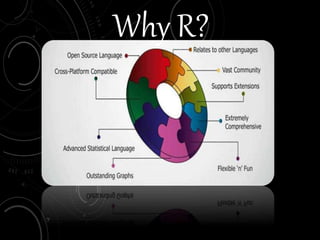
The document presents a comprehensive overview of R, a programming language designed for statistical computing, including its features, advantages, and basic data types. It outlines a structured approach through various modules covering topics such as vectors, matrices, factors, and lists, along with operations and subsetting techniques. The training is designed for educational purposes, focusing on practical applications in data analysis and visualization.