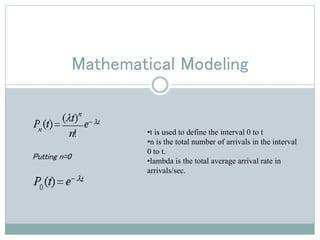
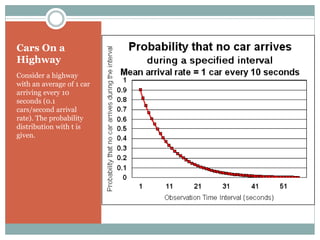
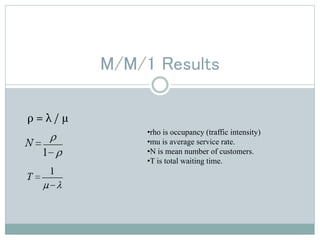
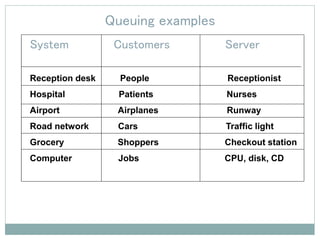
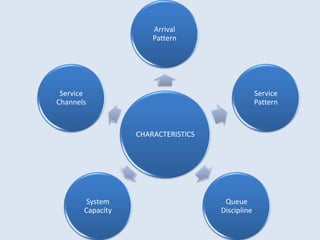
This presentation discusses queuing theory and the M/M/1 queuing model. It defines a queue as any system where jobs arrive looking for service and depart once served. Characteristics of queue systems include the arrival and service patterns, queue discipline, system capacity, and number of service channels. An example M/M/1 queuing simulation is presented using arrival and service times. The assumptions of the M/M/1 model are that the number of customers is large, the impact of each customer is small, and customers are independent with FIFO queue discipline and a single server. Applications of queuing theory include banking, telephone systems, computer networks, computer systems, and toll booths.




![EXAMPLE:
AT=[0,10,15,35,30,10,5,5]
ST=[20,15,10,5,15,15,10,10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarppt1140213-161129183310/85/Queuing-Theory-7-320.jpg)