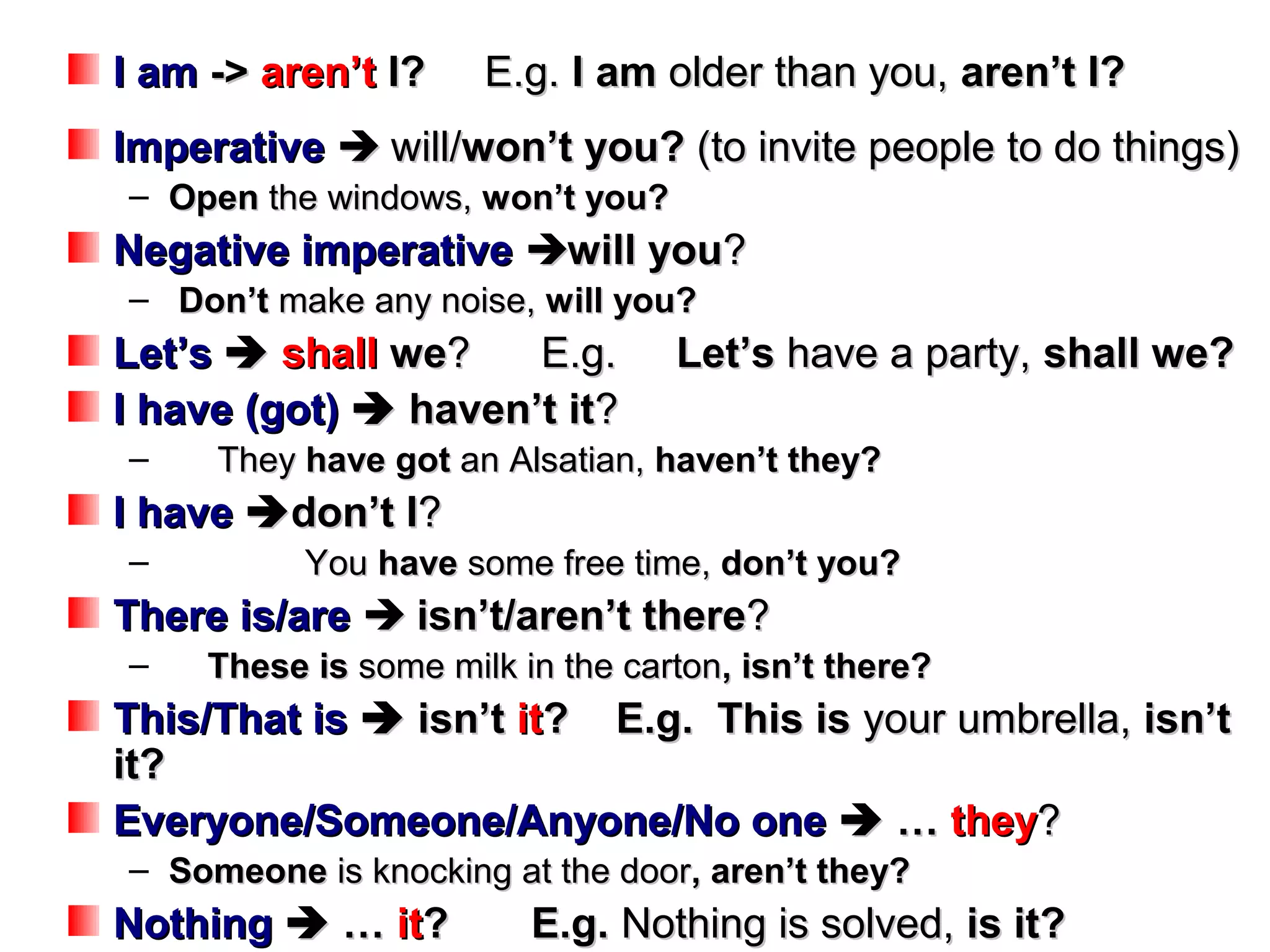
Question tags are short question phrases added to the end of statements. They are used to check information or seek agreement. To form a question tag, identify the verb in the statement and use the opposite auxiliary verb or pronoun. For example, with a positive statement like "It's windy today", the matching question tag is "isn't it?". Question tags follow the subject of the statement and use pronouns like "she", "it", or "they" accordingly. The intonation when saying a question tag indicates whether the speaker is sure of the answer or wants to check information.