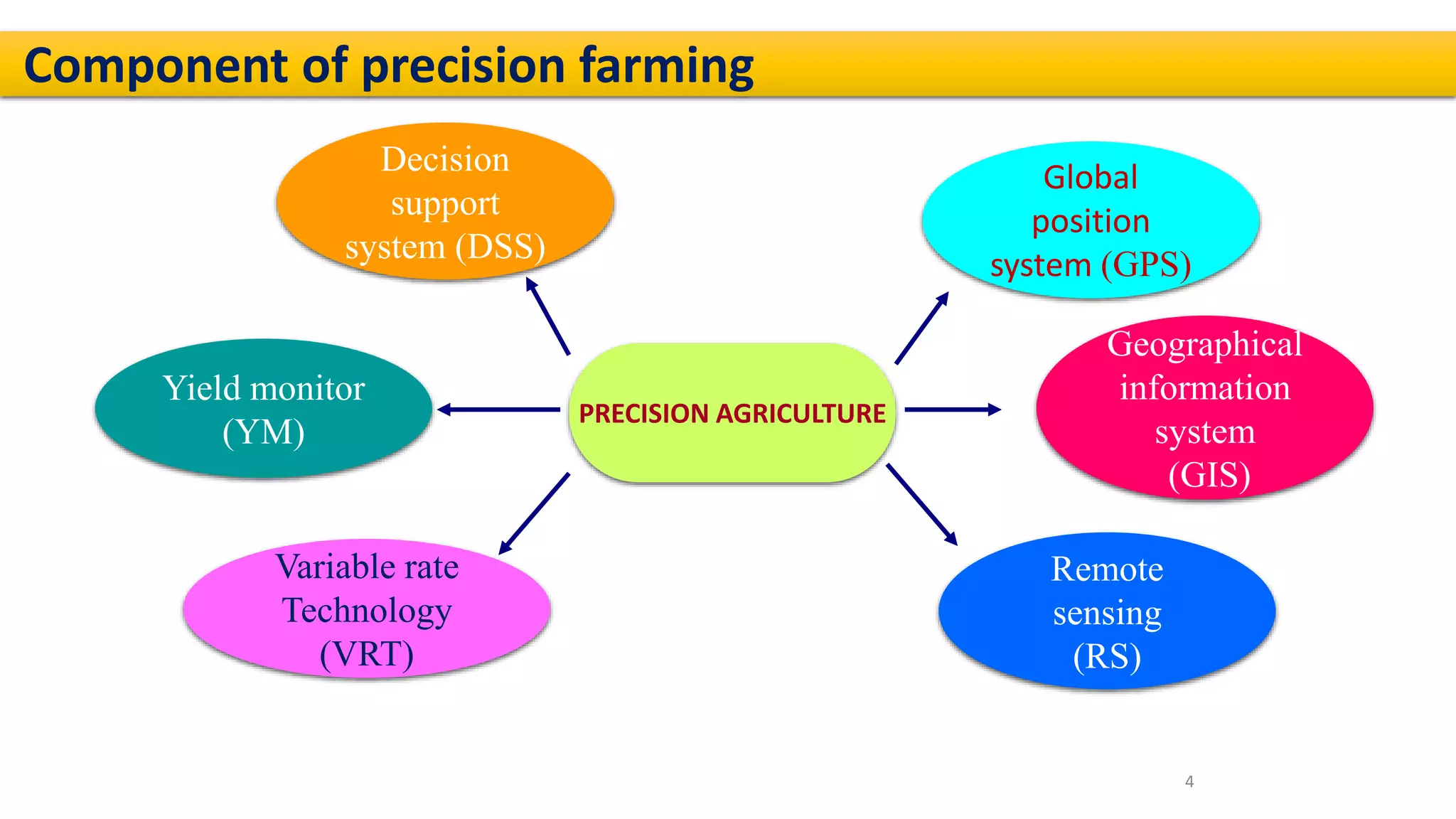
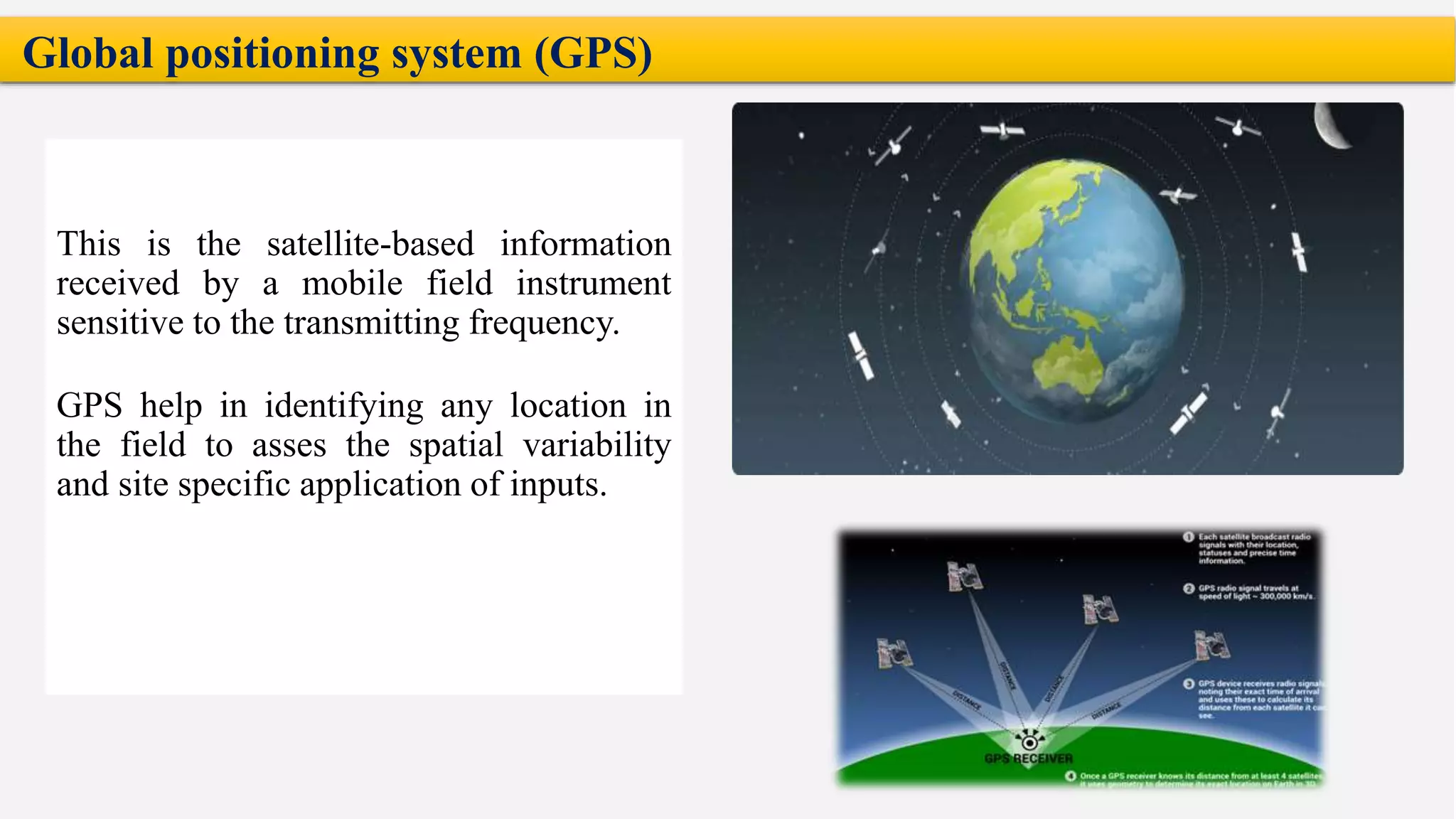
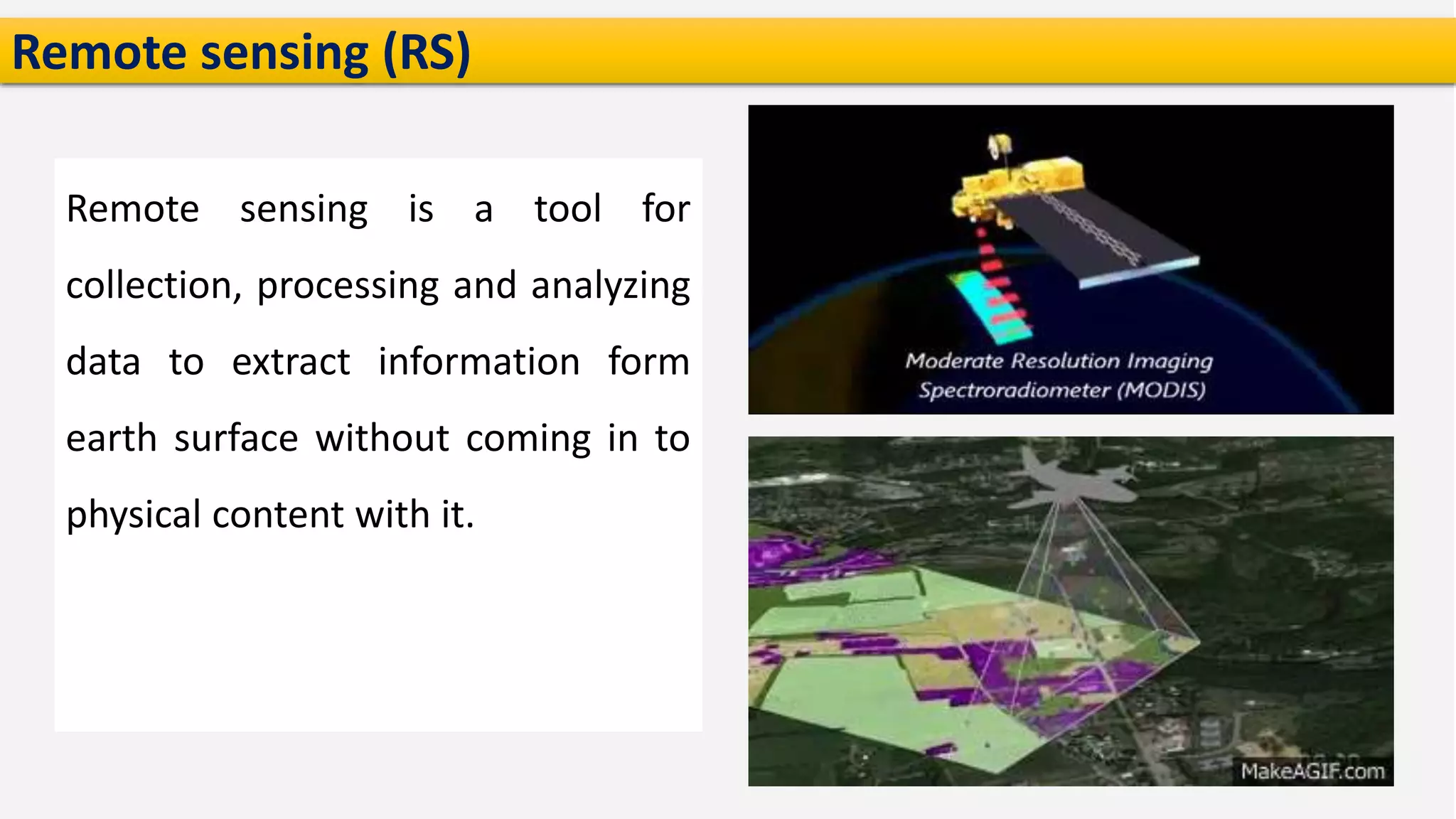
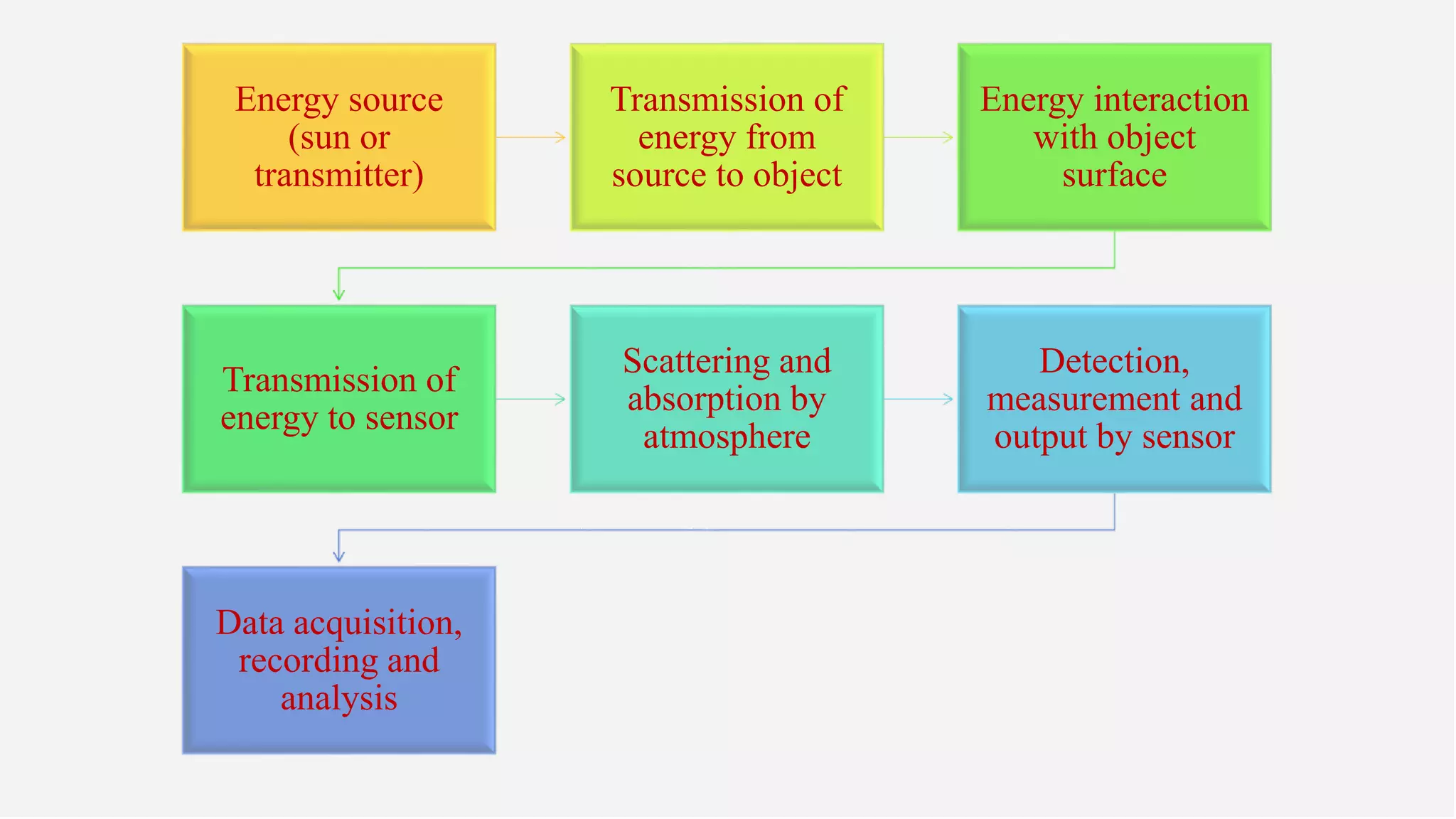
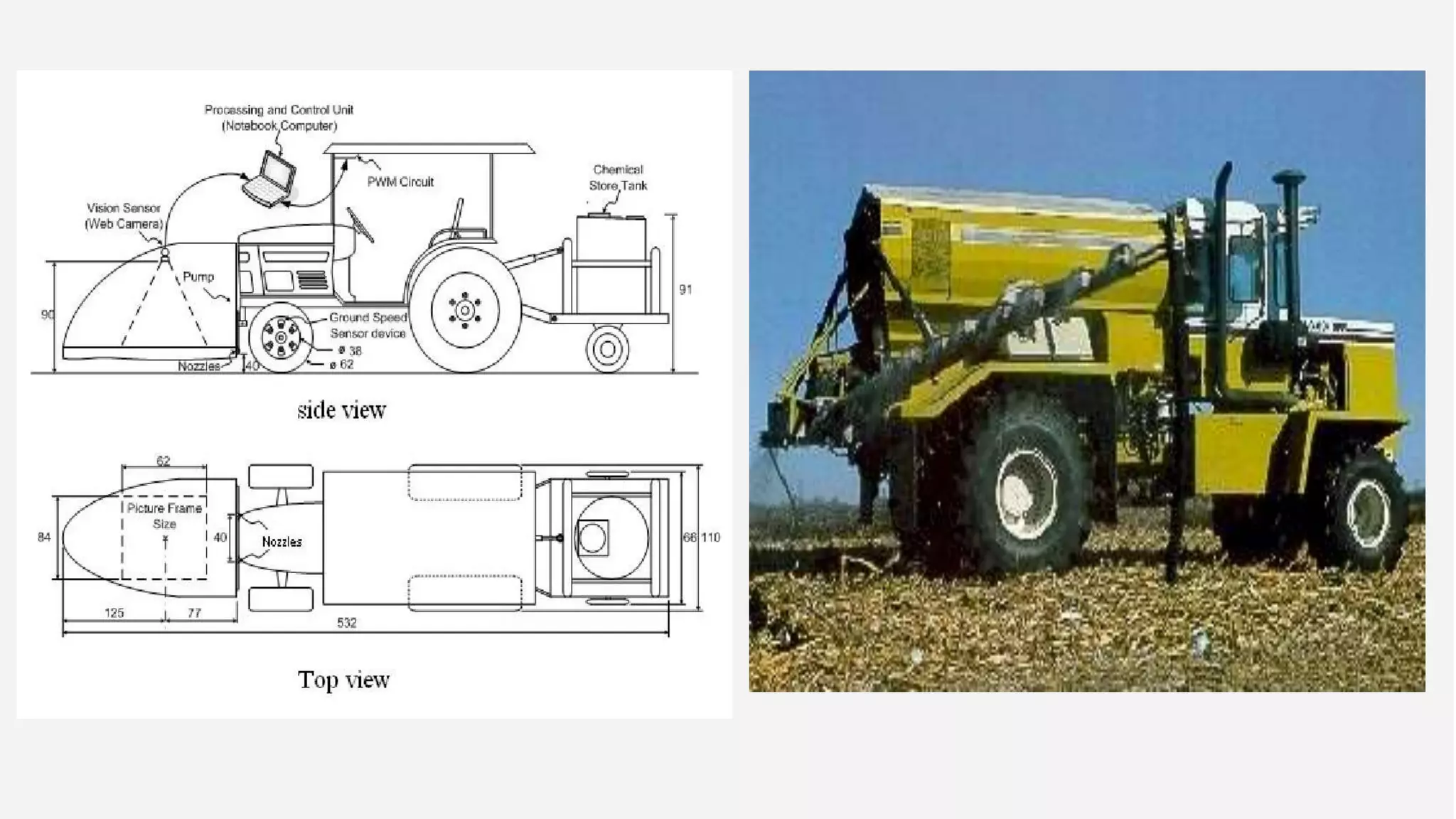
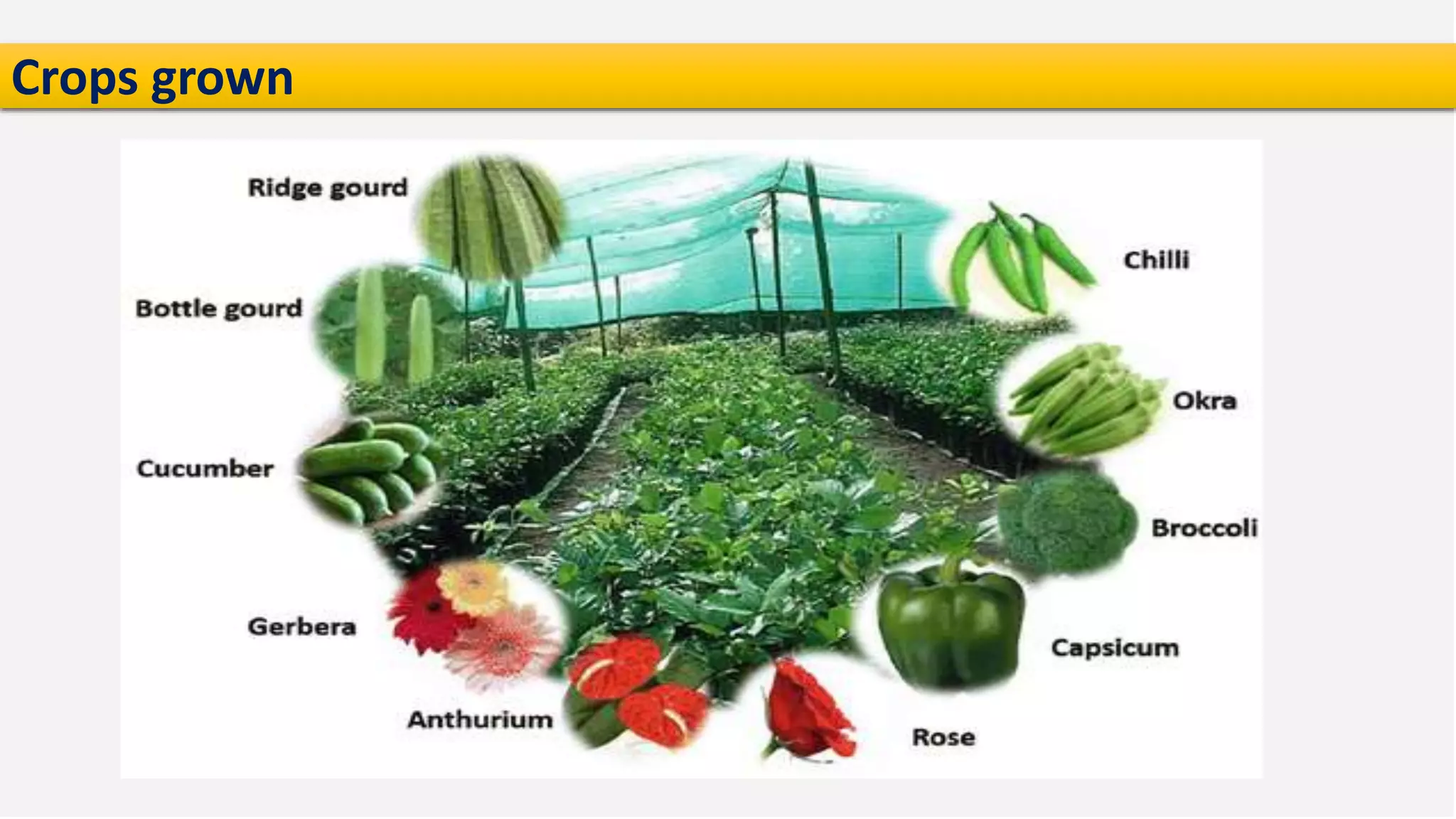
The presentation on precision agriculture discusses the efficient use of resources like water and fertilizers through technologies such as GPS, GIS, and remote sensing for better crop yield and site-specific management. It highlights the importance of variable rate technology and decision support systems to facilitate informed farming decisions, along with future advancements in agriculture like IoT and AI. Additionally, the document covers the concept of protected agriculture, its benefits, and strategies for enhancing production through controlled environments.