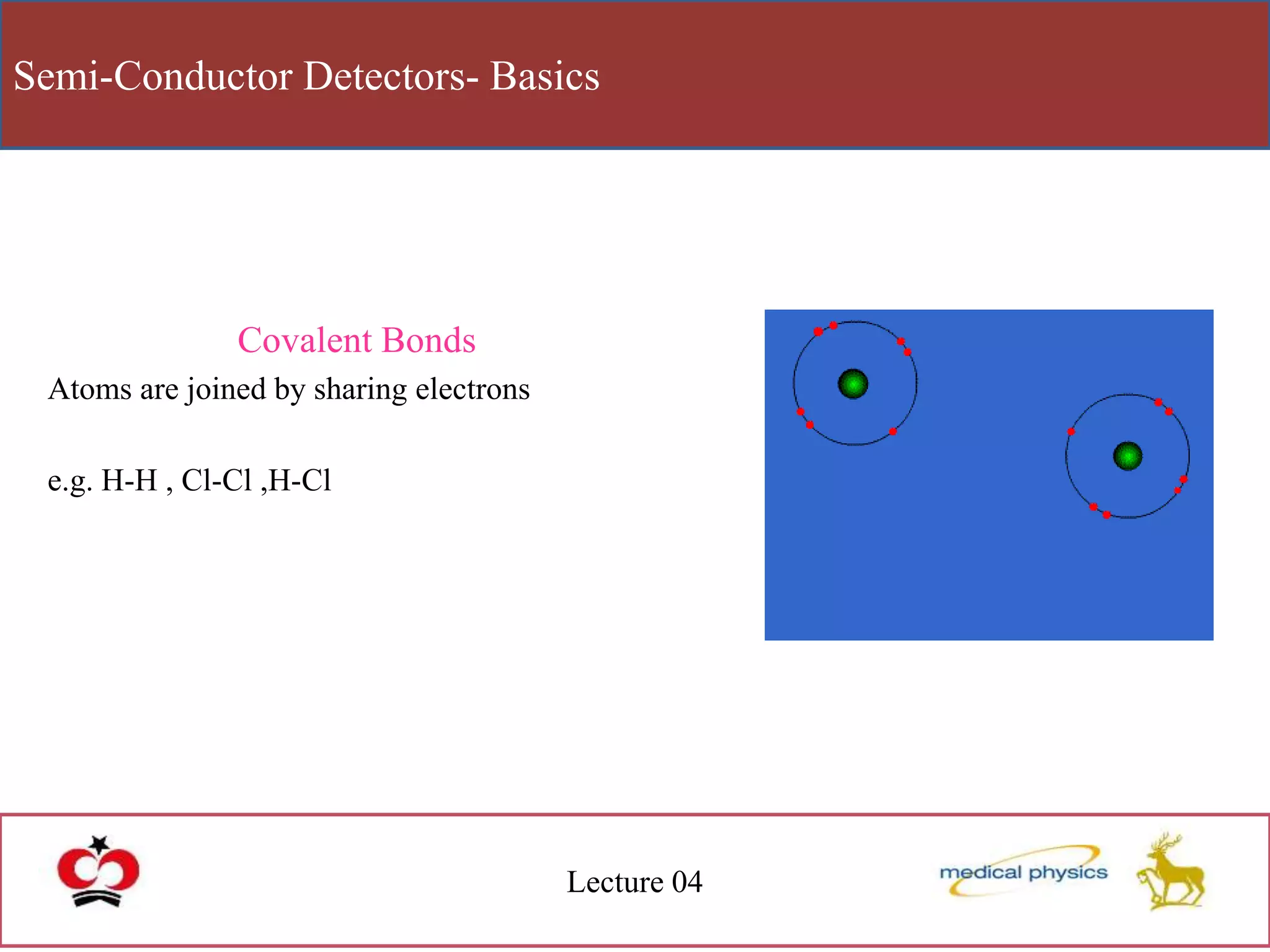
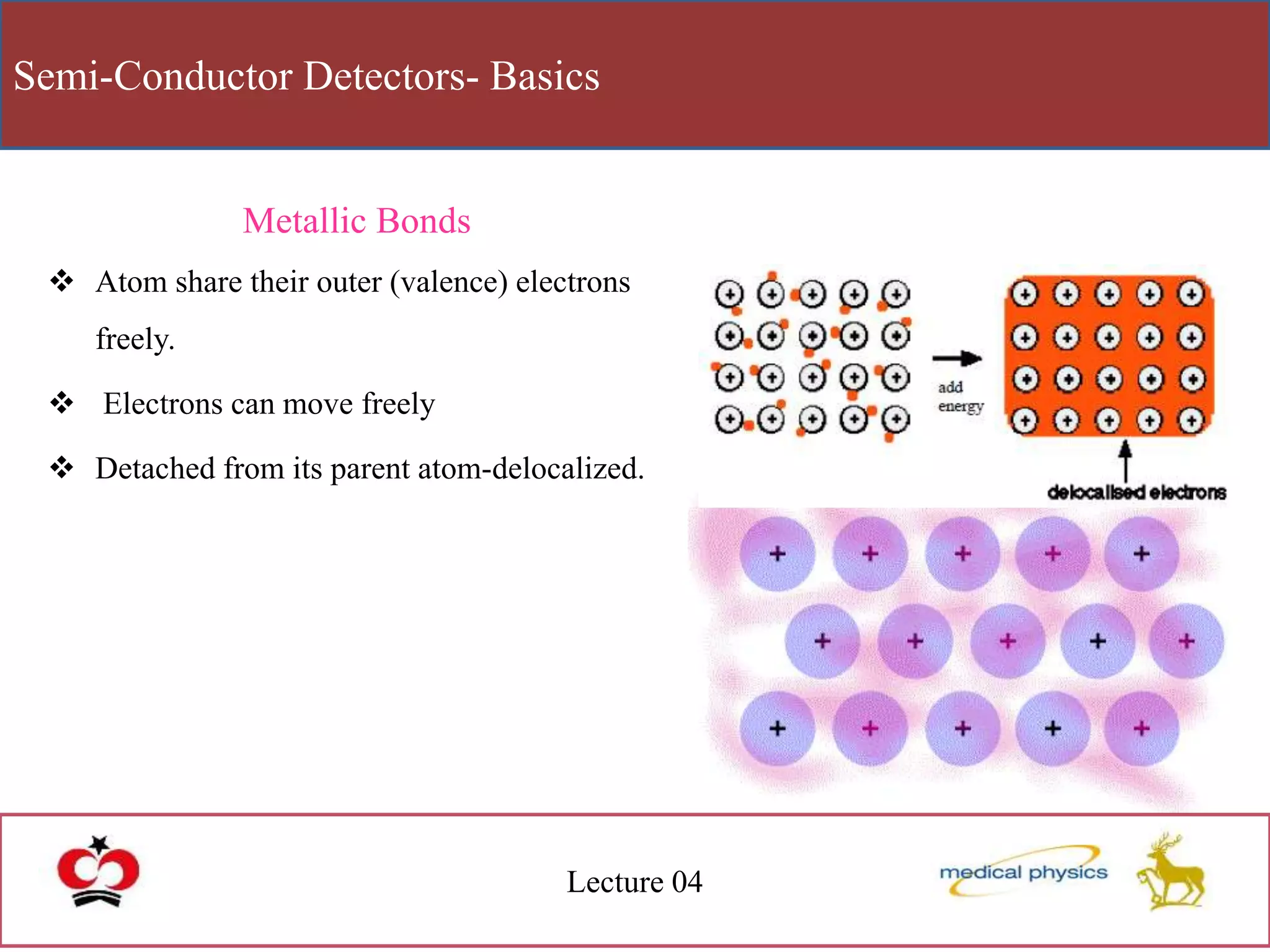
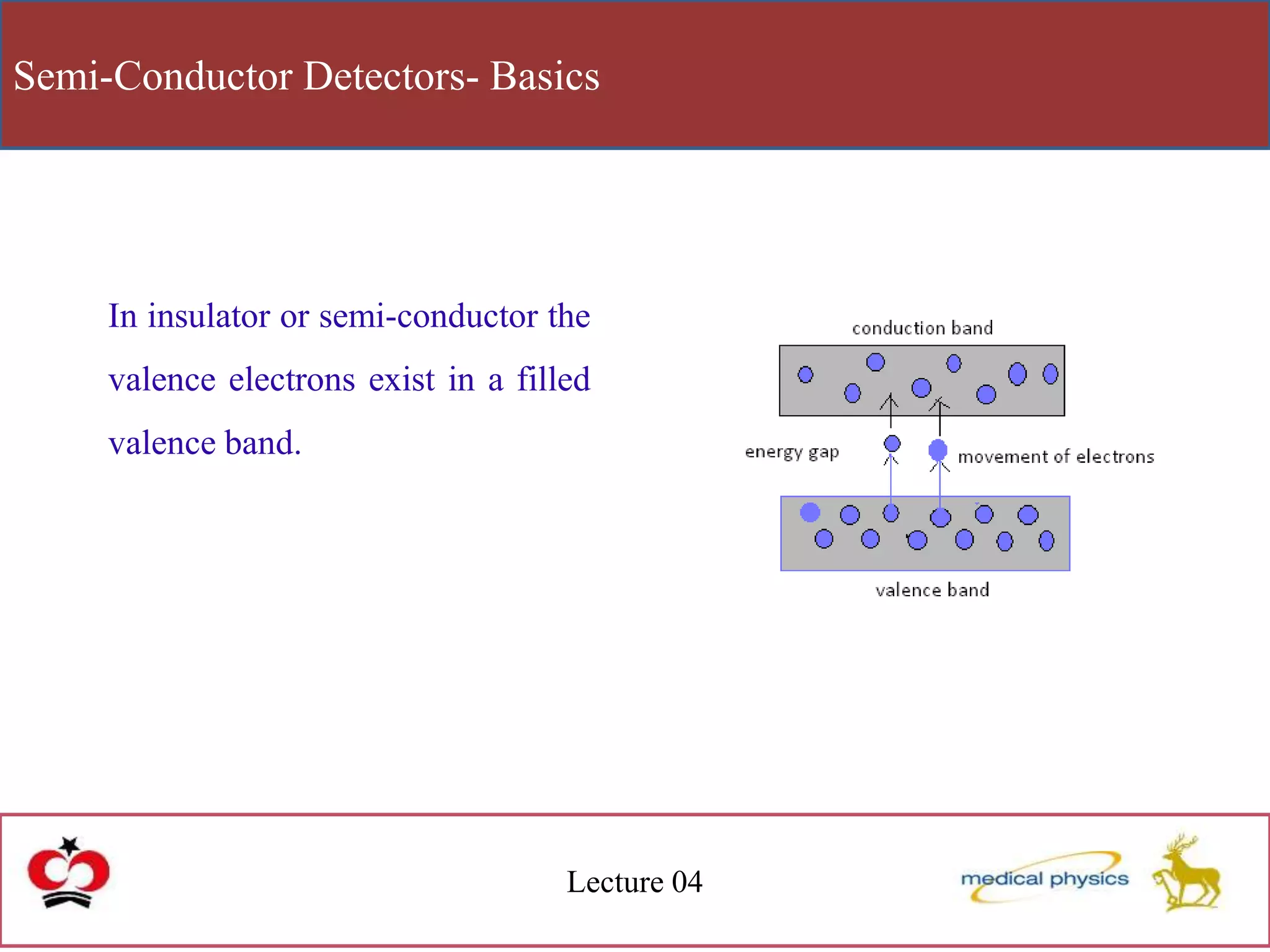
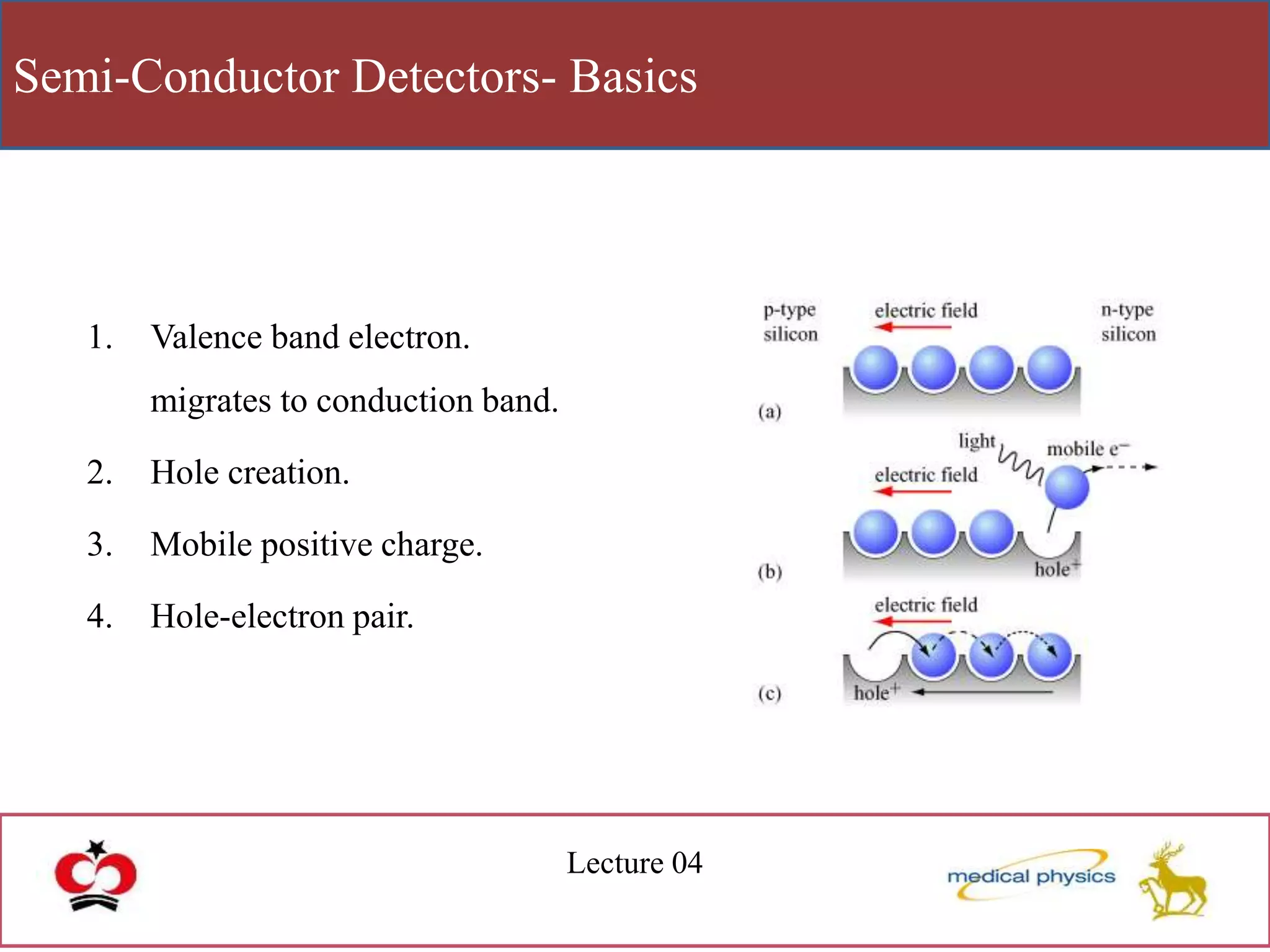
This document discusses semi-conductor detectors and their use in radiation detection. It describes the basic structure of atoms and different types of bonds between atoms. It explains that in crystalline materials like semiconductors, electrons exist in energy bands separated by gaps. In semiconductors and insulators, the valence band is full while the conduction band is empty, allowing electrons to move if given enough energy to cross the band gap. Semiconductors can be "doped" with impurities to create p-type or n-type materials and function as radiation detectors by generating electron-hole pairs when ionizing radiation transfers electrons to the conduction band.